Operating instructions
22
BOC Smootharc Advance II MIG 250C Operating manual
This defect can be prevented by:
→ a uniform travel speed
→ a tighter weaving motion
→ complete slag removal before welding
→ using a smaller electrode
→ keeping the slag behind the arc which is done by shortening the arc,
increasing the travel speed, or changing the electrode angle.
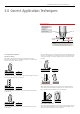
Undercutting
Undercutting is a groove melted in the base metal next to the toe or
root of a weld that is not lled by the weld metal. Undercutting causes a
weaker joint and it can cause cracking.
This defect is caused by:
→ excessive welding current
→ too long an arc length
→ excessive weaving speed
→ excessive travel speed.
On vertical and horizontal welds, it can also be caused by too large
an electrode size and incorrect electrode angles. This defect can be
prevented by:
→ choosing the proper welding current for the type and size of
electrode and the welding position
→ holding the arc as short as possible
→ pausing at each side of the weld bead when a weaving technique is
used
→ using a travel speed slow enough so that the weld metal can
completely ll all of the melted out areas of the base metal.
Lack of Fusion
Lack of fusion is when the weld metal is not fused to the base metal.
This can occur between the weld metal and the base metal or between
passes in a multiple pass weld. Causes of this defect can be:
→ excessive travel speed
→ electrode size too large
→ welding current too low
→ poor joint preparation
→ letting the weld metal get ahead of the arc.
Lack of fusion can usually be prevented by:
→ reducing the travel speed
→ using a smaller diameter electrode
→ increasing the welding current
→ better joint preparation
→ using a proper electrode angle.
Undercutting Lack of FusionSlag Inclusions