Home Theater Server User Manual
Table Of Contents
- Contents
- About This Document
- Network Security
- TCP SYN attacks
- IP TCP syn-proxy
- Granular application of syn-proxy feature
- Syn-def
- No response to non-SYN first packet of a TCP flow
- Prioritizing management traffic
- Peak BP utilization with TRAP
- Transaction Rate Limit (TRL)
- Understanding transaction rate limit
- Configuring transaction rate limit
- Configuring the maximum number of rules
- Saving a TRL configuration
- Transaction rate limit command reference
- Global TRL
- TRL plus security ACL-ID
- security acl-id
- Transaction rate limit hold-down value
- Displaying TRL rules statistics
- Displaying TRL rules in a policy
- Displaying IP address with held down traffic
- Refusing new connections from a specified IP address
- HTTP TRL
- Overview of HTTP TRL
- Configuring HTTP TRL
- Displaying HTTP TRL
- Display all HTTP TRL policies
- Display HTTP TRL policy from index
- Display HTTP TRL policy client
- Display HTTP TRL policy starting from index
- Display HTTP TRL policy matching a regular expression
- Display HTTP TRL policy client index (MP)
- Display HTTP TRL policy client index (BP)
- Display HTTP TRL policy for all client entries (BP)
- Downloading an HTTP TRL policy through TFTP
- HTTP TRL policy commands
- Logging for DoS Attacks
- Maximum connections
- clear statistics dos-attack
- Maximum concurrent connection limit per client
- Firewall load balancing enhancements
- Syn-cookie threshhold trap
- Service port attack protection in hardware
- Traffic segmentation
- DNS attack protection
- Access Control List
- How ServerIron processes ACLs
- Default ACL action
- Types of IP ACLs
- ACL IDs and entries
- ACL entries and the Layer 4 CAM
- Configuring numbered and named ACLs
- Modifying ACLs
- Displaying a list of ACL entries
- Applying an ACLs to interfaces
- ACL logging
- Dropping all fragments that exactly match a flow-based ACL
- Enabling ACL filtering of fragmented packets
- Enabling hardware filtering for packets denied by flow-based ACLs
- Enabling strict TCP or UDP mode for flow-based ACLs
- ACLs and ICMP
- Using ACLs and NAT on the same interface (flow-based ACLs)
- Displaying ACL bindings
- Troubleshooting rule-based ACLs
- IPv6 Access Control Lists
- Network Address Translation
- Syn-Proxy and DoS Protection
- Understanding Syn-Proxy
- Configuring Syn-Proxy
- DDoS protection
- Configuring a security filter
- Configuring a Generic Rule
- Configuring a rule for common attack types
- Configuring a rule for ip-option attack types
