Network Router User Manual
Table Of Contents
- Notices
- Contents
- About This Manual
- Introduction
- Hot Swapping Line Cards and Control Modules
- Bridging Configuration Guide
- Bridging Overview
- VLAN Overview
- Configuring SSR Bridging Functions
- Monitoring Bridging
- Configuration Examples
- SmartTRUNK Configuration Guide
- ATM Configuration Guide
- Packet-over-SONET Configuration Guide
- DHCP Configuration Guide
- IP Routing Configuration Guide
- IP Routing Protocols
- Configuring IP Interfaces and Parameters
- Configuring IP Interfaces to Ports
- Configuring IP Interfaces for a VLAN
- Specifying Ethernet Encapsulation Method
- Configuring Jumbo Frames
- Configuring Address Resolution Protocol (ARP)
- Configuring Reverse Address Resolution Protocol (RARP)
- Configuring DNS Parameters
- Configuring IP Services (ICMP)
- Configuring IP Helper
- Configuring Direct Broadcast
- Configuring Denial of Service (DOS)
- Monitoring IP Parameters
- Configuring Router Discovery
- Configuration Examples
- VRRP Configuration Guide
- RIP Configuration Guide
- OSPF Configuration Guide
- BGP Configuration Guide
- Routing Policy Configuration Guide
- Route Import and Export Policy Overview
- Configuring Simple Routing Policies
- Configuring Advanced Routing Policies
- Multicast Routing Configuration Guide
- IP Policy-Based Forwarding Configuration Guide
- Network Address Translation Configuration Guide
- Web Hosting Configuration Guide
- Overview
- Load Balancing
- Web Caching
- IPX Routing Configuration Guide
- Access Control List Configuration Guide
- Security Configuration Guide
- QoS Configuration Guide
- Performance Monitoring Guide
- RMON Configuration Guide
- LFAP Configuration Guide
- WAN Configuration Guide
- WAN Overview
- Frame Relay Overview
- Configuring Frame Relay Interfaces for the SSR
- Monitoring Frame Relay WAN Ports
- Frame Relay Port Configuration
- Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP) Overview
- Configuring PPP Interfaces
- Monitoring PPP WAN Ports
- PPP Port Configuration
- WAN Configuration Examples
- New Features Supported on Line Cards
Appendix A: New Features Supported on Line Cards
370 SmartSwitch Router User Reference Manual
Identifying a Line Card
ATM, packet-over-SONET, and 16-port 10/100 BASE-TX line cards are T-series line cards
introduced with the 3.1 firmware release. The following Gigabit Ethernet line cards are
also T-series line cards: SSR-GSX31-02, SSR-GLX39-02, and SSR-GTX32-02. Network
administrators can also identify a T-series line card using the system console. The
command “system show hardware” displays “(T-Series)” if the line card is a T-series line
card.
Example 1:
ssr# system show hardware
:
:
Slot 13, Module: 16-10/100-TX (T-Series) Rev. 1.0
The example above shows the display for a T-series line card.
All “-AA” line cards can be identified by the “-AA” suffix in the part number on the
module label. This is the easiest way to verify whether a line card is a “-AA” or “non-AA”
line card. Network administrators can also identify a “-AA” line card using the system
console. A chip ID register called the “Service String” is used to identify the component
used on each line card. The command “system show hardware verbose” displays the “Service
String” for each line card, which can be used to identify the version of the ASICs used.
This command is available in firmware 2.2.0.1 and above.
In the “Service String” output, look at the revision numbers that immediately follow the
letters “D” (or “G” for Gigabit Ethernet line cards), “I,” and “O.” Compare the revision
numbers with the following to determine if the line card is a “non-AA” or “-AA” revision.
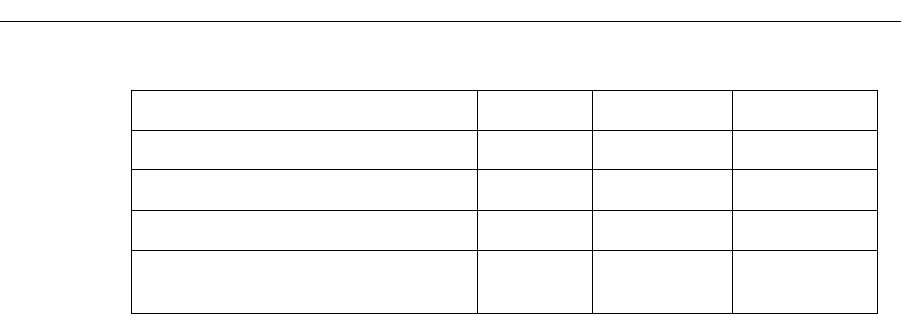
Multiple IPX Encapsulation Interface AA/T-series —
WRED Port T-series —
Aggregate rate limiting Interface T-series —
Port rate limiting Port T-series T-series
Jumbo frame support
Port/
Interface T-series
*
T-series*
*. 10/100 T-series line cards do not support jumbo frames.