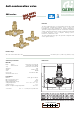
Product Overview
Characteristic components
Wooden biomass and condensation build-up
Wooden solid fuel contains a variable moisture percentage
depending on the type (logs, pellets, woodchips etc.) and
seasoning. Water vapour is released during the solid fuel drying
phase inside the combustion chamber. The presence of cold zones
in the generator or flue gas chimney can lower the temperature of
the flue gas down to the dew point, causing condensation to occur.
Water vapour condenses on the generator surfaces, together with
soot and part of the unburnt hydrocarbons contained in the flue
gas, producing deposits and tar. These substances stick to the
walls of the generator, covering most of the inner surfaces. In
addition to being dangerous due to its flammability, tar is damaging
to the integrity of the generator and limits the efficiency of the flue
gas-system water exchanger.
By keeping the generator walls at the highest possible temperature,
the anti-condensation valve limits the formation of these
substances, thereby increasing the combustion efficiency,
controlling the emissions into the environment and prolonging the
generator life.
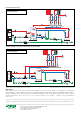
Operating principle
The thermostatic sensor , completely immersed in the medium,
controls the movement of an obturator that regulates the flows
in by-pass and toward the system. At the start-up of the heat
generator, the anti-condensation valve recirculates the flow water
so as to bring the generator up to temperature as quickly as
possible (fig. 1). When the flow temperature Tf exceeds the setting
of the anti-condensation valve Tset, the valve’s cold port starts
opening to produce the water mixing Tmix: in this phase the system
loading begins (fig. 2).
When the return temperature to the generator Tmix is greater than
the setting of the anti-condensation valve by approximately 10°C,
the by-pass port closes and water returns to the generator at
the same temperature as the system return (fig. 3 and fig. 4).
Zone of condensation
forming:
Deposits and tar
Corrosion
Reduction in heat
exchanger efficiency
Flammability
Primary and
secondary air:
Combustion
efficiency
ANTI-CONDENSATION
VALVE
SR
SF
Accumulation of ash
and residues
Flue gas and
emission
control
Flow
by-pass
System
return
Return
to generator
1) Thermostatic sensor
2) Obturator
3) Spring
4) Cap
5) Valve body
6) Temperature gauge holders
SOLID
FUEL
GENERATOR
Tf
Tf
SOLID
FUEL
GENERATOR
Tf
SOLID
FUEL
GENERATOR
TfSOLID
FUEL
GENERATOR
1
Tmix = Tset + 10°C BY-PASS CLOSING
by-pass closed
system return open
Tf > Tmix = Tset +10°C, Tmix=Tr
Tmix > Tset + 10°C SYSTEM LOADED
by-pass closed
system return open
Tf > Tmix > Tset +10°C, Tmix=Tr
Tf > Tset START OF SYSTEM LOADING
by-pass open
system return open
Tf > Tset, Tr < Tset, Tmix=Tset
2
3
4
Tf ≤ Tset SYSTEM START UP TRANSIENT
by-pass open
system return closed
Tf ≤ Tset, Tmix=Tf
Tf = Flow temperature
Tset = Anti-condensation setting temperature
Tmix = Mixed water temperature of generator return
Tr = System return temperature