User's Manual
Table Of Contents
- 1 Introduction
- 2 Getting to know the device
- 3 Computer configurations under different OS, to obtain IP address automatically
- 4 Utility CD execution
- 5 Getting Started with the Web pages
- 6 Overview
- 7 Status
- 8 Internet Access
- 9 Local Network Configuration
- 10 DHCP Settings
- 11 DHCP Static Configuration
- 12 LAN IPv6 Configuration
- 13 Wireless Network
- 14 Routing
- 15 DMZ
- 16 Virtual Server
- 17 NAT Forwarding
- 18 ALG
- 19 NAT Exclude IP
- 20 Port Trigger
- 21 FTP ALG Portl
- 22 Nat IP Mapping
- 23 IP QoS
- 24 CWMP Config
- 25 Port Mapping
- 26 Bridging
- 27 Client Limit
- 28 Tunnel Configuration
- 29 Others
- 30 IGMP Proxy
- 31 UPnP
- 32 SNMP
- 33 DNS Configuration
- 34 Dynamic DNS Configuration
- 35 MAC Filtering
- 36 IP/Port Filtering
- 37 URL Filter
- 38 ACL Configuration
- 39 DoS
- 40 Firmware Update
- 41 Backup/Restore
- 42 Password
- 43 Commit/Reboot
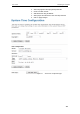
- 44 Time Zone
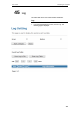
- 45 Log
- 46 Diagnostic
User’s Guide Configuring your Computers
46 Diagnostic
The DSL device supports some useful diagnostic tools.
Ping
Once you have your DSL device configured, it is a good idea to
make sure you can ping the network. A ping command sends a
message to the host you specify. If the host receives the
message, it sends messages in reply. To use it, you must know
the IP address of the host you are trying to communicate with
and enter the IP address in the Host Address field. Click Go! To
start the ping command, the ping result will then be shown in
this page.
2. From the head Maintenance menu, click on Diagnostic ->
Ping. The following page is displayed:
Fields Description
Host The IP address you want to ping.
Function
buttons
Description
PING To start the ping command
3. Type the IP Address in the Host field.
4. Click Ping
187