User Guide
Table Of Contents
- Table of contents
- 1 Introduction
- 2 Installation
- 3 EAGLE Modules and Editions
- 4 A First Look at EAGLE
- 5 Principles for Working with EAGLE
- 6 From Schematic to Finished Board
- 6.1 Creating the Schematic Diagram 87
- 6.2 Considerations Prior to Creating a Board 97
- 6.3 Create Board 108
- Without the Schematic Editor 108
- Specify the Board Outline 108
- Arrange Devices 110
- Boards with Components on Both Sides 111
- Exchanging Packages 112
- Changing the Technology 113
- Define Forbidden Areas 113
- Routing ¾ Placing Tracks Manually 114
- Defining a Copper Plane with POLYGON 115
- DRC ¾ Checking the Layout and Correcting Errors 117
- Creating Manufacturing Data 120
- 6.4 Multilayer Boards 121
- 6.5 Updating Components (Library Update) 132
- 6.6 Print Out Schematic and Layout 133
- 7 The Autorouter
- 7.1 Basic Features 137
- 7.2 What Can be Expected from the Autorouter 138
- 7.3 Controlling the Autorouter 138
- 7.4 What Has to be Defined Before Autorouting 140
- 7.5 How the Cost Factors Influence the Routing Process 144
- cfBase.xx: 0..20 144
- cfVia: 0..99 145
- cfNonPref: 0..10 145
- cfChangeDir: 0..25 145
- cfOrthStep, cfDiagStep 145
- cfExtdStep: 0..30 145
- cfBonusStep, cfMalusStep: 1..3 146
- cfPadImpact, cfSmdImpact: 0..10 146
- cfBusImpact: 0..10 146
- cfHugging: 0..5 146
- cfAvoid 0..10 146
- cfPolygon 0..30 147
- mnVia 0..30 147
- mnSegments 0..9999 147
- mnExtdSteps 0..9999 147
- 7.6 Number of Ripup/Retry Attempts 147
- 7.7 The Autorouter Menu 148
- 7.8 Routing Multi-Layer Boards 150
- 7.9 Backup and Interruption of Routing 151
- 7.10 Information for the User 152
- 7.11 Parameters of a Control File 153
- 7.12 Practical Tips 154
- 8 Component Design Explained through Examples
- 8.1 Definition of a Simple Resistor 158
- 8.2 Defining a Complex Device 169
- 8.3 Supply Voltages 190
- 8.4 Supply Symbols 192
- 8.5 Labeling of Schematic Symbols 194
- 8.6 Pins with the Same Names 194
- 8.7 More about the Addlevel Parameter 195
- 8.8 Drawing Frames 198
- 8.9 Components on the Solder Side 199
- 8.10 Creating New Package Variants 199
- 8.11 Defining Packages in Any Rotation 203
- 8.12 Library and Part Management 205
- 9 Preparing the Manufacturing Data
- 9.1 Data for Board Manufacture 211
- 9.2 Which Files does the Board Maker Need? 213
- 9.3 Rules that Save Time and Money 215
- 9.4 Generating the Data with Ready-Made CAM Jobs 215
- 9.5 Set Output Parameters 220
- 9.6 Names of the Output Files 221
- 9.7 Automating the Output with CAM Processor Jobs 222
- 9.8 Gerber Files for Photoplotters with Fixed Aperture Wheels 225
- 9.9 Device Driver in File eagle.def 228
- 9.10 Film Generation Using PostScript Files 229
- 9.11 Documentation 230
- Appendix
- Index
- A
- Action toolbar 35,37
- Add
- ADD 40,48,57
- Addlevel 195
- Airwire 12
- Alt-X 30
- Always 195
- Annulus aperture 225,226
- Annulus symbol 12,104
- Aperture
- ARC 41,50
- ASSIGN 42,64,79
- AUTO 51
- Automatic naming 73
- Autorouter 137
- Backup 151
- Control file 153
- Cost Factors 144
- Design Rules 140
- Features 137
- Grid 140,141
- Interrupting 151
- Layer 143
- Load parameters 149
- Log file 153
- Memory requirement 142
- Menu 148
- Min. distance/clearance 140
- Minimum grid 137
- Preferred direction 137,143,148
- Restarting 150,151
- Restricted areas 143
- Ripup/Retry 147
- Run 148
- Save parameters 149
- Select signals 149
- Single-sided boards 154
- Status display 152
