User Guide
Table Of Contents
- Table of contents
- 1 Introduction
- 2 Installation
- 3 EAGLE Modules and Editions
- 4 A First Look at EAGLE
- 5 Principles for Working with EAGLE
- 6 From Schematic to Finished Board
- 6.1 Creating the Schematic Diagram 87
- 6.2 Considerations Prior to Creating a Board 97
- 6.3 Create Board 108
- Without the Schematic Editor 108
- Specify the Board Outline 108
- Arrange Devices 110
- Boards with Components on Both Sides 111
- Exchanging Packages 112
- Changing the Technology 113
- Define Forbidden Areas 113
- Routing ¾ Placing Tracks Manually 114
- Defining a Copper Plane with POLYGON 115
- DRC ¾ Checking the Layout and Correcting Errors 117
- Creating Manufacturing Data 120
- 6.4 Multilayer Boards 121
- 6.5 Updating Components (Library Update) 132
- 6.6 Print Out Schematic and Layout 133
- 7 The Autorouter
- 7.1 Basic Features 137
- 7.2 What Can be Expected from the Autorouter 138
- 7.3 Controlling the Autorouter 138
- 7.4 What Has to be Defined Before Autorouting 140
- 7.5 How the Cost Factors Influence the Routing Process 144
- cfBase.xx: 0..20 144
- cfVia: 0..99 145
- cfNonPref: 0..10 145
- cfChangeDir: 0..25 145
- cfOrthStep, cfDiagStep 145
- cfExtdStep: 0..30 145
- cfBonusStep, cfMalusStep: 1..3 146
- cfPadImpact, cfSmdImpact: 0..10 146
- cfBusImpact: 0..10 146
- cfHugging: 0..5 146
- cfAvoid 0..10 146
- cfPolygon 0..30 147
- mnVia 0..30 147
- mnSegments 0..9999 147
- mnExtdSteps 0..9999 147
- 7.6 Number of Ripup/Retry Attempts 147
- 7.7 The Autorouter Menu 148
- 7.8 Routing Multi-Layer Boards 150
- 7.9 Backup and Interruption of Routing 151
- 7.10 Information for the User 152
- 7.11 Parameters of a Control File 153
- 7.12 Practical Tips 154
- 8 Component Design Explained through Examples
- 8.1 Definition of a Simple Resistor 158
- 8.2 Defining a Complex Device 169
- 8.3 Supply Voltages 190
- 8.4 Supply Symbols 192
- 8.5 Labeling of Schematic Symbols 194
- 8.6 Pins with the Same Names 194
- 8.7 More about the Addlevel Parameter 195
- 8.8 Drawing Frames 198
- 8.9 Components on the Solder Side 199
- 8.10 Creating New Package Variants 199
- 8.11 Defining Packages in Any Rotation 203
- 8.12 Library and Part Management 205
- 9 Preparing the Manufacturing Data
- 9.1 Data for Board Manufacture 211
- 9.2 Which Files does the Board Maker Need? 213
- 9.3 Rules that Save Time and Money 215
- 9.4 Generating the Data with Ready-Made CAM Jobs 215
- 9.5 Set Output Parameters 220
- 9.6 Names of the Output Files 221
- 9.7 Automating the Output with CAM Processor Jobs 222
