2007 GOES HI-PERF 300S SERVICE MANUAL FOREWORD This service manual is designed primarily for use by certified Goes Master Service Dealer technicians in a properly equipped shop and should be kept available for reference. All references to left and right side of the vehicle are from the operator's perspective when seated in a normal riding position.
UNDERSTANDING MANUAL SAFETY LABELS AND DIRECTIONS Throughout this manual, important information is brought to your attention by the following symbols: SAFETY ALERT WARNING indicates a potential hazard that may result in severe injury or death to the operator, bystander or person(s) inspecting or servicing the vehicle. SAFETY ALERT CAUTION indicates a potential hazard that may result in minor personal injury or damage to the vehicle.
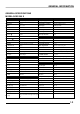
1 GENERAL INFORMATION 1 MAINTENANCE 2 CVT 3 ENGINE 4 TRANSMISSION 5 FUEL SYSTEM 6 BODY / SUSPENSION / STEERING 7 BRAKES 8 ELECTRICAL 9 2 4
GENERAL INFORMATION CHAPTER 1 GENERAL INFORMATION INFORMATION . . . . .……………... . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1.2 ENGINE SERIAL NUMBER LOCATION . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1.2 VEHICLE IDENTIFICATION NUMBER LOCATION. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1.2 GENERAL SPECIFICATIONS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1.
GENERAL INFORMATION 6MODEL INFORMATION VIN Identification Engine Serial Number Location Whenever corresponding about an engine, be sure to refer to the engine serial number. This information can be found stamped on the top LH side of the crankcase as shown below. Vehicle Identification Number Location The vehicle identification number (VIN) and engine serial number are important for identification purposes. See the illustrations. 1.
GENERAL INFORMATION 8 GENERAL SPECIFICATIONS MODEL:GOES 300 S DRIVE SYSTEM ENGINE Type 4 Stroke, Simple overhead camshaft Oil capacity/ type 900 CC/ 80w90 Displacement 272.3 cc Transmission selection Forward, Neutral, Reverse Cooling Water cooled Clutch type Centrifugal clutch Bore and stroke 72.7mm×65.6mm Final drive Chain Compression ratio 10.2 : 1 Forward gear ratio 17/45* 30/47 Number of valve 2 Rocker arm activated Reverse gear ratio 17/49* 21/37* 30/47 Inlet valve O 30.
GENERAL INFORMATION GENERAL VEHICLE INSPECTION AND MAINTENANCE Pre-Ride / Daily Inspection • Throttle - check for free operation Perform the following pre-ride inspection daily, and when • Headlight / Taillight / Brake light - check operation of all servicing the vehicle at each scheduled maintenance.
GENERAL INFORMATION GENERAL SPECIFICATIONS MODEL:TREETRENTAR 330 ON ROAD DRIVE SYSTEM ENGINE Type 4 stroke simple overhead camshaft Oil capacity/ type 900 CC/ 80w90 Displacement 272.3 cc Transmission selection Forward, Neutral, Reverse Cooling Water cooled Clutch type Centrifugal clutch Bore and stroke 72.7mm×65.6mm Final drive Chain Compression ratio 10.
GENERAL INFORMATION Vehicle Component Inspection Location 1.
GENERAL INFORMATION Glossary Of Terms ABDC: After bottom dead center. ACV: Alternating current voltage. Alternator: Electrical generator producing voltage alternating current. ATDC: After top dead center. BBDC: Before bottom dead center. BDC: Bottom dead center. BTDC: Before top dead center. CC: Cubic centimeters. Center Distance: Distance between center of crankshaft and center of driven clutch shaft. Chain Pitch: Distance between chain link pins (No. 35 = 3/8" or 1 cm).
GENERAL INFORMATION OD: Outside diameter. Ohm: The unit of electrical resistance opposing current flow. oz.: Ounce/ounces. Piston Clearance: Total distance between piston and cylinder wall. psi.: Pounds per square inch. PTO: Power take off. qt.: Quart/quarts. Regulator: Voltage regulator. Regulates battery charging system output at approx. 14.5 DCV as engine RPM increases. Reservoir Tank: The fill tank in the liquid cooling system. Resistance: In the mechanical sense, friction or load.
MAINTENANCE CHAPTER 2 MAINTENANCE PERIODIC MAINTENANCE CHART. . . . . . . . . . . . .. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2.3 PERIODIC MAINTENANCE OVERVIEW. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2.3 PRE-RIDE - 40 HOUR MAINTENANCE INTERVAL . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2.4 50 - 300 HOUR MAINTENANCE INTERVAL . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2.5 GENERAL VEHICLE INSPECTION AND MAINTENANCE. . . .
MAINTENANCE SPROCKET INSPECTION . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2.16 ELECTRICAL AND IGNITION SYSTEM . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2.16 BATTERY REMOVAL. . . . . . . ... . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2.16 BATTERY CLEANING . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2.17 BATTERY INSTALLATION. . .
MAINTENANCE PERIODIC MAINTENANCE CHART Periodic Maintenance Overview Careful periodic maintenance will help keep your vehicle in the safest, most reliable condition. Inspection, adjustment and lubrication of important components are explained in the periodic maintenance chart. Inspect, clean, lubricate, adjust and replace parts as necessary. When inspection reveals the need for replacement parts, use genuine Goes parts available from your dealer. NOTE: Service and adjustments are critical.
MAINTENANCE Pre-Ride - 40 Hour Maintenance Interval Periodic Maintenance Chart Maintenance Interval ITEM Remarks (whichever comes first) Hours ■ Steering - Calendar KM Pre-Ride - Check for free operation ◆ Front- Suspension - Pre-Ride - Make adjustments as needed. ◆ Rear- Suspension - Pre-Ride - Make adjustments as needed. Tire - Pre-Ride - Make adjustments as needed. Brake system - Pre-Ride - Check Operation Auxiliary brake - Pre-Ride - Inspect daily; adjust as needed.
MAINTENANCE 50 - 300 Hour Maintenance Interval Periodic Maintenance Chart Maintenance Interval ITEM Remarks (whichever comes first) Hours Calendar KM ◆ General lubrication 50H 3M 800 ■ Carburetor float bowl 50H 6M 800 ■ Throttle cable 50H 6M 800 ■ Choke cable 50H 6M 800 ◆ Carburetor intake flange 50H 6M 800 ■ Brake pads wear 50H 6M 800 Lubricate all grease fittings, pivots, & cables. Drain bowl periodically and prior to storage.
MAINTENANCE GENERAL VEHICLE INSPECTION AND MAINTENANCE Frame, Nuts, Bolts and Fastener Inspection Periodically inspect the torque of all fasteners in accordance with the maintenance schedule. Check that all cotter pins are in place. Refer to specific fastener torques listed in each chapter. Standard Torque Specifications The following torque specifications are to be used as a general guideline. There are exceptions in the steering, suspension, and engine areas.
MAINTENANCE Re-Coil Starter and Operation If the battery becomes too weak to start the engine, use the re-coil starter to start the engine until the battery is serviced. Always stop the engine and refuel outdoors or in a well ventilated area. Do not smoke or allow open flames or sparks in or near the area where refueling is performed or where gasoline is stored. Do not overfill the tank. Fill the tank to the bottom of the filler neck. This will allow for thermal expansion.
MAINTENANC Choke Cable Adjustment Idle Speed Adjustment Verify free play of 1.6-4.76 mm (1/16-3/16”) and smooth 1. Start engine and warm it up thoroughly. operation of choke cable. 2. Adjust idle speed by turning the slide adjustment screw in (clockwise) to increase or out (counterclockwise) to decrease RPM. (Refer to illustration). Idle Speed 1400 ± 100 r.p.m. NOTE: Adjusting the idle speed affects throttle cable freeplay.
MAINTENANCE Air Screw Adjustment Fuel Filter 1. Set idle speed to specification. Always check throttle cable The fuel filter should be replaced in accordance with the freeplay after adjusting idle speed and adjust if necessary. “Periodic Maintenance Chart” or whenever sediment is 2. To adjust the mixture screw setting, you will need to use visible the Adjustment Screwdriver. Slowly turn the mixture screw in the filter. clockwise until engine idle RPM begins to decrease.
MAINTENANCE Carburetor Draining The carburetor float bowl should be drained periodically to remove accumulated moisture or sediment from the bowl, or before extended periods of storage. 1. Place a container beneath the bowl drain hose. 2. Loosen drain screw and allow fuel in the float bowl and fuel line to drain completely. Gasoline is extremely flammable and explosive under certain conditions. Do not smoke or allow sparks in near the area when inspecting fuel valve. 1.
MAINTENANCE Air Filter Service 1. Remove the seat. 2. Release the air box cover spring clips and remove the cover. 6. Reinstall the screen, foam filter and air box cover. Secure the clips. 7. Reinstall the seat. Air Box Sediment Tube Periodically check the air box sediment tube located toward the rear of the machine. Drain whenever deposits are visible in the clear tube. 3. Remove the foam air filter. Wash the foam filter in warm soapy water, then rinse and let it dry.
MAINTENANCE ENGINE Engine Oil and Filter Change Oil Lever 1. Position the vehicle on a level surface. 2. Clean area around the drain plug. 3. Run engine two to three minutes until warm. 4. Stop the engine. To check the oil level: 1. Set machine on a level surface. 2. Start and run engine for 20-30 seconds. This will return oil to its true level in the engine sump. CAUTION 3. Stop engine and check oil level sight glass. 4. Check to see that the oil level is in the ’normal’ range.
