User Manual
Table Of Contents
- Getting Started with DaVinci Resolve
- PART 1 – Introduction
- Introduction to DaVinci Resolve
- The Project Manager
- Preferences and Project Settings
- Switching Among Pages
- The Media Page
- The Cut Page
- The Edit Page
- Motion Graphics and Visual Effects in DaVinci Resolve
- The Fusion Page
- Media Pool
- The Color Page
- The Fairlight Page
- Mixer
- The Monitoring Panel
- The Deliver Page
- Using the DaVinci Resolve Interface
- Working Full Screen vs. Within a Floating Window
- Panels and Panel Focus
- Showing and Hiding Panels Using the Interface Toolbar
- Showing Which Panel Has Focus
- Adjusting the Size of Different Panels
- Using Single vs. Dual Monitor Layouts
- Video Clean Feed
- Saving Custom Screen Layouts
- Resetting to the Default Layout
- Undocking Specific Panels of the Interface
- DaVinci Resolve User Interface Conventions
- The Three Buttons of a Mouse or Other Input Device
- Keyboard Shortcuts
- Undo and Redo in DaVinci Resolve
- Managing Projects and Databases
- System and User Preferences
- Project Settings
- Camera Raw Settings
- Improving Performance, Proxies, and the Render Cache
- Understanding the GPU Status Display
- Prioritizing Audio or Video Playback in the Edit Page
- Performance Mode Improves Overall Performance
- Proxy Mode Improves Effects Performance
- Reducing Decode Quality Improves Raw Media Performance
- Optimized Media Improves Overall Performance
- Creating Optimized Media
- Seeing Which Clips Have Been Optimized
- Using Smart Bins to Keep Track of Clips Needing Optimizing
- Optimized Media for Raw Source Clips
- Customizing the Type of Optimized Media You Create
- Switching Between Optimized and Original Media
- Rediscovering Lost Optimized Media
- Deleting Optimized Media
- Using Optimized Media for Delivery
- Using the Smart or User Cache Improves Effects Performance
- Manually Controlling the Cache
- Using Optimized Media, Proxies, and Caching Together
- Other Project Settings That Improve Performance
- Data Levels, Color Management, and ACES
- Data Levels Settings and Conversions
- DaVinci Resolve Color Management
- Display Referred vs. Scene Referred Color Management
- Resolve Color Management for Editors
- Resolve Color Management and Camera Raw Formats
- Controlling the Input, Timeline, and Output Color Space
- Single Setting vs. Dual Setting RCM
- 203 Nit Support for SDR to HDR
- Gamut Limiting, Restricting Values Within a Larger Gamut
- Gamut Mapping From Timeline to Output Color Space
- Procedures for Using Resolve Color Management
- Resolve Color Management and the Fusion Page
- Exporting Color Space Information to QuickTime Files
- Color Management Using ACES
- HDR Setup and Grading
- High Dynamic Range (HDR) Grading in DaVinci Resolve
- Dolby Vision™
- Mastering Displays for Dolby Vision
- GPU-Accelerated Dolby Vision™ CMU Built-In (Studio Only)
- Simultaneous Master and Target Display Output for Dolby Vision
- Hardware Setup of Master and Target Display Output for Dolby Vision
- Auto Analysis is Available to All Studio Users
- Authorizing DaVinci Resolve to Expose Advanced Dolby Vision Controls
- Dolby Vision Trim Controls in DaVinci Resolve
- Previewing and Trimming At Different Levels
- Managing Dolby Vision Metadata
- Setting Up Resolve Color Management for Grading HDR
- DaVinci Resolve Grading Workflow For Dolby Vision
- Delivering Dolby Vision
- Playing Dolby Vision at Home
- SMPTE ST.2084 and HDR10
- HDR10+™
- Hybrid Log-Gamma (HLG)
- Image Sizing and Resolution Independence
- Introduction to DaVinci Resolve
- PART 2 – Ingest and Organize Media
- Using the Media Page