- 9.8 Gerber Files for Photoplotters with Fixed Aperture Wheels 225
- 9.9 Device Driver in File eagle.def 228
- 9.10 Film Generation Using PostScript Files 229
- 9.11 Documentation 230
- Appendix
- Index
- A
- Action toolbar 35,37
- Add
- ADD 40,48,57
- Addlevel 195
- Airwire 12
- Alt-X 30
- Always 195
- Annulus aperture 225,226
- Annulus symbol 12,104
- Aperture
- ARC 41,50
- ASSIGN 42,64,79
- AUTO 51
- Automatic naming 73
- Autorouter 137
- Backup 151
- Control file 153
- Cost Factors 144
- Design Rules 140
- Features 137
- Grid 140,141
- Interrupting 151
- Layer 143
- Load parameters 149
- Log file 153
- Memory requirement 142
- Menu 148
- Min. distance/clearance 140
- Minimum grid 137
- Preferred direction 137,143,148
- Restarting 150,151
- Restricted areas 143
- Ripup/Retry 147
- Run 148
- Save parameters 149
- Select signals 149
- Single-sided boards 154
- Status display 152
- Supply layer 123,150,223,224
- Supply polygons 151
- Track width 140
- Unreachable SMD 142,143
- Via, drill diameter 140
- Autorouter module 22
- B
- C
- CAM Job
- CAM Processor 43,58
- cam2dxf.ulp 135
- cam2print.ulp 135
- Can 195
- Caption 134
- CHANGE 39,48,57,79,161
- Change package 112
- Checking
- CIRCLE 41,50
- CLASS 42,93
- Clearance 101
- Clk 162
- CLOSE 43
- Color settings 80
- Command language 66
- Command line 36,63
- Command parameters 37
- Command toolbar 36
- Commands
- ADD 40
- ARC 41
- CHANGE 39
- CIRCLE 41
- CLOSE 43
- COPY 39
- CUT 39
- DELETE 40
- DESCRIPTION 58
- DISPLAY 38
- DRC 51
- ERRORS 51
- EXPORT 75
- GATESWAP 40
- GROUP 39
- INFO 38
- INVOKE 41
- MARK 39
- MIRROR 39
- MITER 49
- MOVE 39
- NAME 40
- PACKAGE 57
- PASTE 40
- PINSWAP 40
- POLYGON 41
- PRINT 133
- RECT 41
- ROTATE 39
- SHOW 38
- SMASH 40
- SPLIT 41
- TECHNOLOGY 58
- TEXT 41
- UPDATE 44
- USE 37,44
- VALUE 40,167
- WIRE 41
- WRITE 44
- Component
- Configuration
- CONNECT 57,166,186
- Connector 196
- Consistency 42,78
- Context menu 28
- Control panel 25
- Coordinate display 36,39,47
- Coordinates
- Copper plane 115
- Copy 39
- COPY 39,47,90
- Core 12,124
- Creamframe 106
- Current unit 71
- Cursor appearance 33
- CUT 39,48
- D
- Default
- Delete
- DELETE 40,48
- DELETE SIGNALS 75
- Design Rule Check 51,98
- Design rules 27
- Desktop publishing 230
- Device 13
- Device driver 228
- Device set 13
- Diameter of lands 97
- Dimensions of pads 97
- Directories 30
- Directory
- DISPLAY 38,46
- Distance 101
- Documentation 230
- Documentation print 159
- Dot 162
- DotClk 162
- Drag&Drop 25
- Drawing 198
- DRC 13,51
- Drill 13
- Drill data export
