Home Theater Server User Manual
Table Of Contents
- Contents
- About This Document
- Network Security
- TCP SYN attacks
- IP TCP syn-proxy
- Granular application of syn-proxy feature
- Syn-def
- No response to non-SYN first packet of a TCP flow
- Prioritizing management traffic
- Peak BP utilization with TRAP
- Transaction Rate Limit (TRL)
- Understanding transaction rate limit
- Configuring transaction rate limit
- Configuring the maximum number of rules
- Saving a TRL configuration
- Transaction rate limit command reference
- Global TRL
- TRL plus security ACL-ID
- security acl-id
- Transaction rate limit hold-down value
- Displaying TRL rules statistics
- Displaying TRL rules in a policy
- Displaying IP address with held down traffic
- Refusing new connections from a specified IP address
- HTTP TRL
- Overview of HTTP TRL
- Configuring HTTP TRL
- Displaying HTTP TRL
- Display all HTTP TRL policies
- Display HTTP TRL policy from index
- Display HTTP TRL policy client
- Display HTTP TRL policy starting from index
- Display HTTP TRL policy matching a regular expression
- Display HTTP TRL policy client index (MP)
- Display HTTP TRL policy client index (BP)
- Display HTTP TRL policy for all client entries (BP)
- Downloading an HTTP TRL policy through TFTP
- HTTP TRL policy commands
- Logging for DoS Attacks
- Maximum connections
- clear statistics dos-attack
- Maximum concurrent connection limit per client
- Firewall load balancing enhancements
- Syn-cookie threshhold trap
- Service port attack protection in hardware
- Traffic segmentation
- DNS attack protection
- Access Control List
- How ServerIron processes ACLs
- Default ACL action
- Types of IP ACLs
- ACL IDs and entries
- ACL entries and the Layer 4 CAM
- Configuring numbered and named ACLs
- Modifying ACLs
- Displaying a list of ACL entries
- Applying an ACLs to interfaces
- ACL logging
- Dropping all fragments that exactly match a flow-based ACL
- Enabling ACL filtering of fragmented packets
- Enabling hardware filtering for packets denied by flow-based ACLs
- Enabling strict TCP or UDP mode for flow-based ACLs
- ACLs and ICMP
- Using ACLs and NAT on the same interface (flow-based ACLs)
- Displaying ACL bindings
- Troubleshooting rule-based ACLs
- IPv6 Access Control Lists
- Network Address Translation
- Syn-Proxy and DoS Protection
- Understanding Syn-Proxy
- Configuring Syn-Proxy
- DDoS protection
- Configuring a security filter
- Configuring a Generic Rule
- Configuring a rule for common attack types
- Configuring a rule for ip-option attack types
- Configuring a rule for icmp-type options
- Configuring a rule for IPv6 ICMP types
- Configuring a rule for IPv6 ext header types
- Binding the filter to an interface
- Clearing DOS attack statistics
- Clearing all DDOS Filter & Attack Counters
- Logging for DoS attacks
- Displaying security filter statistics
- Address-sweep and port-scan logging
- Secure Socket Layer (SSL) Acceleration
- SSL overview
- SSL acceleration on the ServerIron ADX
- Configuring SSL on a ServerIron ADX
- Basic SSL profile configuration
- Advanced SSL profile configuration
- Configuring Real and Virtual Servers for SSL Termination and Proxy Mode
- Configuration Examples for SSL Termination and Proxy Modes
- SSL debug and troubleshooting commands
- Displaying socket information
ServerIron ADX Security Guide 129
53-1002440-03
DDoS protection
5
Configuring a rule for ip-option attack types
ServerIron ADX has a set of built-in rules to manage ip-option attack types. In this case, the rule
command is used with a <ip-option-attack> variable specified in Table 14.
The following example configures the "filter2" security filter with a rule to drop packets that are
associated with a ip-option record-route attack.
ServerIronADX(config)# security filter filter2
ServerIronADX(config-sec-filter2)#rule ip-option record-route drop
Syntax: [no] rule ip-option <ip-option-attack> [log | no-log] [drop | no-drop]
The <ip-option-attack> variable is specified as one of the options described in Table 14.
The log parameter directs the ServerIron ADX to log traffic on the bound interface that matches the
rule specified by the configured <ip-option-attack>. The no-log parameter disables this
function.