- Supply layer 123,150,223,224
- Supply polygons 151
- Track width 140
- Unreachable SMD 142,143
- Via, drill diameter 140
- Autorouter module 22
- B
- C
- CAM Job
- CAM Processor 43,58
- cam2dxf.ulp 135
- cam2print.ulp 135
- Can 195
- Caption 134
- CHANGE 39,48,57,79,161
- Change package 112
- Checking
- CIRCLE 41,50
- CLASS 42,93
- Clearance 101
- Clk 162
- CLOSE 43
- Color settings 80
- Command language 66
- Command line 36,63
- Command parameters 37
- Command toolbar 36
- Commands
- ADD 40
- ARC 41
- CHANGE 39
- CIRCLE 41
- CLOSE 43
- COPY 39
- CUT 39
- DELETE 40
- DESCRIPTION 58
- DISPLAY 38
- DRC 51
- ERRORS 51
- EXPORT 75
- GATESWAP 40
- GROUP 39
- INFO 38
- INVOKE 41
- MARK 39
- MIRROR 39
- MITER 49
- MOVE 39
- NAME 40
- PACKAGE 57
- PASTE 40
- PINSWAP 40
- POLYGON 41
- PRINT 133
- RECT 41
- ROTATE 39
- SHOW 38
- SMASH 40
- SPLIT 41
- TECHNOLOGY 58
- TEXT 41
- UPDATE 44
- USE 37,44
- VALUE 40,167
- WIRE 41
- WRITE 44
- Component
- Configuration
- CONNECT 57,166,186
- Connector 196
- Consistency 42,78
- Context menu 28
- Control panel 25
- Coordinate display 36,39,47
- Coordinates
- Copper plane 115
- Copy 39
- COPY 39,47,90
- Core 12,124
- Creamframe 106
- Current unit 71
- Cursor appearance 33
- CUT 39,48
- D
- Default
- Delete
- DELETE 40,48
- DELETE SIGNALS 75
- Design Rule Check 51,98
- Design rules 27
- Desktop publishing 230
- Device 13
- Device driver 228
- Device set 13
- Diameter of lands 97
- Dimensions of pads 97
- Directories 30
- Directory
- DISPLAY 38,46
- Distance 101
- Documentation 230
- Documentation print 159
- Dot 162
- DotClk 162
- Drag&Drop 25
- Drawing 198
- DRC 13,51
- Drill 13
- Drill data export
- Drill table 229
- Drillcfg.ulp 218
- Drivers
- Dxf data 76
- E
- $EAGLEDIR 31
- eagle.def 228,229
- eagle.epf 86
- eagle.scr 83
- eaglecon.exe 236
- eaglerc file 85
- eaglerc, eaglerc.usr 85
- EDIT 43,52
- Edition
- Electrical Rule Check 13,95
- Elongation 104
- Enter key 36
- Environment variable 31
- Eps format 230
- ERC 13,42,51,78,95
- Error correction 117
- Error messages 241
- ERRORS 51,117
- EXCELLON 212
- excellon.cam 217,218
- EXCELLON_RACK 218
- Exit program 30
- EXPORT 43,66,75,96
- F
- G
- H
- I
- J
- K
- L
- M
- N
- O
- P
- Package 13
- PACKAGE 57
- Pad 13
- PAD 53
- Palette 81
- Parameter toolbar 36
- >PART 194
- Parts list 75,230
- Pas 163
- PASTE 40,48
- Path specification 31
- Pbm graphic 76
- Pgm graphic 76
- Photoplotter
- Pin 13
- PIN 54
- Pin/pad connection 166,186
- Pin/pad list 75
- PINSWAP 40,48,94
- >PLOT_DATE_TIME 198
- Png graphic 76
- Polygon
- POLYGON 41,50,115,121
- PostScript 229
- Pour 116
- Power
- Ppm graphic 76
- PREFIX 57
- Prepreg 13,124
- PRINT 43,133
- Printout time 198
- Product information 34
- Product registration 34
- Project
- Prototype manufacture 212
- Pwr 95,163
- Q
- R
- S
- Schematic
- SCRIPT 38
- Script files 65,74
- Search devices 89
- Section 222
- Select objects 45
- Serial number 34
- SET 44,79
- Shape of lands 97
- >SHEET 198
- Sheet
- SHOW 38,46
- Signal 14
- SIGNAL 50
- Signal layers 121
- Silkscreen 159
- SM1000 212
- SM3000 212
- SMASH 40,49,90
- SMD 53,158
- Solder cream mask 106
- Solder stop mask 106,216
- Spaces 67
- Spacing 116
- Spin flag 110
- SPLIT 41,49
- Status display 152
- Stopframe 106
- Sup 95,163
- Superimposed pins 96
- Supply
- Supply layer
- Swaplevel 164
- Symbol 14
- T
- U
- V
- W
- X
- Z
- A
Whenasymbolisdefined,apinisplacedatacertainposition.
