Network Router User Manual
Table Of Contents
- Notices
- Contents
- About This Manual
- Introduction
- Hot Swapping Line Cards and Control Modules
- Bridging Configuration Guide
- Bridging Overview
- VLAN Overview
- Configuring SSR Bridging Functions
- Monitoring Bridging
- Configuration Examples
- SmartTRUNK Configuration Guide
- ATM Configuration Guide
- Packet-over-SONET Configuration Guide
- DHCP Configuration Guide
- IP Routing Configuration Guide
- IP Routing Protocols
- Configuring IP Interfaces and Parameters
- Configuring IP Interfaces to Ports
- Configuring IP Interfaces for a VLAN
- Specifying Ethernet Encapsulation Method
- Configuring Jumbo Frames
- Configuring Address Resolution Protocol (ARP)
- Configuring Reverse Address Resolution Protocol (RARP)
- Configuring DNS Parameters
- Configuring IP Services (ICMP)
- Configuring IP Helper
- Configuring Direct Broadcast
- Configuring Denial of Service (DOS)
- Monitoring IP Parameters
- Configuring Router Discovery
- Configuration Examples
- VRRP Configuration Guide
- RIP Configuration Guide
- OSPF Configuration Guide
- BGP Configuration Guide
- Routing Policy Configuration Guide
- Route Import and Export Policy Overview
- Configuring Simple Routing Policies
- Configuring Advanced Routing Policies
- Multicast Routing Configuration Guide
- IP Policy-Based Forwarding Configuration Guide
- Network Address Translation Configuration Guide
- Web Hosting Configuration Guide
- Overview
- Load Balancing
- Web Caching
- IPX Routing Configuration Guide
- Access Control List Configuration Guide
- Security Configuration Guide
- QoS Configuration Guide
- Performance Monitoring Guide
- RMON Configuration Guide
- LFAP Configuration Guide
- WAN Configuration Guide
- WAN Overview
- Frame Relay Overview
- Configuring Frame Relay Interfaces for the SSR
- Monitoring Frame Relay WAN Ports
- Frame Relay Port Configuration
- Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP) Overview
- Configuring PPP Interfaces
- Monitoring PPP WAN Ports
- PPP Port Configuration
- WAN Configuration Examples
- New Features Supported on Line Cards
Chapter 12: BGP Configuration Guide
156 SmartSwitch Router User Reference Manual
Routers SSR4 and SSR6 inform router C1 about network 172.16.200.0/24 through External
BGP (EBGP). Router SSR6 announced the route with a MED of 10, whereas router SSR4
announces the route with a MED of 20. Of the two EBGP routes, router C1 chooses the one
with a smaller MED. Thus router C1 prefers the route from router SSR6, which has a MED
of 10.
Router SSR4 has the following CLI configuration:
Router SSR6 has the following CLI configuration:
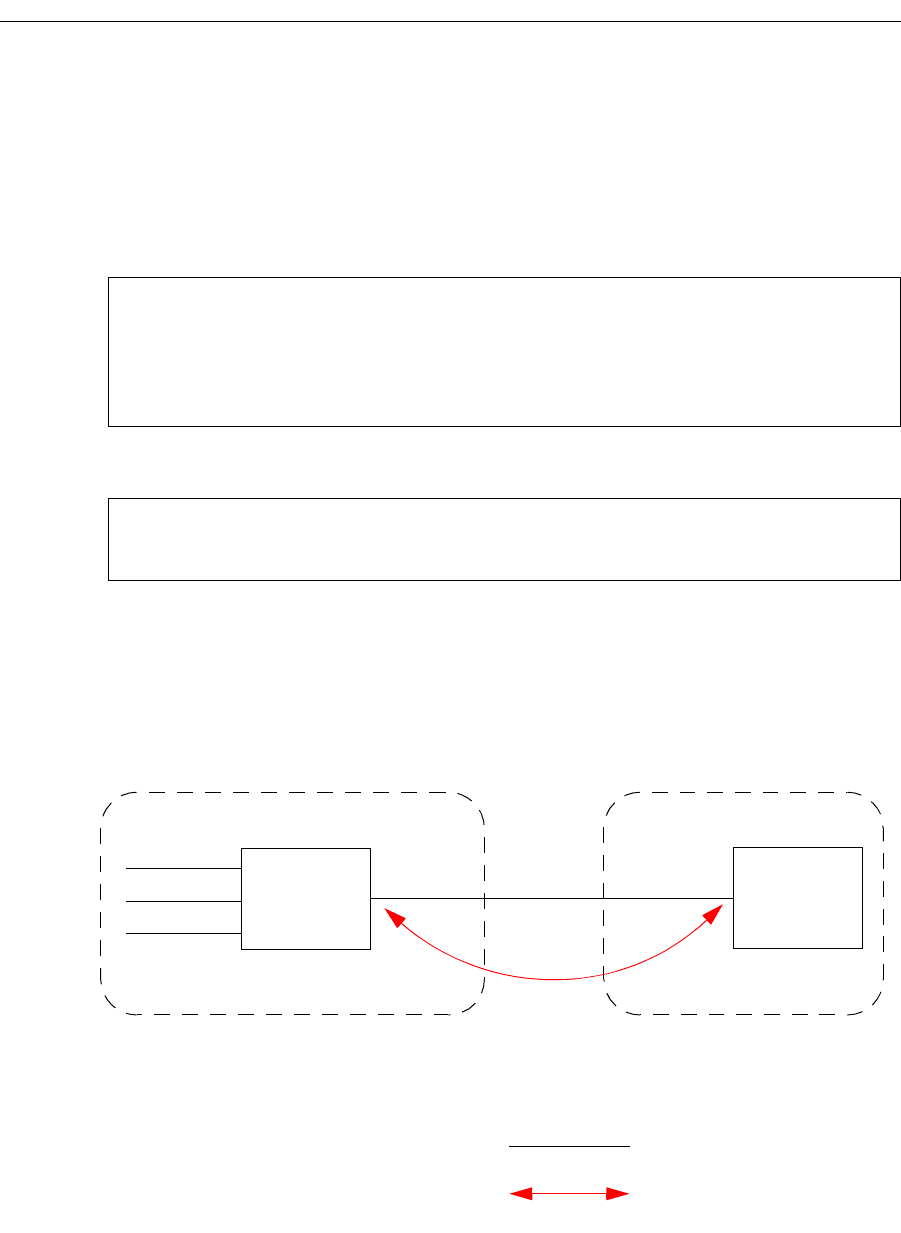
EBGP Aggregation Example
Figure 16 shows a simple EBGP configuration in which one peer is exporting an
aggregated route to its upstream peer and restricting the advertisement of contributing
routes to the same peer. The aggregated route is 212.19.192.0/19.
Figure 16. Sample BGP Configuration (Route Aggregation)
bgp create peer-group pg752to751 type external autonomous-system 64751
bgp add peer-host 10.200.12.15 group pg752to751
#
# Set the MED to be announced to peer group pg752to751
#
bgp set peer-group pg752to751 metric-out 20
bgp create peer-group pg752to751 type external autonomous-system 64751
bgp add peer-host 10.200.12.15 group pg752to751
bgp set peer-group pg752to751 metric-out 10
Physical Link
Legend:
Peering Relationship
AS-64901
SSR8
212.19.199.62/24
SSR9
AS-64900
212.19.198.1/24
212.19.192.2/24
194.109.86.6 194.109.86.5