MAINTENANCE 10. Reinstall the pre-filter drain plug. Torque to 11 ft. lbs. (15 Valve Clearance Adjustment Nm). INTAKE / EXHAUST VALVE CLEARANCE 1. Remove the cylinder head cover to expose the intake and exhaust rocker arms. Crankcase Drain Plug: 15 Nm (11 ft. lbs.) 11. Remove the filler. Add 1800 ml (60 oz.) of recommended oil. Do not overfill. 12. Reinstall the filler . 13. Start the engine. Allow it to idle for one to two minutes. 14. Stop the engine and inspect for leaks. 15. Check the oil level.
MAINTENANCE Engine Mounts TRANSMISSION AND FINAL DRIVE Inspect engine mounts for cracks or damage. Transmission Lubrication The transmission lubricant level should be checked and changed in accordance with the maintenance schedule. Check engine fasteners and ensure they are tight Remember to: • Verify the vehicle is level before proceeding. CVT Drying NOTE: If operating the ATV through water, be sure to • Verify the vent hose is routed properly and is not obstructed.
MAINTENANCE 2. The chain should have 6-12 mm (1/4”-1/2”) deflection. If the chain needs adjustment, use the following procedure. Drive Chain Adjustment 1. Loosen the four rear axle hub mount bolts. 5. Clean and reinstall the drain plug. Torque to 19 Nm (14 ft. lbs.). Transmission Drain Plug: 19 Nm (14 ft. lbs.) 6. Add the recommended lubricant. Maintain the lubricant level 3. Turn the chain adjuster clockwise until chain tension is setting at the bottom of the fill plug hole threads. specification.
MAINTENANCE Sprocket Inspection IMPORTANT: DO NOT activate ATV batteries unless they Inspect the front and rear sprockets for worn, broken or bent will be put into service within 30 days of activation. teeth. The ATV has a Low Maintenance style battery. Do not remove the battery cap strip to check acid level or add water once the battery have been activated. Perform the proper battery tests and charge or replace the battery as required.
MAINTENANCE CAUTION Low-amperage charger (1.2A): 5~10 Hr.s. High-amperage charger(12A): 0.5Hr.s. To reduce the chance of sparks: NOTE: DO NOT use a constant high-amperage Whenever removing the battery, disconnect the battery charger to charge this style of battery. Use a negative (black) cable first. When reinstalling the low-amperage charger capable of charging voltage battery, install the negative cable last. Battery Cleaning Keep the battery terminals and connections free of corrosion.
MAINTENANCE Fuses / Fuse Holder Location 4. Clean with electrical contact cleaner or a glass bead spark A 15 Amp fuse protects the main electrical system, a 30 Amp plug cleaner only. CAUTION: A wire brush or coated fuse protects ignition system and a 10 Amp fuse protects the abrasive should not be used. headlight and taillight. See illustrations for fuse locations. 5. Measure gap with a wire gauge. Refer to specifications for proper spark plug type and gap.
MAINTENANCE STEERING AND SUSPENSION Tie Rod End / Steering Inspection Steering 1. Elevate front end of ATV so front wheels are off the The steering components should be checked periodically for loose ground. Check for any looseness in front hub / wheel fasteners, worn tie rod ends, and damage. Also check to make assembly by grasping the tire firmly at top and bottom first, sure all cotter pins are in place. If cotter pins are removed, they and then at front and rear.
MAINTENANCE 5. Repeat inspection for inner tie rod end (on steering post). 6. Replace any worn steering components. Steering should move freely through entire range of travel without binding. Wheel Alignment Severe injury or death can result from improper toe alignment and adjustment. All tie rod adjustments should be performed by an authorized Goes dealer. LUBRICATION / GREASE POINTS Use the following procedure to check the toe alignment of the There are grease zerks on the upper and lower A-arms.
MAINTENANCE Rear Suspension Inspection BRAKE SYSTEM Compress and release rear suspension. Damping should be smooth throughout the range of travel. 1. Check all rear suspension components for wear or damage. Brake System Inspection 2. Inspect shock for leakage. system in good operating condition. Service life of brake The following checks are recommended to keep the brake system compo nents depends on operating conditions.
MAINTENANCE 4. Measure the distance from the string to the rim at the front • Shorten or lengthen the tie rod until alignment is as required and rear of the front rim. Rear measurement should be 2-3 mm to achieve the proper toe setting – 0~6mm. more than the front measurement. •Important: When tightening the tie rod end jam nuts, the rod ends must be held parallel to prevent rod end damage and premature wear. Damage may not be immediately apparent if done incorrectly. See illustration.
MAINTENANCE Parking Brake Adjustment WHEELS AND TIRES 1. Position the vehicle on a level surface. Wheels 2. Shift the transmission into neutral (if applicable). Inspect all wheels for runout or damage. Check wheel bolts 3. Elevate the rear of the vehicle by placing a suitable stand and ensure they are tight. Do not over tighten the wheel bolts. under the frame. The rear tires should be slightly off the ground. Wheel, Hub and Spindle Torque Table 4.
MAINTENANCE Tire Pressure Tire Pressure Inspection (PSI - Cold) Front Rear 5 psi (34.5 kPa) 5 psi (34.5 kPa) Tire Inspection Operating an ATV with worn tires will increase the possibility of the vehicle skidding and Wheel Installation - Front / Rear possible loss of control. 1. With the transmission in gear and the parking brake Worn tires can cause an accident. locked, place the wheel in the correct position on the wheel Always replace tires when the tread depth hub.
CVT SYSTEM CHAPTER 3 CVT SYSTEM CVT SYSTEM . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3.2 CVT MAINTENANCE / INSPECTION. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3.2 DRIVE CLUTCH OPERATION. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3.2 DRIVEN CLUTCH OPERATION. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3.
CVT SYSTEM CVT SYSTEM Drive Clutch Operation Drive clutches primarily sense engine RPM. The major component which controls shifting function are the shift centrifugal weights (rollers) inside the moveable sheave. Whenever engine RPM is increased, centrifugal force is All CVT maintenance or repairs should be created, causing the rollers to push against the cam plate and performed only by a certified Goes Service Dealer force the moveable sheave toward the drive belt.
CVT SYSTEM CVT System Drying NOTE: If operating the ATV through water, be sure to check the CVT cover and other ATV components for water ingestion. The ATV should be checked immediately. Refer to Owner’s Manual for Safe Riding Tips. 1. To drain any water that may be trapped inside the CVT area, remove the CVT drain plug and O-ring located on the bottom of the crankcase and let the water drain out. The CVT drain plug is shown at right. 2.
CVT SYSTEM CVT EXPLODED VIEW 3.
CVT SYSTEM CVT OVERHEATING/DIAGNOSIS During routinemaintenance or whenever CVT system overheating is evident, it’s important to check the inlet and outlet ducting for obstructions. Obstructions to air flow through the ducts will significantly increase CVT system operating temperatures. The ATV should be operated in LOW RANGE (if equipped) when pulling or plowing heavy loads, or if extended low speed operation is anticipated.
CVT SYSTEM 4. Remove the entire re-coil starter bolt. 5. Remove the lock nut, washer, and the re-coil start pawl from the crankshaft. Clutch Cover Removal 6. Remove all screws from CVT case and case. 1. Remove the left foot rest. 2. Loosen the duct clamps and slide ducts upward off cover. 3. Remove all screws and cover with re-coil start attached. 7. Use two hands to hold the cam plate and the primary sliding sheave together when removing the primary sliding sheave and the cam plate assembly.
CVT SYSTEM 8. Remove the primary sliding sheave and cam plate assembly (D) as one assembly. The re-coil starter recombination. bolts must with loctite when Spike load system Removal NOTE: This assembly utilizes a torque limiting system to prevent transmission damage. Use care removing the clutch assembly, as the torque—limiting 2. Remove the nut by pincer and air wrench. components become free and could fall apart. Mark or 3. Pull the entire clutch off as an assembly. note parts during disassembly.
CVT SYSTEM 2. Set the driven clutch assembly on a flat surface. Remove the cover, spring washer stack, and ball bearing retainer. Inspect components for excessive wear or damage. Replace components as required. Spring Washer Orientation: Additional 1mm washer can be added here to increase spring preload 3. Remove the ball bearings. Use a snap--ring pliers to remove the retainer on the hold cam. Remove the washer. Inspect the hold cam for excessive spline wear or damage. Replace the component if required.
CVT SYSTEM DRIVEN CLUTCH SERVICE 6. Secure the assembly in a clamping device. To Driven Clutch Disassembly and Inspection access the driven spring, mark and remove the 4. Inspect the condition of the clutch drum. Measure the outer sheave retaining nut. Remove the friction inside diameter of the cover at 90 degree intervals using pad assembly and driven spring. a caliper. Inspect the condition and diameter of the drum lining.
CVT SYSTEM 9. Remove the rollers and pins using a needle—nose pliers and inspect all components. Replace if any damage or excess wear is found. Replace the o--rings and seals anytime the driven is apart. 12. Have an assistant available for final assembly. Install the compression spring. Place the friction pad assembly over the spring and compress the driven assembly together with both hands. With the assembly compressed and the threads exposed, have an assistant thread a new retaining nut onto the shaft.
CVT SYSTEM 3. Install the drive belt on driven clutch and move belt as far into the sheaves as possible. 1. Insert new seals into the outer sheave assembly. Fill the outer sheave cavity with fresh grease and slide onto the inner 4. Loop the belt over the drive clutch and install driven clutch on transmission shaft. sheave shaft. Align and insert the roller/pin assemblies. 5. Install driven clutch hub, then the retaining nut and O-ring. Install new o-rings and the outer roller pin cover.