- Understanding the Media Page User Interface
- The Media Storage Browser
- Viewer
- Media Pool
- The Bin List
- Showing Bins in Separate Windows
- Bins, Power Bins, and Smart Bins
- Filtering Bins Using Color Tags
- Sorting the Bin List
- Thumbnail View and List View in the Media Pool
- Display Audio Clip Waveforms in Media Pool and Media Storage
- Searching for Content in the Media Pool
- Taking Advantage of the Media Pool’s Usage Column
- Metadata Editor
- Audio Panel
- Dual Monitor Layout
- Customizing the Media Page
- Undo and Redo in DaVinci Resolve
- Adding and Organizing Media with the Media Pool
- Copying Media Using the Clone Tool
- Adding Media to the Media Pool
- Adding Media to the Cut, Edit, Fusion, and Fairlight Pages
- Removing Media From the Media Pool
- Adding and Removing External Mattes
- Adding Offline Reference Movies
- Extracting Audio in Media Storage
- Manually Organizing the Media Pool
- Sharing Media Among Projects Using Power Bins
- Automated Organization Using Smart Bins
- Duplicating Clips in the Media Pool
- Choosing How to Display Bins
- Finding Clips, Timelines, and Media
- Tracking Media Usage
- Relinking Media Simply
- Using Clip Metadata
- Syncing Audio and Video
- Modifying Clips and Clip Attributes
- Using Scene Detection
- Ingesting From Tape
- Capturing from the Cintel Film Scanner
- Using the Media Page
- PART 3 – The Cut Page
- Introducing the Cut Page
- Importing and Organizing Media in the Cut Page
- Fast Editing in the Cut Page
- Trimming in the Cut Page
- Video and Audio Effects in the Cut Page
- Quick Export
- Using the DaVinci Resolve Editor Keyboard with the Cut Page
- PART 4 – Edit
- Using the Edit Page
- The Edit Page User Interface
- The Interface Toolbar
- Navigating the Edit Page
- The Media Pool
- More About Timelines and Grading
- Using the Effects Library
- Edit Index
- Source and Timeline Viewers
- How Each Clip’s Grade Looks in Each Viewer
- Source and Timeline Viewers vs. Single Viewer Mode
- Viewer Controls
- Simultaneous Audio Waveform Display in the Source Viewer
- Cinema Viewer Mode
- Viewer Indicators
- Other Viewer Options
- Opening Clips in the Source Viewer
- Timeline Viewer Edit Overlays
- Copy and Paste Timecode in Viewer Timecode Fields
- Metadata Editor
- Inspector
- Timeline
- Toolbar
- The Mixer and Meters
- Using Video Scopes
- Floating Timecode Window
- Dual Monitor Layout
- Customizing the Edit Page
- Undo and Redo in DaVinci Resolve
- Creating and Working with Timelines
- Keyboard Shortcuts in This Chapter
- Creating and Duplicating Timelines
- Timeline View Options
- Modifying Timeline Tracks
- Naming Timeline Tracks
- Using Timeline Snapping and Zooming
- Scrolling Through the Timeline
- Resizing the Timeline’s Video and Audio Track Regions
- Tabbed and Stacked Timelines
- Duplicate Frame Detection
- Comparing Timelines
- Preparing Clips for Editing and Viewer Playback
- Keyboard Shortcuts in This Chapter
- Browsing Clips in the Media Pool
- Selecting Clips in the Media Pool to Edit
- Duplicating Clips in the Media Pool
- Viewer Playback and Navigation
- Source and Timeline Viewers vs. Single Viewer Mode
- Opening Clips Into the Source Viewer to Prepare for Editing
- Viewer Transport Controls
- Simple Keyboard Shortcuts for Playback and Navigation
- Using JKL to Control Playback
- Special-Purpose Playback Commands
- Option to “Stop and Go to Last Position”
- Enabling and Disabling Audio Scrubbing
- Playback Post-Roll
- Moving the Playhead Using Timecode
- Gang Viewers (Playhead Ganging)
- Adding Markers
- Setting In and Out Points
- Turning In and Out Points into Markers with Duration and Back Again
- Organizing Media by Creating Subclips
