Network Router User Manual
Table Of Contents
- Notices
- Contents
- About This Manual
- Introduction
- Hot Swapping Line Cards and Control Modules
- Bridging Configuration Guide
- Bridging Overview
- VLAN Overview
- Configuring SSR Bridging Functions
- Monitoring Bridging
- Configuration Examples
- SmartTRUNK Configuration Guide
- ATM Configuration Guide
- Packet-over-SONET Configuration Guide
- DHCP Configuration Guide
- IP Routing Configuration Guide
- IP Routing Protocols
- Configuring IP Interfaces and Parameters
- Configuring IP Interfaces to Ports
- Configuring IP Interfaces for a VLAN
- Specifying Ethernet Encapsulation Method
- Configuring Jumbo Frames
- Configuring Address Resolution Protocol (ARP)
- Configuring Reverse Address Resolution Protocol (RARP)
- Configuring DNS Parameters
- Configuring IP Services (ICMP)
- Configuring IP Helper
- Configuring Direct Broadcast
- Configuring Denial of Service (DOS)
- Monitoring IP Parameters
- Configuring Router Discovery
- Configuration Examples
- VRRP Configuration Guide
- RIP Configuration Guide
- OSPF Configuration Guide
- BGP Configuration Guide
- Routing Policy Configuration Guide
- Route Import and Export Policy Overview
- Configuring Simple Routing Policies
- Configuring Advanced Routing Policies
- Multicast Routing Configuration Guide
- IP Policy-Based Forwarding Configuration Guide
- Network Address Translation Configuration Guide
- Web Hosting Configuration Guide
- Overview
- Load Balancing
- Web Caching
- IPX Routing Configuration Guide
- Access Control List Configuration Guide
- Security Configuration Guide
- QoS Configuration Guide
- Performance Monitoring Guide
- RMON Configuration Guide
- LFAP Configuration Guide
- WAN Configuration Guide
- WAN Overview
- Frame Relay Overview
- Configuring Frame Relay Interfaces for the SSR
- Monitoring Frame Relay WAN Ports
- Frame Relay Port Configuration
- Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP) Overview
- Configuring PPP Interfaces
- Monitoring PPP WAN Ports
- PPP Port Configuration
- WAN Configuration Examples
- New Features Supported on Line Cards
Chapter 9: VRRP Configuration Guide
92 SmartSwitch Router User Reference Manual
Basic VRRP Configuration
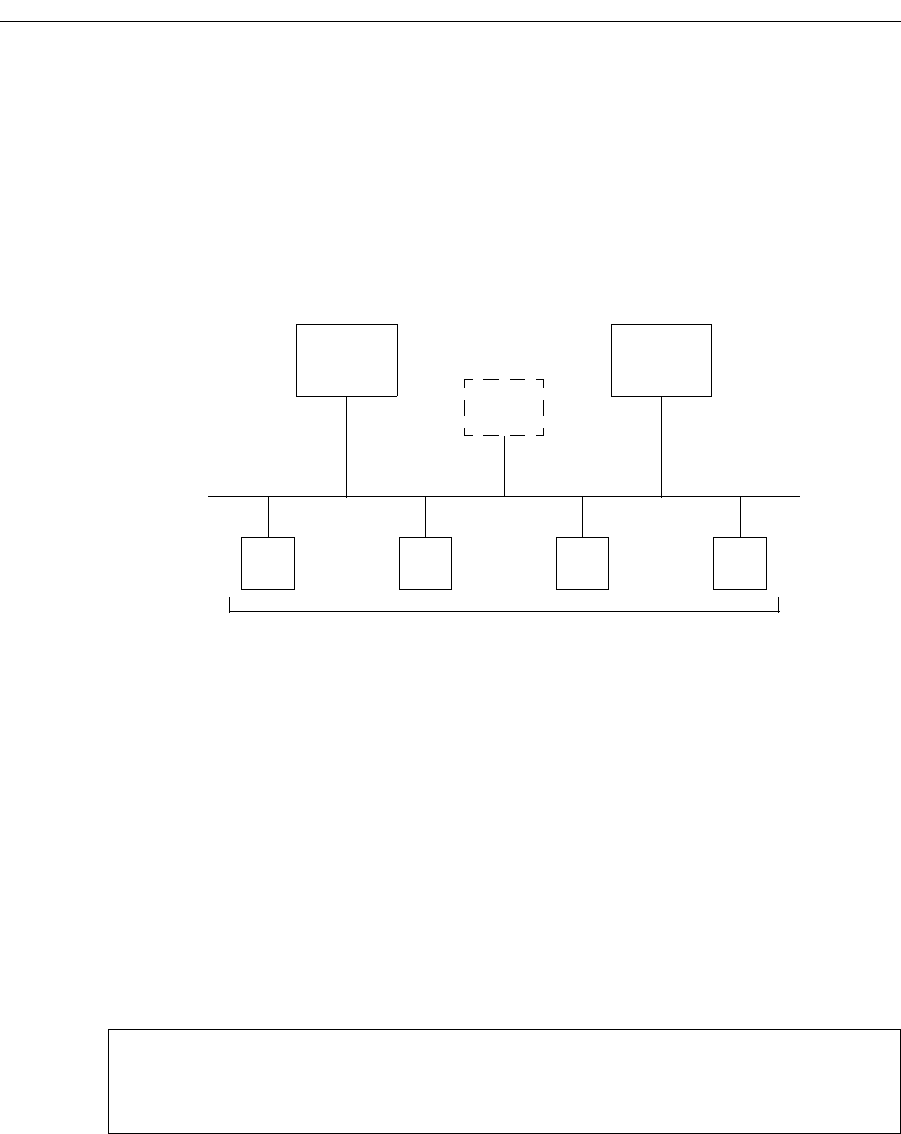
Figure 5 shows a basic VRRP configuration with a single virtual router. Routers R1 and R2
are both configured with one virtual router (
VRID=1). Router R1 serves as the Master and
Router R2 serves as the Backup. The four end hosts are configured to use 10.0.0.1/16 as
the default route. IP address 10.0.0.1/16 is associated with virtual router
VRID=1.
Figure 5. Basic VRRP Configuration
If Router R1 should become unavailable, Router R2 would take over virtual router
VRID=1
and its associated IP addresses. Packets sent to 10.0.0.1/16 would go to Router R2. When
Router R1 comes up again, it would take over as Master, and Router R2 would revert to
Backup.
Configuration of Router R1
The following is the configuration file for Router R1 in Figure 5.
Line 1 adds IP address 10.0.0.1/16 to interface test, making Router R1 the owner of this IP
address. Line 2 creates virtual router
VRID=1 on interface test. Line 3 associates IP address
10.0.0.1/16 with virtual router
VRID=1. Line 4 starts VRRP on interface test.
R1 R2
H1 H2 H3 H4
Default Route = 10.0.0.1/16
Master Backup
VRID=1
10.0.0.1/16
Interface Addr. =
10.0.0.1/16
VRID=1
;
Addr. =
10.0.0.1/16
Interface Addr. =
10.0.0.2/1
6
VRID=1
;
Addr. =
10.0.0.1/16
1: interface create ip test address-netmask 10.0.0.1/16 port et.1.1
2: ip-redundancy create vrrp 1 interface test
3: ip-redundancy associate vrrp 1 interface test address 10.0.0.1/16
4: ip-redundancy start vrrp 1 interface test