CVT SYSTEM DRIVE CLUTCH SERVICE Drive Clutch Disassembly and Inspection 1. Remove outer drive clutch sheave and drive belt. Note parts 6. Inspect sheave faces (E) for grooves or wear. Check assembly order. bushings (F) and seals in the moveable sheave. The sleeve 2. Slide sheave and cam plate off crankshaft as an assembly. should be a close, smooth fit in the bushings and seals should NOTE: When removing primary sliding sheave and cam fit tightly on the sleeve.
CVT SYSTEM Drive Clutch Assembly 5. Open the sheaves of the secondary clutch and push the belt 1. Apply a very light film of grease to the seal lips and drive down between the sheaves. clutch sleeve. Then install the sleeve. 2. Install all rollers with open end facing inward toward divider (A) (the side with inner bushing visible.) 3. Install the cam plate. 6. Install the driven clutch on the transmission input shaft, looping the belt onto the drive clutch sleeve as shown. 7.
ENGINE CHAPTER 4 ENGINE ENGINE SERVICE . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4.3 ENGINE EXPLODED VIEWS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4.3 ENGINE EXPLODED VIEWS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4.4 OIL FLOW DIAGRAM . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4.
ENGINE OIL PUMP DRIVE SPROCKET REMOVAL/ INSPECTION . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4.25 OIL PUMP REMOVAL. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4.26 CRANKCASE DISASSEMBLY . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4.26 CRANKCASE SEPARATION AND CAM CHAIN REMOVAL. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4.26 CRANKSHAFT REMOVAL. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
ENGINE ENGINE EXPLODED VIEW 4.
ENGINE 4.
ENGINE OIL FLOW DIAGRAM 4.
ENGINE The following components require engine removal for service: 1. Cam Chain and Sprockets The piston have an identification mark for piston 2. Cylinder Head placement. 3. Cylinder 4. Piston/RIngs Note the directional and identification marks when 5. Camshaft viewing the pistons from the top. The letters “IN” must 6. Crankshaft always be toward the intake side of the engine. 7. Crankshaft Main Bearings 8. Crankcase The other numbers are used for identification as to 9.
ENGINE Front engine mount, left hand ENGINE INSTALLATION NOTES After the engine is installed in the frame, review this checklist and perform all steps that apply. General Items Install previously removed components using new gaskets, seals, and fasteners where applicable. ◎ ◎ Perform regular checks on fluid levels, controls, and all important areas on the vehicle as outlined in the daily pre-ride inspection checklist (refer to Chapter 2).
ENGINE ENGINE LUBRICATION 4. Align single (TDC) mark on flywheel with in the Oil Type 0--40W Synthetic oil. inspection hole, and the cam sprocket pin (facing upward) Capacity Approximately 1800 cc aligned with the camshaft to crankshaft center line. Drain Plug/ Screen Fitting 20 Nm . . . . . . NOTE: The sprocket marks align with gasket surface, the Oil Pressure Specification: Continuous oil flow out of stator housing plug hole at Idle RPM.
ENGINE CAM CHAIN TENSIONER INSPECTION 1. Allow cam chain tensioner plunger to extend outward to the end of its travel. Inspect tensioner (A) and plunger (B) for wear or damage. 4. Mark or tag rocker arms and shafts to keep them in order for assembly. ROCKER ARM/SHAFT DISASSEMBLY AND 5. Inspect each rocker arm cam follower surface. If there is any damage or uneven wear, replace the rocker arm.
ENGINE 7. Measure O.D. of rocker shafts for out--of --round. Inspect them for wear or damage. Replace if excessive wear is evident. NOTE: Orientation of the rocker shafts is important for reassembly. Place only the exhaust rocker shaft into the exhaust side of the cam support. 9. Inspect rocker adjuster screws for wear, pitting, or damage to threads of the adjuster or locknut. Replace all worn or damaged parts. NOTE: The end of the adjuster is hardened and cannot be ground or re-faced. 8. Measure I.D.
ENGINE 3. If not removing the cylinder for other service, secure Cam Lobe Height the cam chain with a wire to prevent it from falling into the crankcase. Intake 4. Inspect cam sprocket teeth for wear or damage. Std: 35.16 mm Replace if necessary. Limit: 35.11 mm Exhaust Std: 35.05 mm Limit: 35.00 mm 2. Thoroughly clean the cam shaft 3. Measure height of each cam lobe using a micrometer. Replace cam if worn below minimum height. Replace camshaft if damaged or if any part is worn excessively.
ENGINE CYLINDER HEAD REMOVAL NOTE: Cam chain and tensioner must be removed. If no crankshaft service is being performed, secure cam chain with mechanics wire to avoid chain drop into the crankcase. 1. Loosen each of the four cylinder head bolts evenly 1/4 turn each time in a cross pattern until loose. 4. Remove intake manifold nuts. 5. Remove cylinder head and head gasket. 2. Remove the cylinder bolts and tap the cam support tower with a plastic hammer until loose. Remove. 3.
ENGINE Cylinder Head Inspection CYLINDER HEAD DISASSEMBLY 1. Thoroughly clean cylinder head surface to remove all traces of gasket material and carbon. Use care not to damage sealing surface. If there is damage found on the cylinder head combustion chamber, it is recommended the component be replaced. Wear eye protection or a face shield during cylinder head disassembly and reassembly. NOTE: Keep all parts in order with respect to their location in the cylinder head.
ENGINE 4. Measure free length of the inner and outer springs with VALVE INSPECTION a caliper. 1. Remove all carbon from valve with a soft wire wheel. 2. Check valve face for runout, pitting, and burnt spots. To check for bent valve stems, mount valve in a drill or use “V” blocks and a dial indicator. Valve Spring Free Length Outer Spring Limit: 42.0mm Inner Spring Limit: 31.3mm 5. Check spring for squareness as shown. Replace spring 3.
ENGINE 5. Measure diameter of valve stem with a micrometer in VALVE SEAT RECONDITIONING three places and in two different directions (six Valve Seat Inspection Inspect valve seat in cylinder head for pitting, burnt spots, roughness, and uneven surface. If any of the above conditions exist, the valve seat must be reconditioned. If the valve seat is cracked the cylinder head must be replaced. measurements total). Replace if excessive wear is evident. Valve Stem OD LIMIT: Intake Valve Limit: 4.
ENGINE 1. Install pilot into valve guide. 5. To check the contact area of the seat on the valve face, apply a thin coating of PrussianBluetpaste to the valve seat. If using an interference angle (46°) apply black marker to the entire valve face (A). 2. Apply cutting oil to valve seat and cutter. 6. Insert valve into guide and tap valve lightly into place a 3. Place 46° cutter on the pilot and make a light cut. few times. 7.
ENGINE CYLINDER HEAD ASSEMBLY Wear eye protection during assembly. NOTE: Assemble the valves one at a time tomaintain proper order. NOTE: When using an interference angle, the seat 1. Install new valve seals on valve guides. contact point on the valve will be very narrow, and is a normal condition. Look for an even and continuous contact point on the black marker, all the way around the valve face. 8. Clean all filings from the area with hot soapy water, 2. Apply engine oil to valve guides and seats.
ENGINE ENGINE BOTTOM END DISASSEMBLY Cylinder Removal Follow engine disassembly procedures to remove valve cover, camshaft and rocker arms, and cylinder head. 1. Remove cam chain guide at front of cylinder. 2. Remove the two 6 mm cylinder base bolts. 6. Place retainer on spring and install valve spring compressor. Compress spring only enough to allow split keeper installation to prevent loss of spring tension. Install split keepers with the gap even on both sides. 3. Remove coolant tube from cylinder. 7.
ENGINE 4. Rock cylinder forward and backward and lift it from the 3. Remove the compression rings, starting with the top crankcase, supporting piston and connecting rod. ring. Support piston with Piston Support Block. CAM CHAIN FOLLOWER /TENSIONER BLADES 1. Remove bolt securing tensioner blade to crankcase A. *Using a piston ring pliers: Carefully expand ring and lift it off the piston. 2. Remove blades and inspect for cracks, wear, or damage.
ENGINE 3. Inspect cylinder for wear, scratches, or damage. 4. Inspect cylinder for taper and out of round with a telescoping gauge or a dial bore gauge. Measure in two different directions, front to back and side to side, on three different levels (10mm down from top, in the middle, and 10mm up from bottom). HONING TO DEGLAZE A finished cylinder should have a cross-hatch pattern to ensure piston ring seating and to aid in the retention of the fuel/oil mixture during initial break in.
ENGINE PISTON INSPECTION 1. Measure piston outside diameter at a point 7mm up 4. Measure piston pin O.D. Replace piston pin if out--of--round. from the bottom of the piston at a right angle to the direction of the piston pin. 5. Measure connecting rod small end ID. Replace crankshaft if out--of--round. 2. Subtract this measurement from the maximum cylinder measurement obtained earlier. Piston to Cylinder Clearance Std: 0.02-0.05 mm Limit: 0.1 mm 3. Measure piston pin bore.
ENGINE PISTON RING INSTALLED GAP 1. Place each piston ring inside cylinder using piston to push ring squarely into place as shown. Piston Ring Installed Gap Top Ring Std: 0.1--0.3 mm Limit: 0.8 mm Second Ring Std: 0.35--0.5 mm Limit: 1.0 mm Oil Ring Std: 0.2-0.7 mm Limit: 1.5 mm 2. Measure the gap with a feeler gauge at both the top and bottom of the cylinder. NOTE: Measure at two points in the cylinder A difference in end gap indicates cylinder taper.
ENGINE ALTERATOR/ STATER/ OIL PUMP EXPLODED VIEW NOTE: The CVT system, starter motor, starter drive, flywheel, stator, oil pump and transmission can be serviced with the engine in the frame. 4.