- Editing Basics
- Keyboard Shortcuts in This Chapter
- Drag and Drop Editing
- Audio Track Creation While Editing
- Using Keyboard Shortcuts and Three-Point Editing to Assemble a Program
- Making Selections in the Timeline
- Using Auto Select Controls to Define Selections
- Locking Tracks You Don’t Want to Change
- Position Lock for Finishing
- Disabling and Re-Enabling Clips in the Timeline
- Deleting Clips and Gaps from the Timeline
- Audio/Video Linking
- Modifying Clips in the Timeline
- Keyboard Shortcuts in This Chapter
- Moving, Resizing, and Rolling Clips in Selection Mode
- Trimming Gaps
- Modifying Clip Duration Via Timecode
- Resizing or Trimming Clips in the Source Viewer
- Shuffle/Swap Insert Edits
- Splitting and Joining Clips
- Enabling and Disabling Clips and Tracks
- Copying and Pasting Clips in the Timeline
- Duplicating Clips and Transitions in the Timeline
- Clean Up Video Tracks
- Three- and Four‑Point Editing
- Keyboard Shortcuts in This Chapter
- Introduction to Three-Point Editing
- Choosing a Track to Edit to Using Destination Controls
- Setting In and Out Points in the Timeline
- Mark Clip and Mark Current Selection
- Preview Marks During Three‑Point Editing
- The Rules of Three-Point Editing
- Switch Focus to Timeline After Edit
- Different Types of Three‑ and Four‑Point Edits
- Three-Point Editing From the Media Pool
- Marking and Finding Clips in the Timeline
- Using Flags
- Using Markers
- Drawn Annotations on the Viewer
- Frame.io Timeline Markers
- Reading Marker Information
- Using Markers in the Media Pool
- Hiding Markers By Color
- Deleting Markers By Color
- Color Labeling Clips in the Timeline
- Track Colors
- Finding Clips, Media, Markers, Gaps, and Timelines
- Finding Media Using Match Frame Operations
- Finding a Clip in the Media Pool Using a Timeline Clip
- Tracking Media Usage
- Multicam Editing
- Introduction to Multicam Editing
- Creating and Modifying Multicam Clips
- Logging and Editing Multicam Clips
- Setting up a Timeline for Multicam Editing
- Opening and Altering Multicam Clips
- Performing a Multicam Edit
- Multicam Controls in the Source Viewer
- Editing Multicam Clips in the Timeline
- Grading Multicam Clips
- Take Selectors, Compound Clips, and Nested Timelines
- Trimming
- Keyboard Shortcuts in This Chapter
- Summarizing Trim Operations
- Selection-Based Trimming Using the Trim Tool
- Using the Trim Tool With the Mouse
- Trim Tool Operations With the Keyboard
- Trimming Using Timecode Entry
- Commands to Make Selections and Trim
- Trimming Clips in the Source Viewer
- Ripple Editing Rules
- Using Auto Select Controls to Control Trimming
- Trimming Multiple Edits or Clips at Once
- Keyboard Trimming During Looped Playback
- Dynamic JKL Trimming
- Trim Operations that are Targeted Using the Playhead
- Using Transitions
- Working With Transitions
- Adding and Editing Transitions
- Adding Transitions When There’s Not Enough Handles
- Adding Transitions By Dragging to Create Overlap
- Transition Properties in the Inspector
- Favorite Transitions
- Changing the Standard Transition
- Creating Transition Presets
- Video Transitions
- Audio Transitions
- OpenFX Transitions
- Working with Audio in the Edit Page
- Audio in the Edit vs. Fairlight Pages
- Compatible Audio Formats
- Assigning Audio Channels in the Media Pool
- Editing Audio Into the Timeline
- Editing Audio In the Timeline Using In and Out Points
- Resizing Audio Clips in Subframe Increments
- Audio Settings in the Inspector
- Setting Clip Volume
- Clip Pan
- Clip Pitch Controls
- Clip EQ
- Keyframing Audio
- Audio Fade Handles
- Audio Crossfades
- The Audio Mixer
