User's Manual Part 2
Release8InstallationandConfigurationGuide
Issue2,November2007 Draft5forRegulatoryReview 242
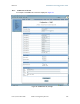
You may set the IP tab parameters as follows.
LAN1 Network Interface Configuration, IP Address
Enter the non-routable IP address to associate with the Ethernet connection on this AP.
(The default IP address from the factory is 169.254.1.1.) If you set and then forget this
parameter, then you must both
1. physically access the module.
2. use an override plug to electronically access the module configuration
parameters at 169.254.1.1. See Overriding Forgotten IP Addresses or
Passwords on AP, SM, or BH on Page 381.
RECOMMENDATION:
Note or print the IP settings from this page. Ensure that you can readily associate
these IP settings both with the module and with the other data that you store
about the module.
LAN1 Network Interface Configuration, Subnet Mask
Enter an appropriate subnet mask for the AP to communicate on the network. The default
subnet mask is 255.255.0.0. See Allocating Subnets on Page 162.
LAN1 Network Interface Configuration, Gateway IP Address
Enter the appropriate gateway for the AP to communicate with the network. The default
gateway is 169.254.0.0.
The values of these four LAN1 network interface configuration parameters are displayed
read only along with the Ethernet speed and duplex state on the Network Interface tab of
the Home page in the AP.
LAN1 Network Interface Configuration, DHCP State
If you select Enabled, the DHCP server automatically assigns the IP configuration
(IP address, subnet mask, and gateway IP address) and the values of those individual
parameters (above) are not used. The setting of this DHCP state parameter is also
viewable, but not settable, in the Network Interface tab of the Home page.
LAN2 Network Interface Configuration (RF Private Interface), IP Address
You should not change this parameter from the default AP private IP address of
192.168.101.1. A /24 CIDR subnet is used to communicate with each of the SMs that are
registered. The AP uses a combination of the private IP and the LUID (logical unit ID) of
the SM.
For example, if an SM is the first to register in an AP, and another SM registers later,
then the AP whose Private IP address is 192.168.101.1 uses the following SM Private IP
addresses to communicate to each:
SM LUID Private IP
First SM registered 2 192.168.101.2
Second SM registered 3 192.168.101.3