ENGINE STARTER DRIVE GEAR REMOVAL/ INSPECTION 5. Inspect gear teeth on starter drive. Replace starter drive if gear teeth are cracked, worn, or broken. 1. Remove water pump tube. 2. Take off water pump bolts. 3. Tap water pump lightly with a plastic hammer in reinforced areas only until loose. FLYWHEEL REMOVAL / INSPECTION The crankshaft end contains an oil passage plunge joint (A) as shown below. The plunger must be able to move in and out freely.
ENGINE FLY WHEEL/ ONE-WAY CLUTCH REMOVAL / INSPECTION 1. Remove the hex bolts that attach the one—way drive clutch to the flywheel. OIL PUMP DRIVE SPROCKET REMOVAL / INSPECTION 1. Remove the oil pump shield. 2. The outer chain is oil and water pump drive chain. 2. Inspect the bearing surfaces and drive teeth for signs of wear or gouging. Replace the one-way clutch as an assembly if it is not working properly. The inner chain is cam chain. 3.
ENGINE 4. Inspect sprocket teeth for wear or damage. CRANKCASE DISASSEMBLY NOTE: Engine must be removed from the frame to perform any crankcase or crankshaft removal. NOTE: The starter, starter drive, flywheel, stator, oil pump and transmission can be serviced with the engine in the frame. CRANKCASE SEPARATION AND CAM CHAIN REMOVAL NOTE: Stator housing, flywheel and gears have are 5. Replace any worn or damaged parts. previously removed for this procedure.
ENGINE CRANKSHAFT / CAM & OIL CHAIN / SPROCKET INSPECTION 1. Inspect the crankshaft main bearings and cam and oil pump chain sprocket for wear or damage. 3. Watch the gap along the crankcase mating surface and separate the crankcase evenly. 4. Once the crankshaft bearing is free from the case, NOTE: Due to extremely close tolerances and the crankshaft and cam chain can be removed by minimal wear, the bearings must be inspected hand for service. visually, and by feel.
ENGINE CRANKCASE / BEARING INSPECTION NOTE: Removal and installation of new seals is recommended anytime the crankcase is disassembled. 1. Inspect the bearings in the crankcase. NOTE: Due to extremely close tolerances and minimal side wear, the bearing must be inspected visually and by feel. Look for signs of discoloration, scoring or galling. Turn the inner race of bearing. The bearing should turn smoothly and quietly. The outer race should fit tightly in the crankcase.
ENGINE CRANKCASE REASSEMBLY 3. Install a new gasket onto the right hand crankcase half. Applying a thin amount of crankcase sealer to the gasket Crankshaft and Cam/ Oil Chain Installation will help hold it in place. Lubricate all bearings with clean engine oil before assembly. 1. Support the crankcase on blocks. 2. Install the balance shaft. Turn the flat up. 4. Install 4 flange bolts (circled) from the right side crankcase. NOTE: Use care not to damage the crankshaft end. 3.
ENGINE 5. Loop the cam chain through the chain room and secure 3. Install chain on oil pump and crankshaft sprocket then with mechanic’s wire. place oil pump sprocket into oil pump shaft OIL PUMP AND CHAIN INSTALLATION 5. Install the circlip into oil pump shaft. NOTE: Oil pump is not a servicable assembly. Do not disassemble pump. Replace entire component. 1. Inspect the oil pump sealing surface on the crankcase. Apply a liberal amount of engine oil to the surfaces and pump. 2.
ENGINE PISTON RING INSTALLATION NOTE: Apply clean engine oil to all ring surfaces and ring lands. Always check piston ring installed gap before rings are installed on piston. If the piston has been in service, clean any accumulated carbon from the ring grooves and oil control ring holes. 1. Place the oil control ring expander in oil ring groove with the end gap facing forward. The expander has no up or down marking and can be installed either way. The ends should butt squarely together and must not overlap.
ENGINE 7. Push the rings into the taper using a metallic, 9. Place piston into blunt--edge tool. blunt--edge tool while holding the cylinder down. This will help push the piston past the ring taper into the cylinder. 9. Use non-metallic rod to push piston until piston through the tool to cylinder. 8. Up-side-down cylinder then place the blunt--edge tool on cylinder. Align it with cylinder. 4.
ENGINE TENSIONER BLADE INSTALLATION 1. Install the tensioner blade and tighten the mounting bolt to specified torque. 3. Install the cam chain guide and dowel pins into the cylinder. Verify the bottom end is seated properly in the crankcase. 4. Pull the cam chain through the cylinder chain room and secure with mechanic’s wire. Tensioner Blade Mounting Bolt Torque: 10 Nm (7.4 ft. lbs.) CYLINDER INSTALLATION 5. Position crankshaft at Top Dead Center (TDC) on compression stroke.
ENGINE 2. Pull the cam chain through the cylinder head chain room and secure with mechanic’s wire. 3. Place the cylinder head on the cylinder. When the stator housing is installed, use Method 2 This method establishes accurate Top Dead Center (TDC) by aligning the single mark on the flywheel with the notch in the timing inspection hole (see Method 2). The camshaft sprocket alignment marks are parallel to the gasket surface, and camshaft lobes are pointing down.
ENGINE 6. Check all cam timing marks to verify proper cam timing, and install the rocker arm assembly. 3. Apply grease , or molybdenum disulfide grease to the Torque the cylinder stud nuts to specification. camshaft main journals and cam lobes. Lubricate NOTE: Do not rotate engine until tensioner and rocker automatic compression release mechanism with clean assembly is installed. engine oil. 7. Install the tensioner and rocker assembly. 4. Orientate the camshaft with the lobes facing 8.
ENGINE ROCKER SHAFT/ARM INSTALLATION 7. Adjust valves according to the “VALVE 1. Assemble arms, shafts and decompression CLEARANCE ADJUSTMENT PROCEDURES” , components into cam support. Page4.39. 8. Install rocker cover and torque bolts to specification. CAM CHAIN TENSIONER INSTALLATION 1. Using a small flat blade screwdriver, turn the tensioner clockwise to retract the plunger (B) all the way into the tensioner body. 2. Install and tighten rocker shaft locking plate. Tighten to specification. 3.
ENGINE CAMSHAFT TIMING - METHOD 1 Method 1 - Camshaft Timing with Stator Housing Removed Sprocket marks aligned with gasket surface at TDC on compression stroke (cam lobes facing downward) 4.
ENGINE CAMSHAFT TIMING - METHOD 2 Method 2 - Camshaft Timing Using Flywheel TDC Mark Sprocket marks aligned with gasket surface at TDC on compression stroke (cam lobes facing downward) Cam Timing (View through timing inspection hole) Position crankshaft at TDC 4.
ENGINE INTAKE VALVE CLEARANCE ADJUSTMENT 1. Verify cam lobes are pointed down. FLYWHEEL INSTALLATION 2. Insert a 0.1mm feeler gauge between end of intake 1. Install flywheel key, flywheel washer, and nut. valve stem and adjuster screw. Torque flywheel nut to specification. 3. When clearance is correct, hold adjuster screw and tighten locknut securely. 4. Re-check the valve clearance. 5. Repeat adjustment procedure if necessary until clearance is correct with locknut secured. VALVE CLEARANCE 0.
ENGINE STATOR HOUSING INSTALLATION SPARK PLUG FOULING TROUBLESHOOTING NOTE: The stator, flywheel, starter drive, and stator ◎ Spark plug cap loose or faulty can be serviced with the engine in the frame. ◎ Choke cable adjustment or plunger/cable sticking 1. Apply a light amount of Crankcase Sealant to the ◎ Foreign material on choke plunger seat or plunger mounting surface and install a new gasket. Install the ◎ Incorrect spark plug heat range or gap dowel pins.
ENGINE TROUBLESHOOTING Piston Failure - Scoring Engine Turns Over But Fails to Start ◎ Lack of lubrication ◎ No fuel ◎ Dirt entering engine through cracks in air filter or ducts ◎ Dirt in fuel line or filter ◎ Engine oil dirty or contaminated ◎ Fuel will not pass through fuel valve Excessive Smoke and Carbon Buildup ◎ Fuel pump inoperative/restricted ◎ Worn rings, piston, or cylinder ◎ Tank vent plugged ◎ Excessive piston-to-cylinder clearance ◎ Carb starter circuit ◎ Worn valves, guides or s
TRANSMISSION CHAPTER 5 TRANSMISSION TRANSMISSION . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5.1 TRANSMISSION ASSEMBLY . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5.2 TRANSMISSION DISASSEMBLY AND INSPECTION . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5.2 SHIFT SYSTEM REMOVAL . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5.
TRANSMISSION Transmission Assembly TRANSMISSION Shift System Removal Transmission Disassembly and Inspection 1. Remove right footwell. NOTE: Engine removal is not required to service 2. Remove sprocket cover and drive sprocket. transmission components. Process shown below is with 3. Remove shift cables from the bracket. engine removed for clarity. 1. Drain the transmission oil from the gear case (A) and engine oil from crankcase (B). 5.
TRANSMISSION 4. Remove shift cover and cables bracket screws. 8. Remove the shift shaft by pulling straight outward. 9. Remove detent ball, spring and socket bolt. 10. Remove shift detent. 5. Remove shift cover and the bracket. 6. Remove gasket and discard. 7. Note timing of shift shaft before removing. The center tooth on shift shaft is positioned between the two dots on the drum Transmission Disassembly 1. Remove the cover screws. teeth. 2. Remove cover or with output shaft.
TRANSMISSION 4. Remove output shaft 7. If input shaft or gear requires service, remove driven clutch 5. Remove main shaft and shift fork as an assembly. as outlined in CVT Chapter. 6. Remove the counter shaft. 8. Remove above two bolts. 9. Remove input shaft from CVT side by plastic hammer until loose. Note: Do not lose those two washers. Transmission Inspection NOTE: Always wear the appropriate protective gear and use caution when operating a press. Drive shaft removal and inspection 1.