- Configuring a rule for icmp-type options
- Configuring a rule for IPv6 ICMP types
- Configuring a rule for IPv6 ext header types
- Binding the filter to an interface
- Clearing DOS attack statistics
- Clearing all DDOS Filter & Attack Counters
- Logging for DoS attacks
- Displaying security filter statistics
- Address-sweep and port-scan logging
- Secure Socket Layer (SSL) Acceleration
- SSL overview
- SSL acceleration on the ServerIron ADX
- Configuring SSL on a ServerIron ADX
- Basic SSL profile configuration
- Advanced SSL profile configuration
- Configuring Real and Virtual Servers for SSL Termination and Proxy Mode
- Configuration Examples for SSL Termination and Proxy Modes
- SSL debug and troubleshooting commands
- Displaying socket information
38 ServerIron ADX Security Guide
53-1002440-03
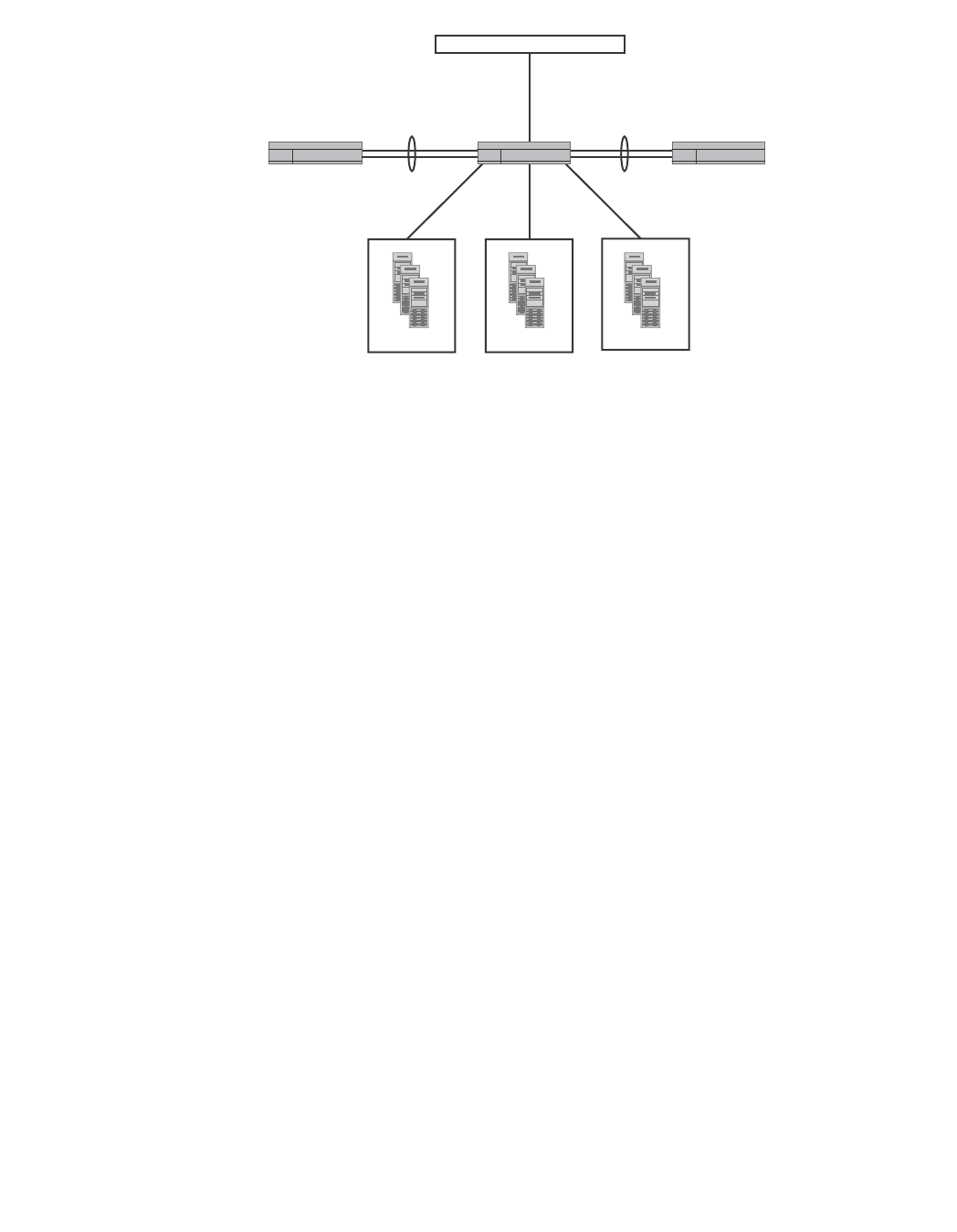
Traffic segmentation
1
Considerations when configuring VLAN bridging
The following considerations apply when configuring VLAN bridging:
• Up to 64 unique-pair VLAN bridges can be configured.
• A VLAN cannot be part of two different VLAN bridges.
• Two VLANs forming a bridge must have the same set of member ports on the ServerIron ADX
where they are joined.
• The Control VLAN (4094) and system default VLAN cannot be used for VLAN bridging.
• The hot-standby scenario is the only High Availability configuration supported with VLAN
bridging. In a hot-standby scenario with one-armed topology, after fail over, the existing session
may not be continued if the Layer-2 Switch in the middle cannot learn the MAC address of the
Gateway through the newly-active ServerIron ADX in time.
• VLAN bridging is only supported with switch code. It is not supported with the ServerIron ADX
router code.
• VLAN bridging is not supported with the SYN-proxy feature.
• All ports within a VLAN bridge must be tagged members of a VLAN and its associated bridged
VLAN.
• MAC learning is shared for VLANs that are bridged together.
Configuring VLAN bridging
The vlan-bridge command is used to configure VLAN bridging. To configure VLAN 10 and VLAN 12
for VLAN bridging, use the following command.
ServerIron(config)# vlan-bridge 10 12
Syntax: [no] vlan-bridge <VLAN-number> <VLAN-number>
The <VLAN-number> variables specify the pair of VLANs that you want to create VLAN bridging for.
Layer-2
Switch
Gateway
ServerIron ADX
(active)
Vlan 2 Vlan 3 Vlan 4
Domain1
Domain2
Domain3
Vlan -Bridging
2-12, 3-13, 4-14
Vlans
2, 3, 4, 12, 13, 14
Vlans
12, 13, 14
Vlans
2, 3, 4, 12, 13, 14
Vlan -Bridging
2-12, 3-13, 4-14
ServerIron ADX
(standby)