The drop parameter directs the ServerIron ADX to drop traffic on the bound interface that matches
the rule specified by the configured <ip-option-attack>. The no-drop parameter disables this
function
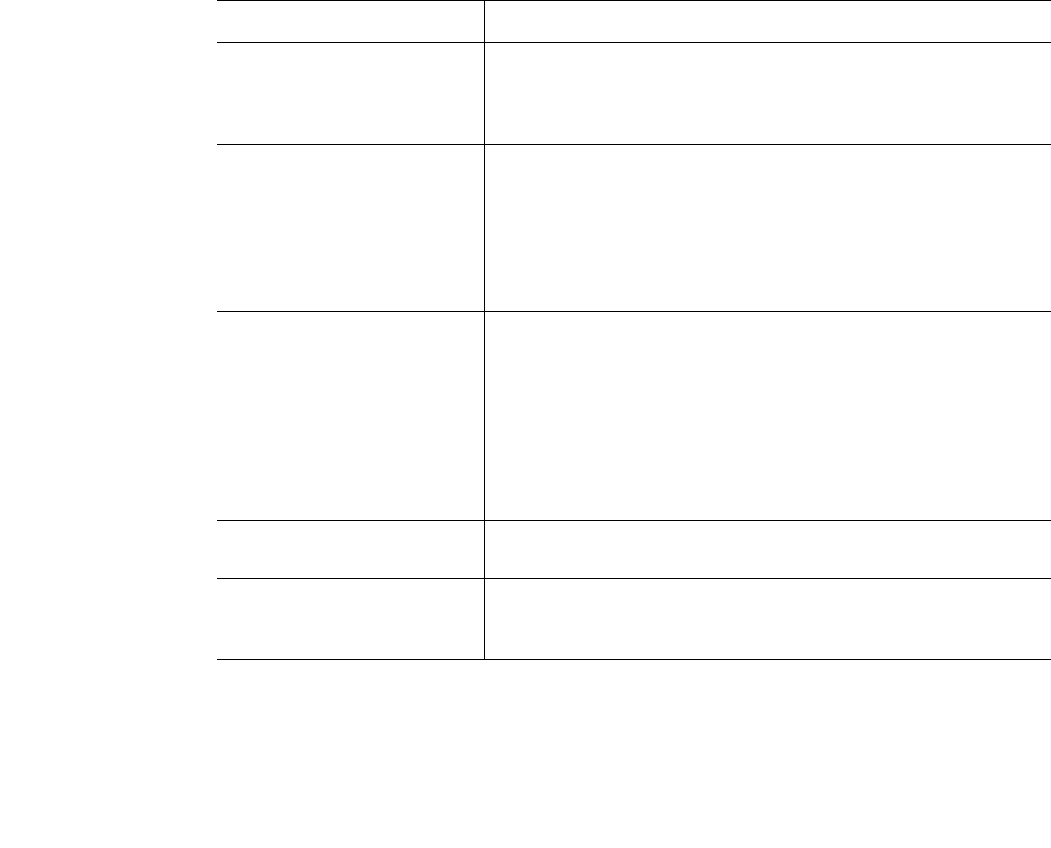
TABLE 14 ip-option attack types and descriptions
Attack Type Description
ip-option record-route The record-route option records the path of the packet, which an attacker
can analyze to learn details about a network’s addressing scheme and
topology.
Use ip-option record-route to drop packets with IP option 7 (record route) set.
ip-option strict-source-route The strict-source option provides a means for the source of a packet to
supply routing information to the gateways forwarding the packet to the
destination, and to record the route information.
With this option, an attacker can gain knowledge on the network’s
addressing scheme.
Use ip-option strict-source-route to drop packets having IP option 9 (strict
source routing).
ip-option loose-source-route The loose-source option provides a means for the source of the packet to
supply routing information to be used by the gateways in forwarding the
packet to the destination.
This option is different from strict-source route because gateway or host IP is
allowed to use any route of any number of other intermediate gateways to
reach the next address in the route. With this option, an attacker can gain
knowledge on the network’s addressing scheme.
Use ip-option loose-source-route to drop packets that have IP option 3 (loose
source routing).
ip-option timestamp Use ip-option timestamp to drop packets where IP option list includes option
4 (Internet timestamp).
ip-option stream-id The stream-ID option provides a way for the 16-bit SATNET stream identifier
to be carried through networks that do not support the stream concept.
Use ip-option stream-id to drop packets where the IP option is 8 (stream ID).