TRANSMISSION 3. The sealed drive shaft bearing has a snap ring that must be removed then drive shaft bearing can be removed. 4. Assemble the drive shaft, bearing, a new snap ring. 2. Substantial axial movement in the forward drive gear is due to liberal oil clearance for the bushing, and is a normal condition. Gear replacement is not required due to axial movement if radial movement (shown in Step 6) passes inspection. Shift fork inspection 3. Radial movement should not exceed 0.05 mm. 1.
TRANSMISSION 4. Remove forward gear and dog components until next snap ring. Snap ring pressure can cause rings and pliers to eject suddenly. Use care during removal. 7. Inspect the shaft and gears visually without excessive wear or crack. Replace any damaged components. 8. Assemble the reverse gear, washer, a new snap ring, and the sliding gear on the shaft. 9. Assemble the forward gear, washer, bush and a new snap ring, on the shaft. 5. Remove second snap ring from main shaft.
TRANSMISSION 2. Remove the gear ring from output shaft. 3. Inspect the shaft and shaft excessive wear or crack. 1. Place the counter shaft into case. 4. Assemble the output gear and a new snap ring on the shaft. 2. Place main shaft washer on bearing housing. Shift drum removal and inspection Spring pressure can cause components to eject suddenly. Use care during removal. Always wear the appropriate protective gear 1. Remove shift sensor from drum shaft. 3. Place main shaft into case.
TRANSMISSION 4. Install the drum shaft. Ensure the shift sensor toward inside. 5. Use caution when installing the gear position indicator spring and pin located in the end of the drum shaft. 6. Insert shift fork into main shaft dog and drum then install fork shaft. 9. Install the drum detent and shift teeth. Ensure all dots must 6. Place flat washer on output shaft bearing. 7. Install the output shaft. 11. Check transmission operation before final assembly, and on center position. 10.
TRANSMISSION 11. Install detent ball, spring, o-ring and bolt. Transmission Trouble shooting Gear Will Not Engage • Shift arm indexed incorrectly • Shift cables loosened • Shift cables broken • CVT Belt broken • Internal trans gear damage • Shift fork broken or bent • Shift shaft broken Pops Out Of Gear 12. Install the shift cover then fasten bolts to 10Nm.
FUEL SYSTEM CHAPTER 6 FUEL/CARBURATOR CARBURETION SYSTEM. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6.2 CARBURETOR FUNCTION. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6.2 CARBURETION SPECIFICATIONS. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6.3 OPERATION OVERVIEW. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6.
FUEL/ CARBURATOR Carburetor Function Carburetor Component Function System Gasoline is extremely flammable and explosive under Main Main Main Components Function Affect certain conditions. Float System Inlet Pipe, Needle Maintains All systems; all Always stop the engine and refuel outdoors or in a well Level Control) and Seat, Float specified fuel throttle ranges ventilated area. and level in float Do not overfill the tank.
FUEL/ CARBURATOR Carburetion Specifications Operation Overview GOES 300 S KEIHIN Type PTG With ACV Air Screw 1 Circuit Jet Needle 2MKNN Slide Valve B34 Pilot Jet #38S Main Jet #108 E-clip Position 4th From Top The engine of a vehicle is operated under a wide range of conditions, from idling with the throttle valve remaining almost closed, to full load or maximum output with the throttle valve fully opened.
FUEL/ CARBURATOR CARBURETOR OPERATION NOTE: It is strongly recommended that Carbon Clean be CARBURETOR JETTING added regularly as directed to the fuel systems. Carbon IMPORTANT: The following guidelines must be followed Clean stabilizes the fuel, preventing clogging of the small when establishing a main jet setting: 1. Select the lowest anticipated temperature at which the passages and orifices common to Youth ATV carburetors, and ensures constant performance, reliability machine will be operated. 2.
FUEL/ CARBURATOR Float System Air Mixture Screw The float system is designed to maintain a constant height of The pilot mixture screw controls the fuel mixture from idle to gasoline during operation. When the fuel flowing from the fuel low speeds. The tapered tip of the mixture screw projects into pump into the float chamber through the needle valve reaches the fuel mixture passage leading to the pilot jet air bleeds. By the constant fuel level, the floats rise.
FUEL/ CARBURATOR Air / Fuel Mixture Ratio Jet Needle The jet needle has five adjustment grooves cut into the upper portion, and is tapered from approximately the middle of the needle to the lower end. The top is fixed to the center of the throttle valve by the needle clip, and the tapered end extends into the needle jet. Fuel flows through the space between the needle jet and jet needle. This space does not vary until the throttle reaches the 1/4 open point.
FUEL/ CARBURATOR Throttle Opening vs. Fuel Flow Main Jet In a full throttle condition the cross sectioned area between the When the throttle opening becomes greater and the area jet needle and the needle jet is larger than the cross sectioned area of the main jet. The main jet therefore has greater control between the needle jet and jet needle increases, fuel flow is metered by the main jet. The number on the jet indicates the over fuel flow.
FUEL/ CARBURATOR Pilot System (Idle - 3/8 Throttle) Slide Cutaway (1/8 - 3/8 Throttle) The pilot system’s main function is to meter fuel at idle and Throttle valve cutaway effect is most noticeable at 1/4 throttle low speed driving. Though its main function is to supply fuel opening. The amount of cutaway is pre-determined for a given at low speed, it does feed fuel continuously throughout the engine to maintain a 14:1 air/fuel ratio at part throttle. A steep entire operating range.
FUEL/ CARBURATOR Jet Needle / Needle Jet (3/8 - 3/4 Throttle) Main System (3/4 to Full Throttle) The main system is designed for delivering fuel between low The jet needle and needle jet have the most effect between 3/8 speed and high speed operation. This system is made up of the and 3/4 throttle opening. Some mixture adjustment can be jet needle, needle jet, and main jet.
FUEL/ CARBURATOR Fuel Delivery VENT SYSTEM The throttle opening chart below demonstrates component relationship to fuel flow versus throttle valve opening. The pilot system’s main function is that of a low speed jet. Its most effective range of fuel delivery is from idle to approximately 3/8 throttle valve opening. The throttle slide controls the rate of engine air by its movement up and down in the carburetor venturi.
FUEL/ CARBURATOR 2. If the carburetor is extremely dirty or contaminated with 5. Open the carb cap then disconnect the throttle cable end fuel residue and varnish, soak for short periods only in from. carburetor cleaner, and rinse in hot water. 3. Replace the jets if they have a buildup of fuel residue or bacterial growth that cannot be removed. Even a small amount of residue will reduce the flow characteristics of the jet. 4.
FUEL/ CARBURATOR Carburetor Disassembly Use the following procedure to disassemble the carburetor. 1. Remove the (3) float bowl screws and float bowl. 4. Remove the pilot jet , main jet , and from the carb body. 2. Remove fuel retainer. 5. Note the position of both the air mixture screw and idle speed adjustment screw and remove both from the carb body. 3. Remove the float pin (A) , float (B) , and inlet needle (C). 6.
FUEL/ CARBURATOR Throttle Valve and Choke Disassembly 5. Remove the choke arm. 1. Loosen the valve cap. 2. Remove cable with valve from the carb body. 3. disconnect throttle cable from slide valve. Spring pressure can cause components to eject suddenly. Use care during removal. 4. Remove choke screw and bracket. 6. Remove the choke spring . Air Cutting Valve disassembly 1. Remove air cutting valve cover and diaphragm. 6.
FUEL/ CARBURATOR Carburetor Inspection 3. Inspect the idle speed adjust screw tip for flat spots and the 1. Inspect jet needle and needle jet for wear. Look for pilot mixture screw tip for damage. If any damage is present discoloration, shiny spots, or an area that looks different on either screw, it must be replaced. than the rest of the needle. The middle to upper portion of the needle contacts the needle jet and is the most likely wear point.
FUEL/ CARBURATOR Float Height Adjustment Needle and Seat Leak Test 1. Illustration 1: Place the the throttle side of the 1. Install the float bowl. carburetor at a level position to remove weight from float 2. Invert the carburetor and install a Mity-Vac™ to the fuel arm. In this position, the float tongue will rest slightly inlet fitting. outward. 3. Apply 5 PSI pressure to inlet fitting. The needle and seat should hold pressure indefinitely. If not, inspect needle and seat and seat O-ring or gasket. 2.
FUEL/ CARBURATOR FUEL LEVEL TEST A fuel level test can be performed on some models if the drain hose fitting is accessible. Be sure to re-attach the bowl drain hose after performing the test. A fuel level test allows you to observe the height of the fuel in the float bowl without removing the carburetor. The fuel level can be observed with the engine either running or shut off, however, engine must run briefly to allow fuel level to stabilize.. 1. Attach a clear line to drain fitting.
FUEL/ CARBURATOR Fuel tank location 6.
FUEL/ CARBURATOR Fuel Tank Removal 5. Disconnect the fuel lever gauge harness. 1. Completely drain fuel from fuel tank. Be sure the fuel. 2. Remove the two bolts that attach the fuel tank to the frame. 6. Place a shop rag or towel underneath the tank and remove fuel line, fuel valve and filter from the tank. 3. Carefully lift up on the fuel tank. 7. Disconnect the fuel tube from tank. 8. To reinstall the tank, reverse the removal procedure. Be sure to torque the tank mounting bolts.
FUEL/ CARBURATOR Air Cleaner Removal 2. Remove the foam air filter. Wash the foam filter in warm 1. Release the screw and remove the cover. soapy water, then rinse and let it dry. If the filter is damaged, install a new foam filter. 6.
