Network Router User Manual
Table Of Contents
- Notices
- Contents
- About This Manual
- Introduction
- Hot Swapping Line Cards and Control Modules
- Bridging Configuration Guide
- Bridging Overview
- VLAN Overview
- Configuring SSR Bridging Functions
- Monitoring Bridging
- Configuration Examples
- SmartTRUNK Configuration Guide
- ATM Configuration Guide
- Packet-over-SONET Configuration Guide
- DHCP Configuration Guide
- IP Routing Configuration Guide
- IP Routing Protocols
- Configuring IP Interfaces and Parameters
- Configuring IP Interfaces to Ports
- Configuring IP Interfaces for a VLAN
- Specifying Ethernet Encapsulation Method
- Configuring Jumbo Frames
- Configuring Address Resolution Protocol (ARP)
- Configuring Reverse Address Resolution Protocol (RARP)
- Configuring DNS Parameters
- Configuring IP Services (ICMP)
- Configuring IP Helper
- Configuring Direct Broadcast
- Configuring Denial of Service (DOS)
- Monitoring IP Parameters
- Configuring Router Discovery
- Configuration Examples
- VRRP Configuration Guide
- RIP Configuration Guide
- OSPF Configuration Guide
- BGP Configuration Guide
- Routing Policy Configuration Guide
- Route Import and Export Policy Overview
- Configuring Simple Routing Policies
- Configuring Advanced Routing Policies
- Multicast Routing Configuration Guide
- IP Policy-Based Forwarding Configuration Guide
- Network Address Translation Configuration Guide
- Web Hosting Configuration Guide
- Overview
- Load Balancing
- Web Caching
- IPX Routing Configuration Guide
- Access Control List Configuration Guide
- Security Configuration Guide
- QoS Configuration Guide
- Performance Monitoring Guide
- RMON Configuration Guide
- LFAP Configuration Guide
- WAN Configuration Guide
- WAN Overview
- Frame Relay Overview
- Configuring Frame Relay Interfaces for the SSR
- Monitoring Frame Relay WAN Ports
- Frame Relay Port Configuration
- Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP) Overview
- Configuring PPP Interfaces
- Monitoring PPP WAN Ports
- PPP Port Configuration
- WAN Configuration Examples
- New Features Supported on Line Cards
SmartSwitch Router User Reference Manual 227
Chapter 16: Network Address Translation Configuration Guide
Dynamic NAT with IP Overload (PAT) Configuration
The following example configures a dynamic address binding for inside addresses
10.1.1.0/24 to outside address 192.50.20.0/24:
The first step is to create the interfaces:
Next, define the interfaces to be NAT “inside” or “outside”:
Then, define the NAT dynamic rules by first creating the source ACL pool and then
configuring the dynamic bindings:
Using Dynamic NAT with IP Overload
Dynamic NAT with IP overload can be used when the local network (inside network) will
be initializing the connections using TCP or UDP protocols. It creates a binding at run
time when the packet comes from a local network defined in the NAT dynamic local ACL
pool. The difference between the dynamic NAT and dynamic NAT with PAT is that PAT
uses port (layer 4) information to do the translation. Hence, each global IP has about 4000
ports that can be translated. NAT on the SSR uses the standard BSD range of ports from
1024-4999 which is fixed and cannot be configured by the user. The network administrator
does not have to worry about the way in which the bindings are created; he/she just sets
et.2.2
(192.50.20.1/24)
et.2.1
(10.1.1.1/24)
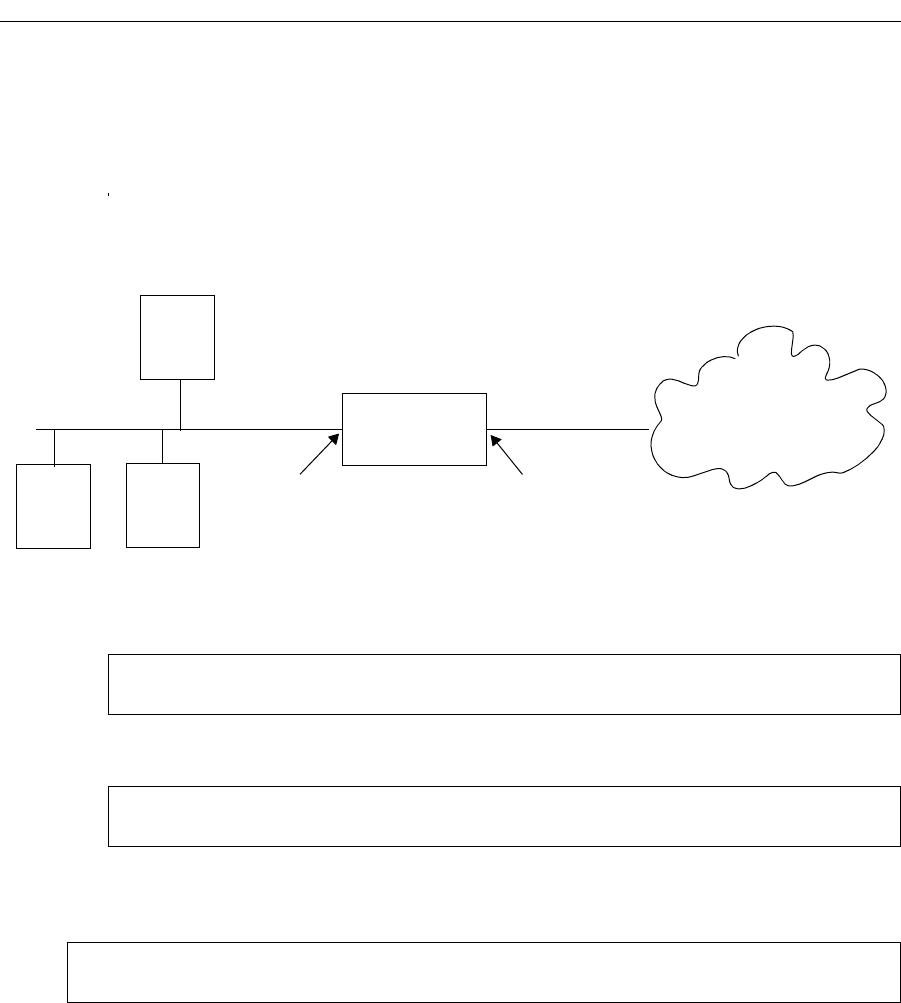
Global Internet
IP network 10.1.1.0/24
Router
interface 10-net interface 192-net
10.1.1.4
10.1.1.2
10.1.1.3
Outbound: Translate source pool 10.1.1.0/24 to global pool 192.50.20.1-192.50.20.3
interface create ip 10-net address-netmask 10.1.1.1/24 port et.2.1
interface create ip 192-net address-netmask 192.50.20.1/24 port et.2.2
nat set interface 10-net inside
nat set interface 192-net outside
acl lcl permit ip 10.1.1.0/24
nat create dynamic local-acl-pool lcl global-pool 192.50.20.1-192.50.20.3