- Audio Compound Clips
- Audio Playback for Variable Speed Clips
- Using Audio Filters
- The Fairlight Page
- Pro Tools Export
- Media Management
- Using the DaVinci Editor Keyboard with the Edit Page
- Using the Edit Page
- PART 5 – Edit Page Effects
- Editing, Adding, and Copying Effects and Filters
- Titles, Generators, and Stills
- Compositing and Transforms in the Timeline
- Speed Effects
- Subtitles and Closed Captioning
- Keyframing Effects in the Edit Page
- VFX Connect
- PART 6 – Import and Conform Projects
- Preparing Timelines for Import and Comparison
- Preparing to Move Your Project to DaVinci Resolve
- Importing Effects when Conforming Edits
- About Supported Color Corrections
- About Supported Transitions
- Transition Names
- About Supported Opacity, Position, Scale, and Rotation Settings
- About Flip and Flop Support
- Pitch and Yaw
- About “Ken Burns Effect” and Dynamic Zoom
- About Speed Effects
- About Nested Sequences and Compound Clips
- About Supported Composite Modes
- About Supported Still Image Formats
- About Supported Alpha Channels
- About Imported Text Effects
- About Imported Audio in AAF Projects
- Verifying Imported Timelines Using Offline References
- Conforming and Relinking Clips
- Conforming and Relinking Media
- The Difference Between Unlinked and Missing Clips
- Duplicate Clips are Considered Separate Sources
- Summary of Methods for Conforming and Relinking
- Unlinking Clips
- Conforming Clips During XML and AAF Import
- Importing Clips Before Importing an EDL, AAF, or XML
- Conform Missing Clips by Importing Their Source Media
- Using the Import Additional Clips Command
- Using Conform Lock As a Command
- Relinking Clips to Media Files on Disk
- Using “Change Source Folder” to Relink Clips
- Using the “Reconform From Bins” Command
- Using Reconform From Media Storage
- Understanding, Fixing, and Using Reel Conflicts
- Re-editing Media Directly to the Timeline
- How Grades Are Linked to Multiple Timelines
- Creating Digital Dailies for Round Trip Workflows
- Conforming XML Files
- Conforming AAF Files
- Supported Media Types in AAF Workflows
- Logged Errors When Importing AAF
- Simple AAF Import
- Performing an AAF Avid Round Trip
- Step 1–Create a Project in Media Composer
- Step 2–Exporting an AAF for DaVinci Resolve
- Step 3–Conforming Your AAF in DaVinci Resolve
- Step 4–Continue Editing, Grading, and Finishing the Project
- Step 5–Render Graded Media and Export a New AAF
- Step 6–Copy the Graded Media to Avid MediaFiles
- Step 7–Import the Graded AAF
- Relinking Transcoded Media to AMA Media
- Audio AAF Import from ProTools
- Conforming EDL Files
- Preparing Timelines for Import and Comparison
- PART 7 – Fusion Fundamentals
- Introduction to Compositing in Fusion
- Exploring the Fusion Interface
- The Fusion User Interface
- Interface Toolbar
- Viewers
- Time Ruler and Transport Controls
- Time Ruler Controls in the Fusion Page
- Time Ruler Controls in Fusion Studio
- The Playhead
- Zoom and Scroll Bar
- Transport Controls in the Fusion Page
- Transport Controls in Fusion Studio
- Changing the Time Display Format
- Keyframe Display in the Time Ruler
- The Fusion RAM Cache for Playback
- Displaying Cached Frames
- Toolbar
- Node Editor
- Status Bar
- Effects Library
- The Inspector
- Keyframes Editor
- Spline Editor
- Thumbnail Timeline in the Fusion Page
- The Media Pool in the Fusion Page
- Bins in Fusion Studio
- The Console
- Customizing Fusion
- Fusion Studio Keyboard Remapping
- Undo and Redo
- Getting Clips into the Fusion
- Rendering Using Saver Nodes
- Rendering Overview
- Rendering with the Saver Node
- Using the Render Settings Dialog