FUEL/ CARBURATOR 3. Loosen the intake boot clamp between the carburetor and 6. Reinstall the foam filter, foam and air box cover. Secure the air cleaner. clips. 4. Loosen oil separator hoses then remove air cleaner box. The air intake on cover must toward front of vehicle. 5. Apply commercially available foam filter oil to the foam filter. 6.
FUEL/ CARBURATOR TROUBLESHOOTING Poor Idle Fuel Starvation / Lean Mixture Idle Too High Symptoms: Hard start or no start, bog, backfire, popping • Idle adjusted improperly / air mixture screw damaged through intake / exhaust, hesitation, detonation, low power, • Throttle cable sticking, improperly adjusted, routed spark plug erosion, engine runs hot, surging, high idle, idle incorrectly speed erratic.
BODY / SUSPENSION / STEERING CHAPTER 7 BODY / SUSPENSION / STEERING GENERAL INFORMATION . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7.2 TORQUE SPECIFICATIONS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7.2 BODY REMOVAL . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7.2 FRONT CAB REMOVAL. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
BODY / SUSPENSION / STEERING GENERAL INFORMATION Torque Specifications Fastener Torque Suspension Fasteners A–Arm Attaching Bolt 42 Nm (31 ft. lbs.) BODY REMOVAL Front Cab Removal 1. Pull out the seat latch on tail and remove the seat. 2. Remove the 4 screws and the fuel tank cover. A-Arm Ball Joint Stud Nut 50 Nm (37 ft. lbs.) Shock Mounting Bolts Front: 44 Nm (33 ft. lbs.) Rear: 50 Nm (37 ft. lbs.) Swing Arm Mounting Bolt 90 Nm (66 ft. lbs.) Rear Axle Hub Bolt 35 Nm (26 ft.lbs.
BODY / SUSPENSION / STEERING 5. Remove the 2 bolts attaching the body to the footwells on each side. 6. Remove radiator wind shield bolts on each side. 9. Disconnect the main switch (ignition) harness. 10. Disconnect power supplier wires. 7. Remove the 8 screws attaching front and rear cabs to the footwells on each side. 11. Disconnect both front indicator plugs. 8. Remove the 2 bolts attaching the body to the front cab on each side. 7.
BODY / SUSPENSION / STEERING 12. Disconnect the headlight harness. 13. Remove shift lever grip. 2. Remove the 4 bolts of rear cab. 3. Disconnect the taillight harness. 14. Completely remove the front cab from body. Rear Cab Removal 1. Remove 2 footwells from body. 4. Remove the 2 bolts attaching the rear cabs then take off taillight. 7.
BODY / SUSPENSION / STEERING 5. Cut off the straps of rear indicators then disconnects indicator plugs with main harness. Front Bumper Removal / Installation 1. Remove the (4) mounting bolts retaining the front bumper and remove the bumper from the ATV. 6.Remove Rear cab from cab. Treetrentar 330 Headlight housing Removal 2. Reverse the previous procedure to reinstall the bumper. 1.The front cab removal procedure same as Goes 300 S except 3. Torque mounting bolts to 87 in. lbs. (9.8 Nm).
BODY / SUSPENSION / STEERING 7.
BODY / SUSPENSION / STEERING SUSPENSION Front Shock Removal 1. Elevate front end of the ATV off the ground to remove shock spring tension. Front Shock Mounting Bolt Torque: 44 Nm (32 ft. lbs.) Severe injury could occur if machine tips or falls. 2. Remove the upper shock mounting bolts from the frame and the lower shock mounting bolts from the front suspension arm / A-arm. 3. Replace the shock or spring as required. 4. Install shock as shown above Exploded Figure. 5.
BODY / SUSPENSION / STEERING Rear Shock Removal 1. Elevate rear end of the ATV off the ground to remove shock spring tension. Severe injury could occur if machine tips or falls. 2. Remove the upper shock mounting bolt from the frame and the lower shock mounting bolt from the swing arm. 3. Replace the shock, spring or adjuster cam as required 4. Install the shock as shown above Exploded Figure. 5. Torque shock mounting bolts to specification. Rear Shock Mounting Bolt Torque: 50 Nm (37 ft. lbs.) 7.
BODY / SUSPENSION / STEERING FRONT A-ARM A-arm Replacement 3. Remove brake caliper bolts and caliper. 1. Elevate front end of ATV off the ground far enough to remove the wheel. Severe injury could occur if machine tips or falls. 4. Remove wheel hub and brake disc. 2. Remove wheel nuts and remove wheels. 7.
BODY / SUSPENSION / STEERING 5. Remove the upper and lower ball joint cotter pins 9. Examine the A-arm shafts (E). Replace if worn. (K) from the ball joint studs (I & L) at wheel end of Discard hardware. A-arm. Remove the ball joint nuts until the nuts are flush 10. Insert A-arm shaft (E) into the new A-arm(C & H). with end of the ball joints studs. 11. Install new A-arm assembly onto vehicle frame (upper and lower). Torque bolts to 42Nm (30 ft. lbs.). 12.
BODY / SUSPENSION / STEERING SWING ARM Removal 1. Elevate rear end of ATV off the ground far enough to remove the rear wheels. Severe injury could occur if machine tips or falls. 2. Remove the dust cap and cotter pin from 2 rear wheels 3. Remove 2 rear wheels nut and remove wheel and hub as an assembly. 7.
BODY / SUSPENSION / STEERING 4. Remove rear brake caliper bolts then brake caliper. 7. Loosen 2 nuts from rear axle. Ensure do not lose those washers. 5. Remove chain protector bolts then chain protector. 8. Bend the lock bracket back the remove bolts and sprocket. 6. Take off the master link from chain by pliers then remove 9. Pull the axle with disc toward left way, some time need to chain from sprocket. use soft hammer on right of rear axle. Ensure do not damaged axle thread. . 7.
BODY / SUSPENSION / STEERING 10. Remove external cir-clip and brake caliper mount. 11. There is a o-ring in caliper mount. 12. Loosen 4 bolts then remove axle hub toward right hand away. 13. Inspect adjusting tooth and cam surface for wear, replace the hub if the component fail inspection. 14. Inspect the axle hub main bearings for worn or damaged. The bearing must be inspected visually and by turning feel. The bearing should turn smoothly and quietly. 15. Remove the rear shock upper blot. 16.
BODY / SUSPENSION / STEERING 7.
BODY / SUSPENSION / STEERING STEERING POST ASSEMBLY 1. Torque the steering axle nut (A) to 60Nm. 4. Check the steering. The handlebars must move freely 2. Align the cotter pin hole. and easily from full left to full right without binding. Check 3. Install the cotter pin (B) and bend both ends of the all cables and electrical wires for binding and route as cotter pin around the nut in opposite directions. needed. 7.
BODY / SUSPENSION / STEERING HANDLEBAR BLOCK INSTALLATION PROCEDURE 1. Position the two steering post blocks (D) properly onto the 4. Install the four handlebar bolts and pod bracket (C) handlebars. loosely into the blocks. 2. Install the front block bolts (A) first and evenly tighten 5. Install the handlebar pod (E) and screws (F). the bolts down. Evenly torque the 2 front bolts to 15--18 Nm (11--13 ft.lbs.). NOTE: There will be a slight gap on the backside of 3.
BODY / SUSPENSION / STEERING DECAL REPLACEMENT The following procedure involves the use of an open flame. Perform this procedure in a well ventilated area, away from gasoline or other flammable materials. Be sure the area to be flame treated is clean and free of gasoline or flammable residue. Do not flame treat components that are installed on the vehicle. Remove the component from the vehicle before flame treating. The side panels, front and rear fender cabs are plastic polyethylene material.
BRAKES CHAPTER 8 BRAKES SPECIFICATIONS. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8.2 GENERAL SPECIFICATIONS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8.2 TORQUE SPECIFICATIONS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8.2 BRAKE SYSTEM SERVICE NOTE . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8.
BRAKES SPECIFICATIONS General Specifications Front Brake Disc Item Standard Service Limit Brake Pad Thickness 7.6 mm (0.298”) 4.3 mm (0.17”) Brake Disc Thickness 4mm (0.16”) 3.5mm ( 0.14”) -- 0.05mm ( 0.002”) -- 0.25mm (0.01”) Brake Disc Thickness Variance Between Measurements Brake Disc Runout Rear Brake Disc Item Standard Service Limit Brake Pad Thickness 7.8 mm (0.20”) 4.5 mm (0.18") Brake Disc Thickness 4.2 mm (0.17”) 3.8mm (0.15”) Brake Disc Thickness Variance -- 0.
BRAKES BRAKE SYSTEM SERVICE NOTES ◎ Inspect caliper piston seals for foreign material that Disc brake systems are light weight, low maintenance, could prevent caliper pistons from returning freely. and perform well in the conditions ATVs routinely ◎ Perform a brake burnishing procedure after installing encounter. There are a few things to remember when new pads to maximize service life.
BRAKES BRAKE SYSTEM OPERATION The front brake system is hydraulically actuated. The foot brake system is hydraulically actuated. When the right front brake lever (master When the right foot brake lever (master cylinder) cylinder) is applied, the two front brake calipers is applied, the two front brake calipers and a rear are active and under pressure. caliper are active and under pressure. The rear brake system is hydraulically actuated. The parking brake system operates using mechanical brake cables.
BRAKES FRONT BRAKE The front brake system consists of the following components or assemblies: brake lever; master cylinder; hydraulic hose; brake calipers (slave cylinder); brake pads; and brake discs, which are secured to the drive line. When the hand activated brake lever (A) is applied it contacts a piston (B) within the master cylinder. As the master cylinder piston moves inward it closes a small opening (compensating port) (C) within the cylinder and starts to build pressure within the brake system.