- Drill table 229
- Drillcfg.ulp 218
- Drivers
- Dxf data 76
- E
- $EAGLEDIR 31
- eagle.def 228,229
- eagle.epf 86
- eagle.scr 83
- eaglecon.exe 236
- eaglerc file 85
- eaglerc, eaglerc.usr 85
- EDIT 43,52
- Edition
- Electrical Rule Check 13,95
- Elongation 104
- Enter key 36
- Environment variable 31
- Eps format 230
- ERC 13,42,51,78,95
- Error correction 117
- Error messages 241
- ERRORS 51,117
- EXCELLON 212
- excellon.cam 217,218
- EXCELLON_RACK 218
- Exit program 30
- EXPORT 43,66,75,96
- F
- G
- H
- I
- J
- K
- L
- M
- N
- O
- P
- Package 13
- PACKAGE 57
- Pad 13
- PAD 53
- Palette 81
- Parameter toolbar 36
- >PART 194
- Parts list 75,230
- Pas 163
- PASTE 40,48
- Path specification 31
- Pbm graphic 76
- Pgm graphic 76
- Photoplotter
- Pin 13
- PIN 54
- Pin/pad connection 166,186
- Pin/pad list 75
- PINSWAP 40,48,94
- >PLOT_DATE_TIME 198
- Png graphic 76
- Polygon
- POLYGON 41,50,115,121
- PostScript 229
- Pour 116
- Power
- Ppm graphic 76
- PREFIX 57
- Prepreg 13,124
- PRINT 43,133
- Printout time 198
- Product information 34
- Product registration 34
- Project
- Prototype manufacture 212
- Pwr 95,163
- Q
- R
- S
- Schematic
- SCRIPT 38
- Script files 65,74
- Search devices 89
- Section 222
- Select objects 45
- Serial number 34
- SET 44,79
- Shape of lands 97
- >SHEET 198
- Sheet
- SHOW 38,46
- Signal 14
- SIGNAL 50
- Signal layers 121
- Silkscreen 159
- SM1000 212
- SM3000 212
- SMASH 40,49,90
- SMD 53,158
- Solder cream mask 106
- Solder stop mask 106,216
- Spaces 67
- Spacing 116
- Spin flag 110
- SPLIT 41,49
- Status display 152
- Stopframe 106
- Sup 95,163
- Superimposed pins 96
- Supply
- Supply layer
- Swaplevel 164
- Symbol 14
- T
- U
- V
- W
- X
- Z
- A
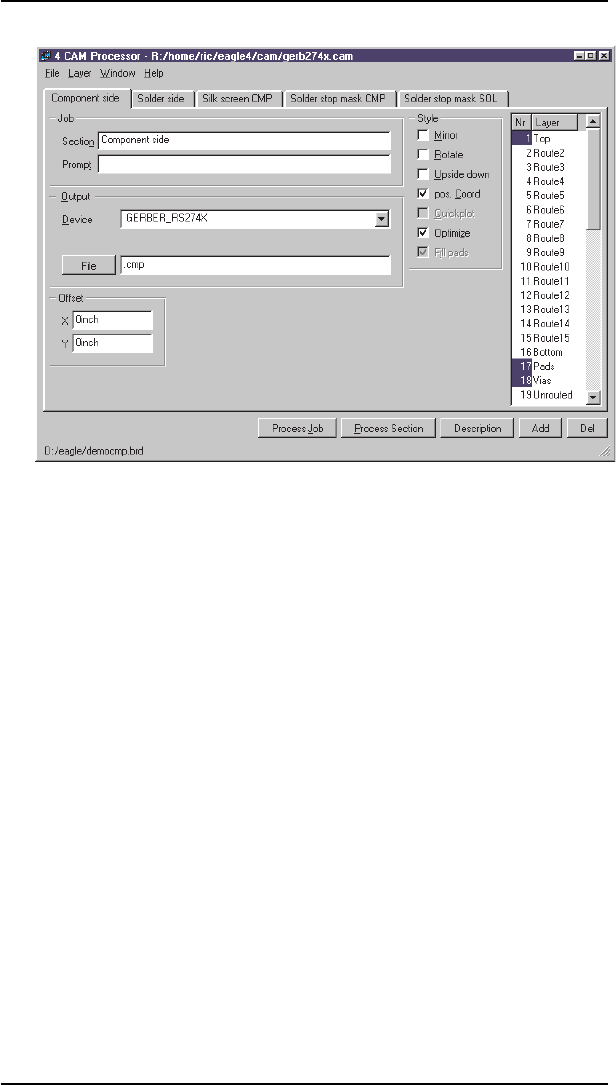
CAMProcessor
GenerateData
Load JobFile
A job defines the sequence of several output steps. You can, for exam
-
ple, use a job to generate individual files containing the Gerber data for
severalpcblayers.
A job is loaded with the File menu of the CAM Processor or via the
ControlPanel.
A job is not absolutely essential for output. All the settings can be made
manually.
LoadBoard
Before you can generate an output you must open the File menu and
load a board. At the bottom left in the CAM Processor window you can
seetheBRDfileforwhichdataisbeinggenerated.
OutputParameters
If a job file is loaded, the output parameters are already adjusted. A job
can contain several sections with different parameter sets. The various
peripheraldevicesacceptdifferentparameters.
59
AFirstLookatEAGLE