- Setting Up Network Rendering in Fusion Studio
- Submitting Comps to Network Render
- Preparing Compositions for Network Rendering
- Other Uses of Network Rendering
- When Renders Fail
- Managing Memory Use
- Limitations of Render Nodes
- Troubleshooting
- Working in the Node Editor
- Learning to Use the Node Editor
- Navigating within the Node Editor
- Adding Nodes to a Composition
- Selecting and Deselecting Nodes
- Loading Nodes into Viewers
- Connecting and Disconnecting Nodes
- Connecting Merge Nodes
- Connection Options and Routers
- Swapping Node Inputs
- Extracting and Inserting Nodes
- Cut, Copy, and Paste Nodes
- Instancing Nodes
- Keeping Node Trees Organized
- Node Thumbnails
- Finding Nodes
- Custom Node Settings
- Node Modes Including Disable and Lock
- Node Editor Options
- Node Tooltips and the Status Bar
- Node Groups, Macros, and Fusion Templates
- Groups
- Macros
- Creating Fusion Templates
- Getting Started with a Fusion Title Template
- Saving a Title Macro
- Using Your New Title Template
- Getting Started with a Fusion Transition Template
- Creating a Fusion Transition Template
- Using Your New Transition Template
- Getting Started with a Fusion Generator Template
- Creating a Fusion Generator Template
- Using Your New Generator Template
- Using Viewers
- Viewer Overview
- Loading Nodes into Viewers
- Position and Layout
- Zooming and Panning into Viewers
- Flipbook Previews
- Onscreen Controls
- Toolbars
- A/B Buffers
- Subviews
- Viewing Selective Channels
- The 3D Viewer
- Quad View
- Guides
- Domain of Definition and Region of Interest
- Managing Viewer Lookup Tables (LUTs)
- Viewer Preferences and Settings
- The Viewer Options Menu
- Locking the Viewer (Command-L)
- Additional Viewer Options
- Status Bar Information
- Editing Parameters in the Inspector
- Overview of the Inspector
- Customizing the Inspector
- Opening Nodes in the Inspector
- Pinning Multiple Nodes in the Inspector
- Hiding Inspector Controls
- Using the Inspector Header
- Versioning Nodes
- Parameter Tabs
- Inspector Controls Explained
- Animating Parameters in the Inspector
- Connecting Parameters
- Contextual Menus
- Customizing Node Parameters with User Controls
- Animating in Fusion’s Keyframes Editor
- Animating in Fusion’s Spline Editor
- Animating with Motion Paths
- Using Modifiers, Expressions, and Custom Controls
- Bins
- Fusion Connect
- Preferences
- Controlling Image Processing and Resolution
- Managing Color for Visual Effects
- Understanding Image Channels
- Compositing Layers in Fusion
- Rotoscoping with Masks
- Paint
- Using the Tracker Node
- Introduction to Tracking
- Tracker Node Overview
- Basic Tracker Node Operation
- Viewing Tracking Data in the Spline Editor
- Tracker Inspector Controls
- Motion Tracking Workflow In Depth
- Dealing with Obscured Patterns
- Stabilizing with the Tracker Node
- Using the Tracker Node for Match Moving
- Connecting to Trackers’ Operations
- Using the Tracker as a Modifier
- Match Moving Text Example
- Planar Tracking
- Using OpenFX, ResolveFX, and Fuse Plug-Ins
- 3D Compositing Basics
- An Overview of 3D Compositing
- 3D Compositing Fundamentals
- The Elements of a 3D Scene
- Software vs. GPU Rendering
- Loading 3D Nodes into the Viewer
- Transparency Sorting
- Material Viewer
- Transformations
- Parenting
- Cameras
- Lighting and Shadows
- Materials and Textures
- Projection Mapping
- Geometry
- Fog 3D and Soft Clipping
- Material and Object IDs
- World Position Pass
- Point Clouds
- 3D Camera Tracking
- Particle Systems
- Optical Flow and Stereoscopic Nodes
- PART 8 – Fusion Page Effects
- 3D Nodes
- Alembic Mesh 3D [ABC]