BRAKES FRONT BRAKE EXPLODED VIEW 8.
BRAKES FRONT BRAKE REPLACEMENT/ BLEEDING PROCEDURE 4. Remove the cotter pin, nut and washer. NOTE: When bleeding the brakes or replacing the fluid always start with the caliper farthest from the master cylinder. Always wear safety glasses during these procedures. Brake fluid will damage finished surfaces. Do not allow brake fluid to come in contact with finished surfaces. 5. Remove the caliper two fastens bolts on knuckle and the banjo bolt on caliper and oil tube. 6.
BRAKES 8. Remove the disc blots then disc. 9. Remove the speedometer sensor. 4. The shunt system is hydraulically actuated. ◎When the right foot brake lever (master cylinder) is applied, the two front brake calipers and a rear caliper are active and under pressure. ◎When the right front brake lever (master cylinder) is applied, the two front brake calipers are active and under pressure. ◎When the right front brake lever (master cylinder) is applied, the rear brake caliper is active and under pressure. 10.
BRAKES 1. Clean reservoirs cover thoroughly. 2. Remove screws, cover, and diaphragm from reservoir. 8. While maintaining lever pressure, open bleeder screw. Close bleeder screw and release brake lever. 3. Inspect vent slots in cover and remove any debris or NOTE: Do not release lever before bleeder screw is tight or blockage. 4. If changing fluid, remove old fluid from reservoir with air may be drawn into caliper. a Mity Vacuum or similar tool. 9.
BRAKES 12. Add brake fluid to the proper level. MASTER CYLINDER REMOVAL Master Cylinder Fluid Level: 1. Clean master cylinder and reservoir assembly. Make MAX level inside reservoir sure you have a clean work area to disassemble brake Sight glass must look dark, if sight components. glass is clear, fluid level is too low 2. Place a shop towel under brake line connection at master cylinder. Loosen banjo bolt; remove bolt and sealing washers. 13. Install diaphragm, cover, and screws. 14.
BRAKES MASTER CYLINDER INSTALLATION 3. Fill reservoir with DOT4 Brake Fluid. 1. Install master cylinder on handlebars. Torque mounting bolts to 3 Nm (25 in. lbs.). Torque the top bolt first. NOTE: To speed up the brake bleeding procedure the master cylinder can be purged of air before brake line is 4. Follow bleeding procedure on Pages 8.8. attached. Fill with DOT4 Brake Fluid and pump lever Check all connections for leaks and repair if necessary.
BRAKES 3. Remove the brake pads out of the caliper assembly. 4. Measure the thickness of the pad material. Replace pads if worn beyond the service limit. 2. Install caliper on the steering knuckle, and torque mounting bolts. (If previously removed.) Front Brake Pad Thickness New 7.6mm( 0.298〃) Service Limit 4.30mm ( 0.170〃 ) Front Caliper Mounting Bolts FRONT PAD ASSEMBLY If the brake pads are contaminated with grease, oil, or liquid soaked do not use the pads, use only new clean pads. 1.
BRAKES FRONT DISC INSPECTION 1. Visually inspect the brake disc for nicks, scratches, or damage. 2. Measure the disc thickness at 8 different points around the pad contact surface using a 0-1〃 micrometer. Replace disc if worn beyond service limit. Brake Disc Runout Service Limit . 0.25 mm ( 0.01” ) FRONT BRAKE DISC REMOVAL / REPLACEMENT Brake Disc Thickness Service Limit 3.8mm ( 0.15” ) New . 4.2mm ( 0.17” ) Brake Disc Thickness Variance Service Limit 0.05 mm ( 0.002” ) difference between measurements.
BRAKES REAR BRAKE Rear Brake Removal and Inspection NOTE: Follow the “Swing Arm Removal” procedure outlined in Chapter 6 to access the rear brake components. 1. Follow the “Swing Arm Removal” procedure to the point where the rear brake disc housing can be accessed on “Chapter 7”. NOTE: You do not need to fully disassemble the rear axle / swing arm to service the rear brakes. 2. Inspect the brake pads contact disc surface and the axle housing seal surface for excessive wear, pitting, or damage.
BRAKES Rear Brake Pad Thickness: Service Limit: (2 mm) Rear Caliper Fluid Replacement and Air Bleeding Brake fluid draining 1. Remover the master cylinder cover. 4. Pump the brake lever until no more fluid flow out of the bleed screw. Rear caliper fluid filling/ bleeding Follow the “Front Brake-Bleeding Procedure” on page 8.8 to 8.10. NOTE: 2. Connect the bleed house to bleed screw. 3. Loosen the bleed screw of rear caliper and shunt. 1.
BRAKES Foot Brake Removal Note: The foot brake system is hydraulically actuated. Where is 2. Remove the cotter pin from foot brake lever and foot brake master cylinder. under right hand rear cab. When the right foot brake lever (master cylinder) is applied, the brake oil output to shunt. The two front brake calipers and a rear caliper are active and under pressure. 3. Loosen foot brake lever and brake sensor return spring with long nose pliers. 1. Remove right hand foot well from body. 4.
BRAKES 5. Remove 2 master cylinder bolts, banjo bolt and oil tank 2. Add brake fluid to the upper level mark on reservoir. bolt. Remove master cylinder and oil tank as an assembly. NOTE: Do not move foot brake lever when reservoir fluid level is low. 3. Begin bleeding procedure with the caliper that is farthest from the master cylinder. Install a wrench on the top caliper bleeder 5. Remove foot brake lever and other components, arrange screw. them order. Foot brake fluid filling/ bleeding 1.
BRAKES 7. Repeat procedure until clean fluid appears in bleeder hose and all air has been purged. Add fluid as necessary to maintain level in reservoir. NOTE: If brake pressure is hard to built, repeat breeding procedure with shunt breeding screw When removing and installing the parking braking system. The spring may cause serious bodily injury. Always wear safety glasses during these procedures. 1. Loosen the adjusting nut to the left end. 2. Remove the parking lever clamp blot, parking lever and 8.
BRAKES 3. Loosen rear caliper fastener nut, adjusting bolt then remove swing arm. 4. 3. Install the both spring and swing to caliper. 4. Ensure the upper return spring 50~60mm with cable adapter. Remove the return spring and cable from swing arm. 5. Install the adjusting bolt and fastener nut an assembly. 6. Fully turn the adjusting bolt to end then loosen it 3/4 circuit. Fasten the nut present and security. Parking brake installation, inspection and 7.
BRAKES 8. Position the left hand master cylinder aligned with dot BRAKE TROUBLESHOOTING mark on handle bar. Brakes Squeal 9. Install parking lever on handlebars. Torque ◎ Dirty/contaminated friction pads mounting bolts to 5Nm. Torque the top bolt first.
ELECTRICAL CHAPTER 9 ELECTRICAL GENERAL INFORMATION . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9.3 ELECTRICAL SYSTEM SERVICE NOTES . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9.3 WIRE COLOR LETTER LIST . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9.3 TRAMISSION SWITCH SERVICE . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9.
ELECTRICAL NO SPARK, WEAK OR INTERMITTENT SPARK . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .. . . . . . . . . . . . .9.17 CHARGING SYSTEM . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9.17 MAIN FUSE ASSEMBLY . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9.17 VOLTAGE REGULATOR / RECTIFIER . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9.17 CHARGING SYSTEM TESTING . . . . . . . .
ELECTRICAL GENERAL INFORMATION Electrical System Service Notes TRANSMISSION SWITCH SERVICE Reference the following notes when diagnosing electrical Switch Removal/Test problems. 1. Remove the CVT cover. The indicator switch will be visible • Refer to wiring diagram for stator and electrical component resistance specifications. • When measuring resistance of a component that has a low between the drive and driven clutch. Refer to Chapter 3 for CVT cover removal and install.
ELECTRICAL Switch Installation 5. Once repairs are completed, reinstall the shift pin and spring into the shift drum (arrow). NOTE: assembly lube can be used to “stick” parts together for ease of assembly. 6. Install the indicator switch and o--ring (arrow), routing the wires in the same manner as during disassembly. 7. Install the retaining screws. Torque to 5Nm (45 in. lbs).
ELECTRICAL Left Hand Switch Assembly The following illustration shows the internal operation of the LH switch assembly. If any part of the switch is faulty, the entire LH switch assembly must be replaced. 9.
ELECTRICAL Key Switch The key switch can be tested with an ohm meter. When the key switch is turned to the “ ” position, there should be continuity between the red/whore (R/W) and brown/white (Br/W) wires. There should also be continuity between the brown (Br) and yellow/red (Y/R) wires. HEADLIGHTS The headlights are powered by an AC current from the Generator / Stator. When headlight switch on but working, perform the following: 1. Disconnect the harness from the faulty light. 2.
ELECTRICAL Headlight Lamp Replacement 4. Pull the position bulb and replace it. If the headlights do not operate, lamp replacement may be required. Install only the recommended replacement lamps. 1. Remove the socket rubber seal. 4. Reinstall the socket into the housing and Start the engine to make sure the lights come on. If the lights do not operate, check the charging system and related wiring for 2. Remove the socket rubber seal. possible malfunction.
ELECTRICAL 4. Observe headlight aim. The most intense part of the 2. Remove the LED lamp and replace it with a new headlight beam should be aimed 5.1 cm (2”) below the recommended LED lamp. Apply Dielectric Grease to the lamp mark placed on the wall. terminals. NOTE: Rider weight must be included on the seat. For machines with separate low beam lights, the drop should be 20.3 cm (8〃) in 25’. 5. Adjust beam to desired position by moving headlight. 3. Test the light for proper operation. 4.