PIN'GND'PWRNONESHORTR180(0.20.4);
Youdrawarectangularforbiddenareainlayer41 tRestrict:
LAYERTRESTRICT;
RECT(0.50.5)(2.54);
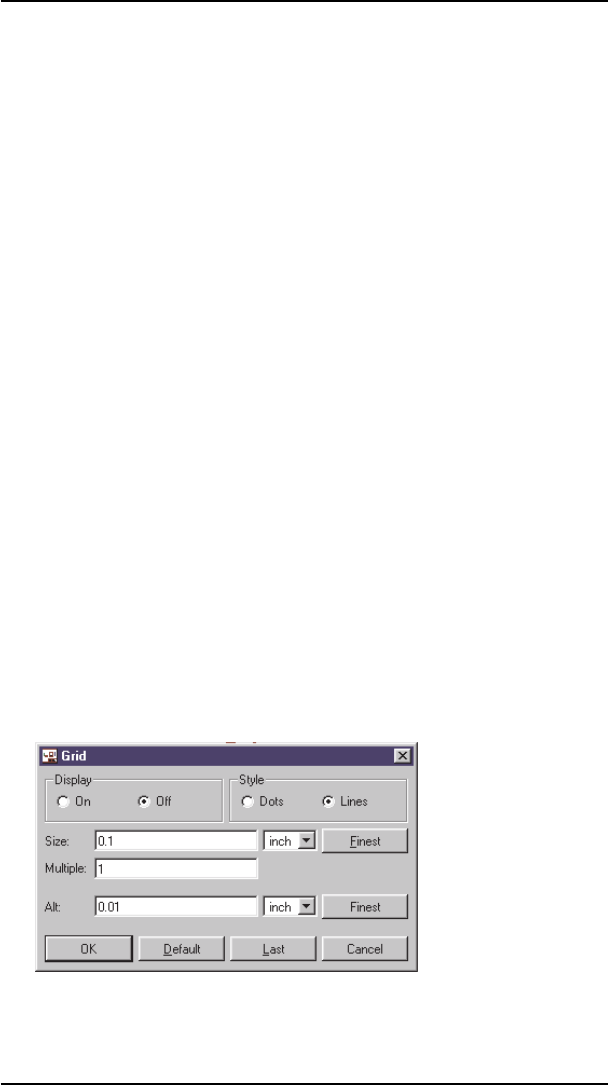
5.3 Gridsandthe CurrentUnit
EAGLEperformsitsinternalcalculationsusingabasicgridsizeof
1/10 000 mm (0.1 micron). Any multiple of that can be set as the work
-
inggrid.
Microns, mils, inches and mm can be used for the unit. The current unit
assetwiththeGRIDcommandappliestoallvalues.
You should always use the pre-set 0.1 inch grid for schematic diagrams.
This grid should also be used when defining schematic diagram symbols
intheLibraryEditor.
When starting the design of circuit boards or libraries it pays to give
prior thought to the question of which grid size (or sizes) will be used
as a basis. For example, it is only the origin of a package that will be
pulled onto the board’s placement grid. All other objects constituting
the package (such as pads) are placed relative to that point on the board,
justasitwasdefinedinthelibrary.
The basic rule for boards is: always make the grid as big as possible and
assmallasnecessary.
Various grid sizes can be preset in the eagle.scr file for different types of
editorwindows(seepage 79).
TheGridMenu
71
PrinciplesforWorkingwithEAGLE