- Bender 3D [3BN]
- Camera 3D [3CM]
- Cube 3D [3CB]
- Custom Vertex 3D [3CV]
- Displace 3D [3DI]
- Duplicate 3D [3DP]
- FBX Exporter 3D [FBX]
- FBX Mesh 3D [FBX]
- Fog 3D [3FO]
- Image Plane 3D [3IM]
- Locator 3D [3LO]
- Merge 3D [3MG]
- Override 3D [3OV]
- Point Cloud 3D [3PC]
- Projector 3D [3PJ]
- Renderer 3D [3RN]
- Replace Material 3D [3RPL]
- Replace Normals 3D [3RPN]
- Replicate 3D [3REP]
- Ribbon 3D [3RI]
- Shape 3D [3SH]
- Soft Clip [3SC]
- Spherical Camera [3SC]
- Text 3D [3TXT]
- Transform 3D [3XF]
- Triangulate 3D [3TRI]
- UV Map 3D [3UV]
- Weld 3D [3WE]
- Modifier
- The Common Controls
- 3D Light Nodes
- 3D Material Nodes
- 3D Texture Nodes
- Blur Nodes
- Color Nodes
- Auto Gain [AG]
- Brightness Contrast [BC]
- Channel Booleans [BOL]
- Color Corrector [CC]
- Color Curves [CCV]
- Color Gain [CLR]
- Color Matrix [CMX]
- Color Space [CS]
- Copy Aux [CPA]
- Gamut [GMT]
- Hue Curves [HCV]
- OCIO CDL Transform [OCD]
- OCIO Color Space [OCC]
- OCIO File Transform [OCF]
- Set Canvas Color [SCV]
- White Balance [WB]
- The Common Controls
- Composite Nodes
- Deep Pixel Nodes
- Effect Nodes
- Generator Nodes
- Film Nodes
- Filter Nodes
- Flow Nodes
- Flow Organizational Nodes
- Fuses
- I/O Nodes
- LUT Nodes
- Mask Nodes
- Matte Nodes
- Metadata Nodes
- Miscellaneous Nodes
- Optical Flow
- Paint Node
- Particle Nodes
- Particle Nodes
- pAvoid [pAv]
- pBounce [PBN]
- pChangeStyle [pCS]
- pCustom [pCu]
- pCustomForce [pCF]
- pDirectionalForce [pDF]
- pEmitter [pEm]
- pFlock [pFl]
- pFollow [pFo]
- pFriction [pFr]
- pGradientForce [pGF]
- pImage Emitter [PIe]
- pKill [pKI]
- pMerge [pMg]
- pPoint Force [pPF]
- pRender [pRn]
- pSpawn [pSp]
- pTangent Force [pTF]
- pTurbulence [pTr]
- pVortex [pVt]
- The Common Controls
- Position Nodes
- Resolve Connect
- Stereo Nodes
- Tracker Nodes
- Transform Nodes
- VR Nodes
- Warp Nodes
- Modifiers
- 3D Nodes
- PART 9 – Color
- Introduction to Color Grading
- Using the Color Page
- Viewers, Monitoring, and Video Scopes
- Using the Viewer
- The Viewer Title Bar
- Turning Grades and/or Fusion Effects Off
- Viewing Isolated Channels
- The Viewer Toolbar
- The Onscreen Control (OSC) Menu
- Zooming into the Viewer
- Using the Jog Bar and Transport Controls
- Viewer and Transport Timecode Displays
- Enhanced, Full, and Cinema Viewing
- Safe Area Overlays in the Viewer
- Use Gray Background
- Monitor Calibration
- Viewing Broadcast Safe Exceptions
- Comparing Clips in the Viewer
- Marker Overlays and Navigation
- Using Video Scopes
- Color Page Timeline and Lightbox
- Automated Grading Commands and Imported Grades
- Primary Grading Controls
- Color Controls Covered in This Chapter
- Camera Raw
- Color Wheels Palette
- Opening the Color Wheels Palette Using the DaVinci Control Panel
- HDR Grading Using Color Wheels Palette Controls
- How to Use Color Balance Controls and Master Wheels
- Understanding the Primaries Wheels Controls
- Shared Adjustment Controls
- The Log Mode of the Color Wheels Palette
- The Primaries Bars Mode of the Color Wheels Palette
- RGB Lift/Gamma/Gain Sliders
- Offset Sliders, Offset Wheel, and Printer Points
- RGB Mixer Palette
- Curves
- Secondary Qualifiers
- Secondary Qualifiers
- Basic Qualification Using the 3D Keyer
- Basic Qualification Using the HSL Keyer
- HSL Qualifier Presets
- Using Highlight to See What You’re Isolating
- Showing Picker RGB Values
- Qualifier Parameters
- Matte Finesse Controls
- The Many Ways to Invert a Key
- Combining Qualifiers and Windows
- Manipulating Keys Using Additional Nodes
- Secondary Windows and Tracking
- Motion Tracking Windows
- Using the Gallery
- Using the Gallery
- Where are Stills Saved?
