User's Manual
Table Of Contents
- Installation and Operation Manual
- Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Installation
- Cautionary Notes
- Pre-RF Connection Tests
- OPERATION
- Signal flow
- System Components
- Field Adjustments
- Maintenance and Repair
- Recommended replacement parts
- Conversion Chart
TXRX Systems Inc. Manual 7-9408-1.2 07/25/05 Page 13
61-38-05 UserMan page 13 of 38
3) The analyzer input attenuator should be set to
observe input signal levels from approximately -
80 dBm to 0 dBm.
4) Connect the analyzer to the section of the sig-
nal distribution system that is going to serve as
the input for the branch you want to observe
(see
Figure 5
).
5) Record the power level (in dBm) of all carriers in
the passband frequency range that are signifi-
cantly greater than the noise floor displayed on
the analyzer.
6) Repeat steps 1 through 5 for the remaining sig-
nal booster channels.
7) To find the total power being applied to the
channel, the calculations listed below must be
performed. The conversion chart at the rear of
the manual can be used. Here are the steps:
a) Convert all values in dBm to Watts
b) Total the power for all carriers in Watts
c) Convert the total power in Watts to dBm
Repeat the calculation for all of the branches in the
system. For example: suppose we have a signal
booster with a maximum gain of 70 dB. After
checking the input signal levels, it was determined
that there are three signals that are significantly
greater than the noise floor displayed on the ana-
lyzer. These signals have strengths of -45 dBm, -
43 dBm and -41 dBm.
First we use the conversion chart at the end of this
manual to convert the power levels in dBm to watts
so that we can add them together. The power in
watts is written in scientific notation but the chart
uses computer notation. For example, in the chart,
an exponent may be written as E-08. In conven-
tional mathematical notation E-08 is written 10
-8
.
The total power must be written as a number
between 0 and 10 to use the chart. Look up
1.611E-7 in the Watts column. This number falls
between -38 and -37 dBm so we chose -37
because it is the next higher value.
Power (dBm) Power (watts)
-45 dBm
3.16 x 10
-8
-43 dBm
5.01 x 10
-8
-41 dBm
7.94 x 10
-8
TOTAL
16.11 x 10
-8
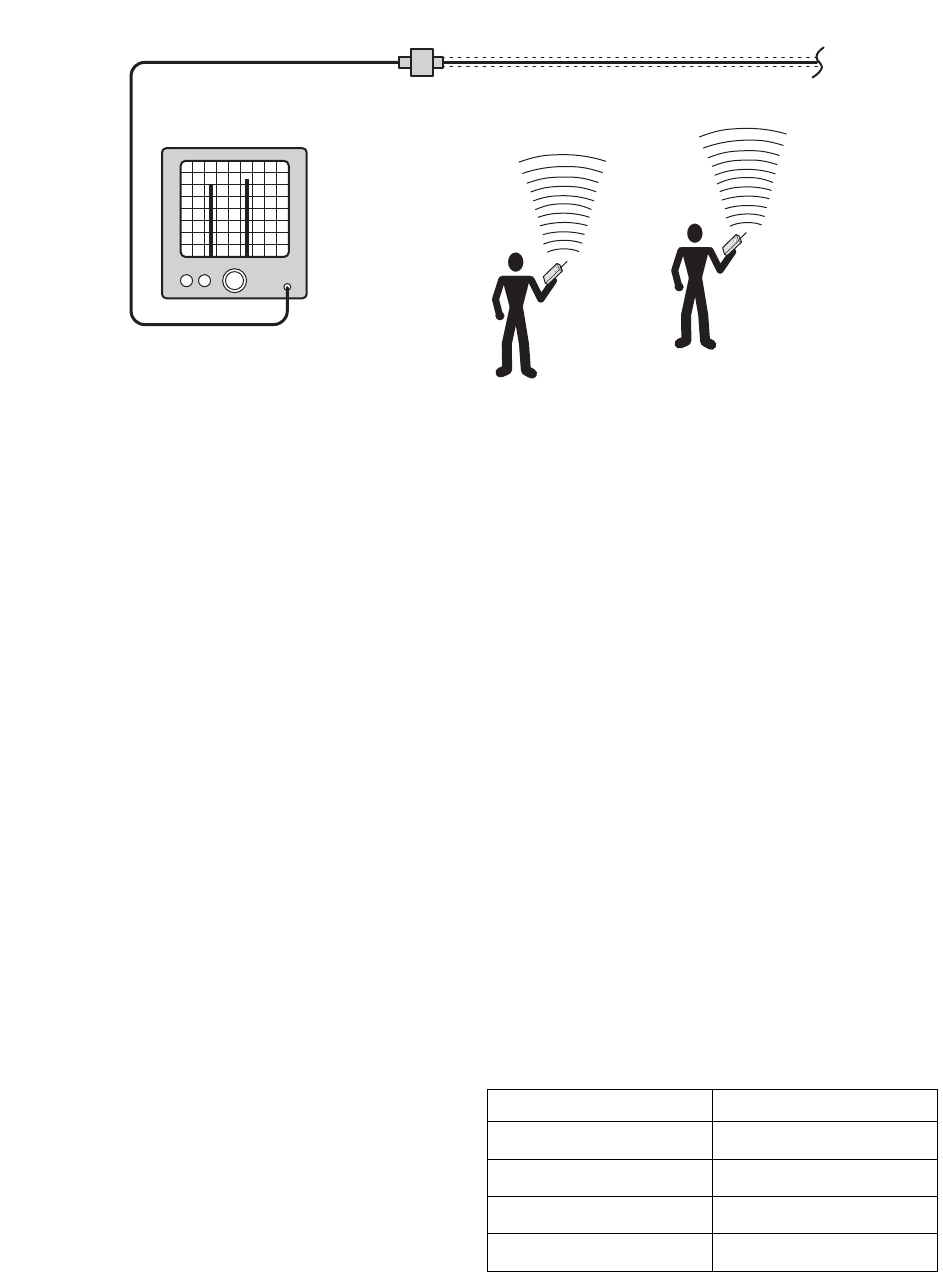
S p e c t r u m A n a l y z e r
R a d i o 1
R a d i o 2
S I G N A L D I S T R I B U T I O N S Y S T E M
Figure 5
: Typical test equipment setup for measuring input signal levels.