Network Router User Manual
Table Of Contents
- Notices
- Contents
- About This Manual
- Introduction
- Hot Swapping Line Cards and Control Modules
- Bridging Configuration Guide
- Bridging Overview
- VLAN Overview
- Configuring SSR Bridging Functions
- Monitoring Bridging
- Configuration Examples
- SmartTRUNK Configuration Guide
- ATM Configuration Guide
- Packet-over-SONET Configuration Guide
- DHCP Configuration Guide
- IP Routing Configuration Guide
- IP Routing Protocols
- Configuring IP Interfaces and Parameters
- Configuring IP Interfaces to Ports
- Configuring IP Interfaces for a VLAN
- Specifying Ethernet Encapsulation Method
- Configuring Jumbo Frames
- Configuring Address Resolution Protocol (ARP)
- Configuring Reverse Address Resolution Protocol (RARP)
- Configuring DNS Parameters
- Configuring IP Services (ICMP)
- Configuring IP Helper
- Configuring Direct Broadcast
- Configuring Denial of Service (DOS)
- Monitoring IP Parameters
- Configuring Router Discovery
- Configuration Examples
- VRRP Configuration Guide
- RIP Configuration Guide
- OSPF Configuration Guide
- BGP Configuration Guide
- Routing Policy Configuration Guide
- Route Import and Export Policy Overview
- Configuring Simple Routing Policies
- Configuring Advanced Routing Policies
- Multicast Routing Configuration Guide
- IP Policy-Based Forwarding Configuration Guide
- Network Address Translation Configuration Guide
- Web Hosting Configuration Guide
- Overview
- Load Balancing
- Web Caching
- IPX Routing Configuration Guide
- Access Control List Configuration Guide
- Security Configuration Guide
- QoS Configuration Guide
- Performance Monitoring Guide
- RMON Configuration Guide
- LFAP Configuration Guide
- WAN Configuration Guide
- WAN Overview
- Frame Relay Overview
- Configuring Frame Relay Interfaces for the SSR
- Monitoring Frame Relay WAN Ports
- Frame Relay Port Configuration
- Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP) Overview
- Configuring PPP Interfaces
- Monitoring PPP WAN Ports
- PPP Port Configuration
- WAN Configuration Examples
- New Features Supported on Line Cards
SmartSwitch Router User Reference Manual 155
Chapter 12: BGP Configuration Guide
For example, in Figure 14, routers SSR12, SSR13, and SSR14 have the following line in
their CLI configuration files:
• The value of the set-pref option should be consistent with the import policy in the
network.
The metric value should be set high enough to avoid conflicts between BGP routes and
IGP or static routes. For example, if the import policy sets GateD preferences ranging
from 170 to 200, a set-pref metric of 170 would make sense. You should set the metric
high enough to avoid conflicts between BGP routes and IGP or static routes.
Multi-Exit Discriminator Attribute Example
Multi-Exit Discriminator (MED) is a BGP attribute that affects the route selection process.
MED is used on external links to discriminate among multiple exit or entry points to the
same neighboring AS. All other factors being equal, the exit or entry point with a lower
metric should be preferred. If received over external links, the MED attribute may be
propagated over internal links to other BGP speakers within the same AS. The MED
attribute is never propagated to other BGP speakers in neighboring autonomous systems.
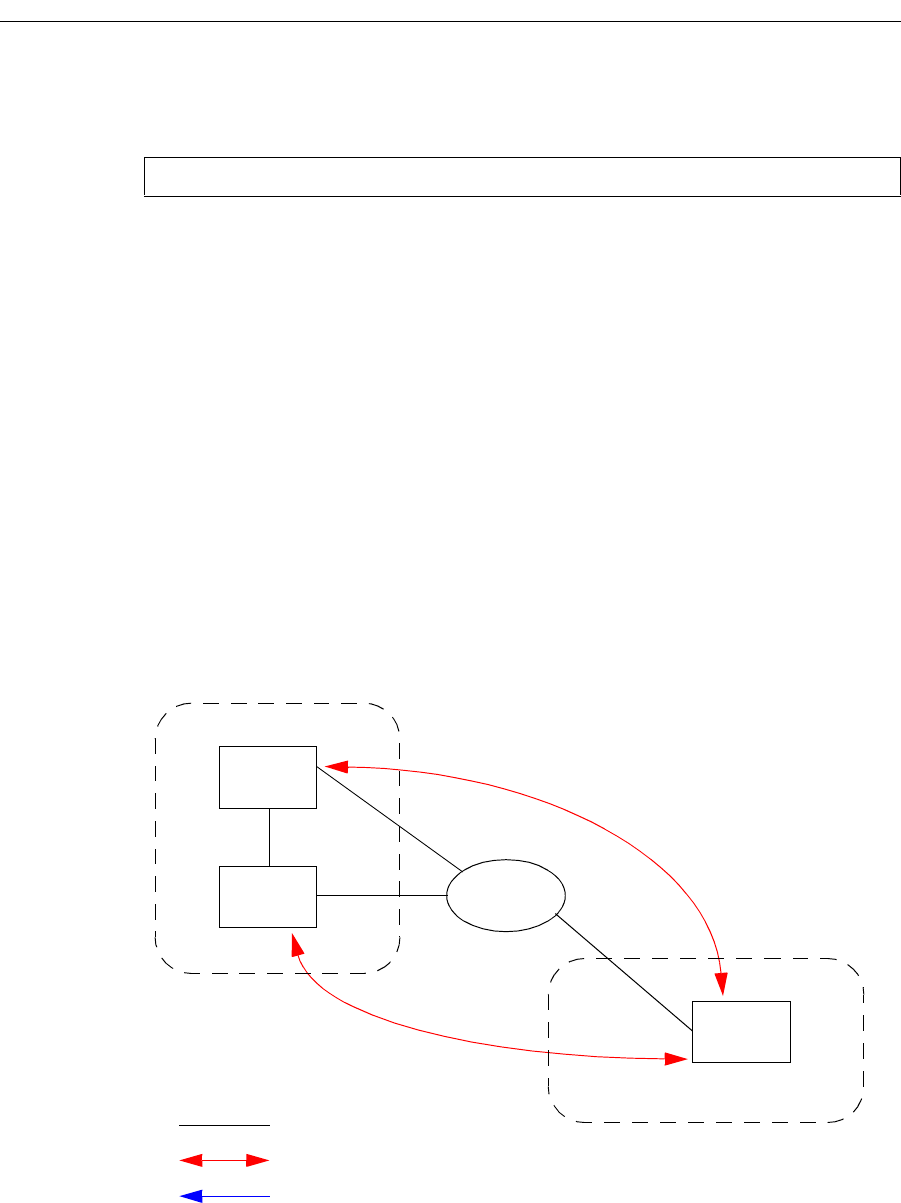
Figure 15 shows a sample BGP configuration where the MED attribute has been used.
Figure 15. Sample BGP Configuration (MED Attribute)
bgp set peer-group as901 set-pref 100
Physical Link
Legend:
Peering Relationship
Information Flow
C1
AS 64752
N1
10.200.12.15/24
10.200.12.4/24
10.200.12.0/24
10.200.12.6/24
AS 64751
172.16.200.4/24
172.16.200.6/24
SSR4
SSR6