- Live Previews of Gallery Stills
- Playing Stills and Setting Up Image Wipes
- Timeline Wipes
- Labeling and Searching for Stills and Sources
- Gallery Options
- Organizing Stills Using Albums
- Browse all Grades from the Current Timeline
- The Gallery Management Window
- Importing and Exporting Stills
- Using and Organizing Memories
- Grade Management
- Using Versions to Manage Grades
- Copying Grades
- Protecting Adjustments with the Copy Grade Options
- Clip Grades and Timeline Grades in Saved Stills
- Choosing Which Aspect of a Grade to Copy with All/Color/Sizing
- Choosing How to Copy Keyframes
- Copying Grades Using the Mouse
- Copy Forward Commands
- Copying Using Memories
- Copying Using Preview Memory
- Copying from Stills in the Gallery
- Append Node Graph
- Aligning Keyframes to a Specific Frame While Copying Grades
- Copying Individual Nodes and Settings
- Rippling Adjustments Among Multiple Clips
- Appending a Node to Multiple Clips
- Scroll Copy Grades Using the DaVinci Control Panel
- Rippling Changes Using the DaVinci Control Panel
- Using Shared Nodes
- Using Adjustment Clips
- Using Groups
- Exporting Grades and LUTs
- Node Editing Basics
- Node Editor Basics
- Turning Grades and/or Fusion Effects Off
- Resetting Nodes
- Previewing and Restoring Node Trees
- Caching Specific Nodes to Improve Performance
- Editing Node Trees
- Keeping Node Trees Organized
- Using Compound Nodes
- Identifying Nodes
- Putting Nodes into HDR Mode
- Clip vs. Timeline Grading
- Grading Order of Operations
- Serial, Parallel, and Layer Nodes
- Combining Keys and Using Mattes
- Channel Splitting and Image Compositing
- Isolating, Splitting, and Converting Color Channels
- Enabling, Disabling, and Converting Node Channels
- Splitting Channels with the Splitter/Combiner Nodes
- Multi-Channel RED HDRx Support
- Introduction to Compositing Using the Alpha Output
- Using a Qualifier Key to Create Transparency
- Using a Matte to Create Transparency
- Use an OFX Plug-in to Create Transparency
- Keyframing in the Color Page
- Copying and Importing Grades Using ColorTrace
- Using LUTs
- PART 10 – Color Page Effects
- DaVinci Resolve Control Panels
- Using OpenFX and ResolveFX
- Sizing and Image Stabilization
- The Motion Effects and Blur Palettes
- Dust Removal
- Data Burn
- PART 11 – ResolveFX
- ResolveFX
- ResolveFX Blur
- ResolveFX Color
- ResolveFX Generate
- ResolveFX Light
- ResolveFX Refine
- ResolveFX Revival
- ResolveFX Sharpen
- ResolveFX Stylize
- ResolveFX Texture
- ResolveFX Transform
- ResolveFX Warp
- PART 12 – Fairlight
- Using the Fairlight Page
- The Fairlight Page User Interface
- The Interface Toolbar
- Showing Which Panel Has Focus
- The Audio Timeline
- Toolbar
- Customizing Clip Display in the Timeline
- Customizing the Timeline’s Display
- Mixer
- The Monitoring Panel
- The Media Pool
- Importing Media Into the Media Pool on the Fairlight Page
- Media Pool Preview Player
- Bins, Power Bins, and Smart Bins
- Showing Bins in Separate Windows
- Filtering Bins Using Color Tags
- Sorting the Bin List
- Filtering Clips With Audio in the Fairlight Page
- Searching for Content in the Media Pool
- Taking Advantage of the Media Pool’s Usage Column
- Effects Library
- ADR
- Sound Library Browser
- Index
- Inspector
- Metadata Editor
- Test Tone Settings for Generating Tone, Noise, and Beeps
- Pro Tools AAF Import
- Dual Monitor Layout
- Customizing the Fairlight Page
- Undo and Redo in DaVinci Resolve
- Setting Up Tracks, Buses, and Patching
- Transport Controls, Timeline Navigation, and Markers
- Recording
- ADR (Automated Dialog Replacement)
- Editing Basics in the Fairlight Page
- Compatible Audio Formats
- Editing Audio Clips Into the Timeline
- Making Audio Clip Selections in the Timeline
- Locking Audio Tracks You Don’t Want to Change
- Splitting Clips
- Trimming Clips Without Rippling the Timeline
- Disabling and Re-Enabling Clips in the Timeline
- Deleting Audio Clips and Regions
- Cut, Copy, and Paste
- Paste and Remove Attributes
- Audio Clip Layering
- Audio Compound Clips
- Audio Crossfades
- Fades and Crossfades
- Finding Clips in the Media Pool
- Changing Clip Color in the Timeline
- Editing Audio Clips in External Editors
- Bouncing Audio Clips to External Files
- Sample Editing
- Audio Clip Specific Inspector Adjustments
- Mixing in the Fairlight Page
- Introduction to Mixing
- The Mixer
- Customizing the Onscreen Mixer Controls
- Selecting Channel Strips and Tracks