ELECTRICAL SIGNAL Front Signal Replacement 5. Remove and replace lamp. If the headlights do not operate, lamp replacement may be required. Install only the recommended replacement lamps 1. Take off the front signal wire plug from harness. 2. Remove front signal and bracket from cab as picture. 6. Reinstall all front signal components. Rear Signal Replacement 1. Remove rear signal and bracket from cab as picture. 2. Use small blade drive screw to remove lens. 3. Remove rubber waterproof cap. 3.
ELECTRICAL Speedometer and Indicator 1. Remove the handlebar pod to access the speedometer. Speedometer Replacement 2. Disconnect the speedometer wire connections from the harness. 9.
ELECTRICAL Speedometer Digital Display Functional 1. Speed/ Hour: There are metric and English. Turn the key 3.2 In “TRIP A” press “zero” button after two seconds to switch “off”. Press both mode and zero button then turn “on” clear the mileage. the key switch as show. The KM/H and MILE/H symbol will twinkle. Press right button to select desire. Press left button twice to finish selection. 3.3 In “TRIP B” press “zero” button after two seconds to clear the mileage. 2.
ELECTRICAL 5. Radiator temperature scale: There are 10 scales, the The Bimetal valve locates at right hand of cylinder. th fan will start at 7 scale (80℃). The temperature table list If the valve is faulty, replace the entire assembly. as following. The water pump locates at right hand of crank cover. The Remove and reinstall procedure referent as chapter 4.
ELECTRICAL 6.2 Press right button to setting tire diameter. If you pass the IGNITION COIL TESTING desire number continue pressing right button it will repeat again. The setting code from d 15-0 to d 28-7. The setting code show as following table Tire Spec. Rim OD. Tire OD. Tire circle Code 18x7-7 7 inch 457 mm 1436 mm d 18-0 18x9.
ELECTRICAL TEST 3: Measure AC Voltage Output of Each Stator Leg at Charging RPM with a voltmeter set to Volts AC. 1. Place the red lead on the tester in the 10A jack. 2. Turn the selector dial to the Volts AC position. 3. Start the engine and let it idle. 4. Separately test each ’leg’ of the stator by connecting the meter leads to the wires leading from the alternator (Y1 to Y2, Y1 to Y3, Y2 to Y3). Alternator Current Output Reading should be no less than 30--40V AC above 2000 RPM on each ’leg’.
ELECTRICAL CDI CRANKING OUTPUT TEST CDI WIRES The following peak voltage tests will measure the amount PLUG of output directly from each component. A peak reading voltmeter can be used to perform the tests. A variety of 2-WIRE peak reading adaptors are commercially available for use with the Fluket 77 DigitalMultimeter and other digital 4-WIRE VOMs, which will allow peak voltage tests to be performed accurately. Follow the directions provided with the adaptor. All measurements are indicated in Volts.
ELECTRICAL IGNITION SYSTEM TESTING Whenever troubleshooting an electrical problem you should first check all terminal connections to be sure they are clean and tight. Also be sure that colors match when wires are connected. Use the following pages as a guide for troubleshooting. The resistance values are also given on the specification pages. Condition: No Spark or intermittent spark Verify 12 Volt DC power is present on the wire to CDI. Replace Spark Plug.
ELECTRICAL No Spark, Weak or Intermittent Spark NOTE: Use only the recommended fuse capacity, as ◎ No12 volt power or ground to CDI use of a higher amperage fuse to correct blown—fuse ◎ Spark plug gap incorrect situations could lead to electrical component ◎ Fouled spark plug damage. ◎ Faulty spark plug cap or poor connection to high tension lead Voltage Regulator / Rectifier ◎ Related wiring loose, disconnected, shorted, or 1.
ELECTRICAL Charging System Testing Whenever charging system problems are suspected, proceed with the following system checks: Using a multitester set on D.C. volts, measure the battery open circuit voltage (see procedure later in chapter). It should be 12.4 volts or more. Is it? NO Remove the battery and properly service. Reinstall the fully charged battery or a fully charged shop battery.
ELECTRICAL ◎ Connect a tachometer according to manufacturer’s instructions. ◎ With engine off and the key and kill switch in the ON position, the ammeter should read negative amps Do not connect or disconnect the battery cable or (battery discharge). Reverse meter leads if a positive ammeter with the engine running. Damage will occur to reading is indicated. light bulbs and speed limiter. ◎ Shift transmission into neutral and start the engine.
ELECTRICAL BATTERY BATTERY IDENTIFICATION NOTICE: It is important to identify what type of battery you have installed in your ATV. Different types of batteries require different service procedures. Proper servicing and upkeep of your battery is very important for maintaining long battery life. Your ATV may have a Conventional Battery or a Sealed Low Maintenance Battery.
ELECTRICAL NEVER attempt to add electrolyte or water to a Low Maintenance battery. Doing so will damage the case and shorten the life of the battery. Refer to the Battery Activation and Maintenance Video (PN SEALED LOW MAINTENANCE BATTERY INSPECTION/ REMOVAL The battery is located under the seat. 9917987) for proper instruction on servicing Low Maintenance batteries. NEVER attempt to add electrolyte or water to a Low Maintenance battery. Doing so will damage the case and shorten the life of the battery.
ELECTRICAL SEALED LOW MAINTENANCE BATTERY TESTING A battery may indicate a full charge condition in the OCV Whenever a service complaint is related to either the starting or charging systems, the battery should be checked first. Following are three tests which can easily be made on a battery to determine its condition: OCV Test, Specific Gravity Test and Load Test.
ELECTRICAL NOTE: Stored batteries lose their charge at the rate of up to 1% per day. Recharge to full capacity every 30 to 60 days during a non-use period. If the battery is stored during the winter months, electrolyte will freeze at higher temperatures as the battery discharges. The chart below Battery electrolyte is poisonous. It contains sulfuric acid. indicates freezing points by specific gravity. Serious burns can result from contact with skin, eyes or Electrolyte Freezing Points clothing.
ELECTRICAL 6. Check specific gravity of each cell with a hydrometer to assure each has a reading of 1.270 or higher. BATTERY TERMINALS/TERMINAL BOLTS Refill using only distilled water. Tap water contains Use corrosion resistant grease on battery bolts. See minerals that are harmful to a battery. Battery Installation. CONVENTIONAL BATTERY INSPECTION/ REMOVAL The battery is located under the seat and the right rear Do not allow cleaning solution or tap water inside the fender see page 9.20. battery.
ELECTRICAL CONVENTIONAL BATTERY OCV - OPEN CIRCUIT VOLTAGE TEST Battery voltage should be checked with a digital multitester. Readings of 12.6 volts or less require further battery testing and charging. See charts and Load Test on below. NOTE: Lead-acid batteries should be kept at or near a full OPEN CIRCUIT VOLTAGE State of charge 100% 75% Charged 50% Charged 25% Charged 0% Charged Conventional Lead-acid 12.60V 12.40V 12.10V 11.8V Less than Low Maintenance Type 12.70V 12.50V 12.20V 12.0V Less than 11.
ELECTRICAL CONVENTIONAL BATTERY OFF SEASON STORAGE To prevent battery damage during extended periods of non-use, the following basic battery maintenance items must be performed: ◎ Remove the battery from the machine and wash the case and battery tray with a mild solution of baking soda and water. Rinse with lots of fresh water after cleaning. NOTE: Do not get any of the baking soda into the battery or the acid will be neutralized.
ELECTRICAL STARTER SYSTEM Starter Relay Use the illustration below when troubleshooting a “No Start” condition. Take off the right side panel. The starter relay locates under right hand rear cab. The starter relay consists of a simple 2-way circuit. Power is present at the (R/B) wire from the battery.
ELECTRICAL 1. Disconnect the negative battery cable and starter motor Starter Brush Inspection / Replacement harness. Remove the (2) bolts from the starter and pull it from the engine. 1. Release the brush coil spring away. 2. Push the armature out of case. 2. Remove the 2 main screws. 3. Using an Ohmmeter, measure the resistance between the cable terminal and the insulated brush. The reading should be .3 ohms or less. Measure the resistance between the cable terminal and brush housing.
ELECTRICAL 4. Check commutator bars for discoloration. Bars discolored in pairs indicate shorted coils, requiring replacement of the discoloration. See Armature Test. starter motor. 4. Be sure that the terminal bolt insulation washer is properly 5. Place armature in a growler. Turn growler on and position seated in the housing and the tab on the brush plate engages the a hacksaw blade or feeler gauge lengthwise 3mm(1/8〃) notch in the brush plate housing. above armature coil laminates. Rotate armature 360°.
ELECTRICAL STARTER SYSTEM TESTING Condition: Starter fails to turn motor. NOTE: Make sure engine crankshaft is free to turn before proceeding with dynamic testing of starter system. A digital multitester must be used for this test. With the tester on the VDC position, place the tester’s black lead on the battery negative and the red lead on the battery positive. Reading should be 12.4 volts or Remove battery and properly service. Install fully NO charged shop battery to continue test.
ELECTRICAL STARTER SYSTEM TROUBLESHOOTING Starter Motor Does Not Turn ◎ Battery discharged - low specific gravity ◎ Loose or faulty battery cables or corroded connections (see Voltage Drop Tests) ◎ Related wiring loose, disconnected, or corroded ◎ Poor ground connections at battery cable, starter motor or starter solenoid (see Voltage Drop Tests)1 ◎ Faulty starter button ◎ Faulty ignition switch (Do other systems function?) ◎ Faulty starter relay starter motor.
ELECTRICAL 9.