Network Router User Manual
Table Of Contents
- Notices
- Contents
- About This Manual
- Introduction
- Hot Swapping Line Cards and Control Modules
- Bridging Configuration Guide
- Bridging Overview
- VLAN Overview
- Configuring SSR Bridging Functions
- Monitoring Bridging
- Configuration Examples
- SmartTRUNK Configuration Guide
- ATM Configuration Guide
- Packet-over-SONET Configuration Guide
- DHCP Configuration Guide
- IP Routing Configuration Guide
- IP Routing Protocols
- Configuring IP Interfaces and Parameters
- Configuring IP Interfaces to Ports
- Configuring IP Interfaces for a VLAN
- Specifying Ethernet Encapsulation Method
- Configuring Jumbo Frames
- Configuring Address Resolution Protocol (ARP)
- Configuring Reverse Address Resolution Protocol (RARP)
- Configuring DNS Parameters
- Configuring IP Services (ICMP)
- Configuring IP Helper
- Configuring Direct Broadcast
- Configuring Denial of Service (DOS)
- Monitoring IP Parameters
- Configuring Router Discovery
- Configuration Examples
- VRRP Configuration Guide
- RIP Configuration Guide
- OSPF Configuration Guide
- BGP Configuration Guide
- Routing Policy Configuration Guide
- Route Import and Export Policy Overview
- Configuring Simple Routing Policies
- Configuring Advanced Routing Policies
- Multicast Routing Configuration Guide
- IP Policy-Based Forwarding Configuration Guide
- Network Address Translation Configuration Guide
- Web Hosting Configuration Guide
- Overview
- Load Balancing
- Web Caching
- IPX Routing Configuration Guide
- Access Control List Configuration Guide
- Security Configuration Guide
- QoS Configuration Guide
- Performance Monitoring Guide
- RMON Configuration Guide
- LFAP Configuration Guide
- WAN Configuration Guide
- WAN Overview
- Frame Relay Overview
- Configuring Frame Relay Interfaces for the SSR
- Monitoring Frame Relay WAN Ports
- Frame Relay Port Configuration
- Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP) Overview
- Configuring PPP Interfaces
- Monitoring PPP WAN Ports
- PPP Port Configuration
- WAN Configuration Examples
- New Features Supported on Line Cards
SmartSwitch Router User Reference Manual 365
Appendix A: New Features Supported on Line Cards
When load balancing is implemented in a single system, the ports that attach to both
incoming and outgoing interfaces must reside on -AA or T-series line cards. If the servers
are load-sharing across multiple networks, ports assigned to the interfaces must also
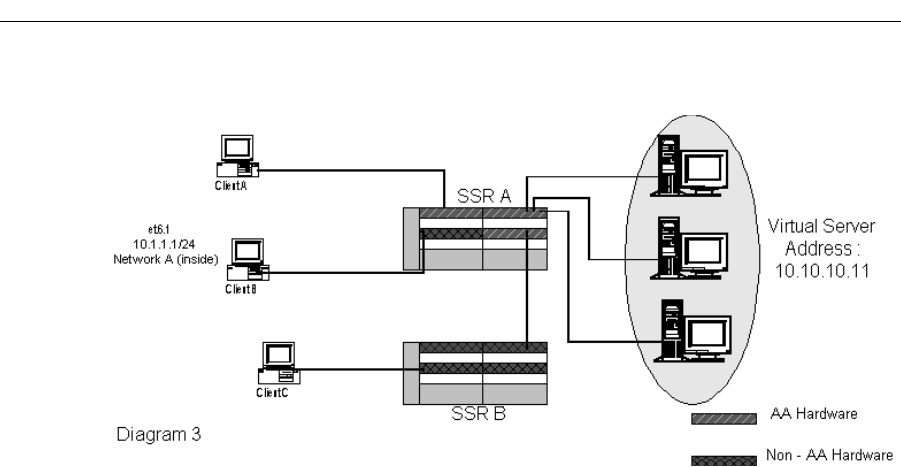
reside on -AA or T-series line cards. In Diagram 3, Client A can access the Virtual Server
Address, but Client B cannot access the Virtual Server Address because Client B is
connected to a non -AA line card.
However, if clients are connected through another system, as long as the final incoming
and outgoing ports to the Virtual Server Address reside on -AA or T-series line cards, the
clients are able to take advantage of the load-sharing feature. Client C in Diagram 3 can
access the Virtual Server Address even though Client C is connected to Router B with a
non -AA line card.
Layer 4 Bridging
Layer 4 bridging allows the administrator to set up a layer 3 and layer 4 “lookup” for
bridged packets. Traffic that is switched at layer 2 through the SSR can apply QoS and
security filters (ACLs) based on the layer 3/4 information contained in the packet. Unlike
the traditional implementation, where ACLs or QoS must be applied on the router
interface, you can now apply ACLs or QoS on the physical ports.
Layer 4 bridging is enabled on a per-VLAN basis. A network administrator first creates a
VLAN to contain the ports that require layer 4 bridging. By enabling layer 4 bridging
mode on the VLAN, the administrator can then apply ACLs or QoS on ports that are in
layer 4 bridging mode. Different ACLs or QoS can be applied to ports that are in the same
layer 4 bridging VLAN. Ports that are included in a layer 4 bridging VLAN must reside on
-AA or T-series line cards. The system does not allow ports that are on non -AA line cards
to be included in layer 4 bridging VLANs.