- Track Organization
- Input
- Effects
- Insert
- EQ
- Dynamics
- Aux
- Pan
- Bus Assignment Buttons
- Fader Groups (VCA Groups)
- Arm, Solo, and Mute Buttons
- Fader Controls
- Bouncing Audio
- Third-Party Control Panel Support for Mixing
- Automation Recording
- Audio Effects
- FairlightFX
- Audio Meters and Audio Monitoring
- Signal Flow Diagrams
- Using the Fairlight Audio Editor
- Fairlight Consoles
- Using the Fairlight Page
- PART 13 – Deliver
- Delivery Effects Processing
- Delivery Effects Processing
- When Rendering a Single Clip or When Outputting to Tape
- When Rendering Individual Source Clips for Round-Trip Workflows
- More About Rendering Speed Effects
- Determining the Rendered Output Resolution of Clips in Mixed Timelines
- Rendering Edit and Input Sizing Adjustments
- Rendering Mixed Frame Rate Timelines
- Export Alpha Channels
- Delivery Effects Processing
- Using the Deliver Page
- Rendering Media
- Using Presets for Fast Rendering
- Choosing a Location to Render
- Single Clip vs. Individual Clips
- All Other Render Settings for Output
- Additional Outputs
- How to Avoid Overwriting Clips When Rendering Output Media
- Defining a Range of Clips and Versions to Render
- Using the Render Queue
- Rendering Jobs from Multiple Projects at Once
- Remote Rendering
- Delivering DCP and IMF
- Delivering to Tape
- Exporting Timelines and Metadata
- Exporting to AAF/XML
- More About Exporting to AAF
- Exporting an EDL
- Exporting a Missing Clips EDL
- Exporting Timeline Markers to EDL
- Exporting to CDL
- Exporting the Edit Index as a CSV or TXT File
- Exporting to ALE
- Exporting to ALE with CDL
- Exporting Timeline Markers to EDL
- Exporting and Importing Media Pool Metadata
- Delivery Effects Processing
- PART 14 – Advanced Workflows
- Frame.io Integration
- Resolve Live
- Stereoscopic Workflows
- Stereoscopic Workflows
- Hardware Requirements for Working in Stereo 3D
- Supported Stereo 3D Media
- Creating Stereo 3D Clips From Separate Files
- Converting Clips Between Stereo and Mono
- Attaching Mattes to Stereo 3D Clips
- Organizing and Grading Stereo 3D Dailies
- Conforming Projects to Stereo 3D Media
- Adjusting Clips using the Stereo 3D Palette
- Outputting Stereo 3D Media in the Deliver Page
- Using Variables and Keywords
- Creating DCTL LUTs
- TCP Protocol for DaVinci Resolve Transport Control
- Immersive Audio Workflows
- PART 15 – Project Databases, Collaborative, and Remote Workflows
- Managing Databases and Project Servers
- Collaborative Workflow
- Remote Grading
- PART 16 – Other Information
Material Components
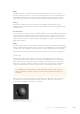
All the standard illumination models share certain characteristics that must be understood.
Diuse
The Diffuse parameters of a material control the appearance of an object where light is
absorbed or scattered. This diffuse color and texture are the base appearance of an object,
before taking into account reflections. The opacity of an object is generally set in the diffuse
component of the material.
Alpha
The Alpha parameter defines how much the object is transparent to diffuse light. It does not
affect specular levels or color. However, if the value of alpha, either from the slider or a Material
input from the diffuse color, is very close to or at zero, those pixels, including the specular
highlights, will be skipped and disappear.
Opacity
The Opacity parameter fades out the entire material, including the specular highlights. This
value cannot be mapped; it is applied to the entire material.
Specular
The Specular parameters of a material control the highlight of an object where the light is
reflected to the current viewpoint. This causes a highlight that is added to the diffuse
component. The more specular a material is, the glossier it appears. Surfaces like plastics and
glass tend to have white specular highlights, whereas metallic surfaces like gold have specular
highlights that tend to inherit their color from the material color.
Specularity is made up of color, intensity, and exponent. The specular color determines the
color of light that reflects from a shiny surface. Specular intensity is how bright the
highlight will be.
Three spheres, left to right: diffuse only, specular only, and combined.
The specular exponent controls the falloff of the specular highlight. The larger the value, the
sharper the falloff and the smaller the specular component will be.
Chapter – 76 3D Compositing Basics 1563