User's Manual
Table Of Contents
- 1 Introduction
- 2 Getting to know the device
- 3 Computer configurations under different OS, to obtain IP address automatically
- 4 Utility CD execution
- 5 Getting Started with the Web pages
- 6 Overview
- 7 Status
- 8 Internet Access
- 9 Local Network Configuration
- 10 DHCP Settings
- 11 DHCP Static Configuration
- 12 LAN IPv6 Configuration
- 13 Wireless Network
- 14 Routing
- 15 DMZ
- 16 Virtual Server
- 17 NAT Forwarding
- 18 ALG
- 19 NAT Exclude IP
- 20 Port Trigger
- 21 FTP ALG Portl
- 22 Nat IP Mapping
- 23 IP QoS
- 24 CWMP Config
- 25 Port Mapping
- 26 Bridging
- 27 Client Limit
- 28 Tunnel Configuration
- 29 Others
- 30 IGMP Proxy
- 31 UPnP
- 32 SNMP
- 33 DNS Configuration
- 34 Dynamic DNS Configuration
- 35 MAC Filtering
- 36 IP/Port Filtering
- 37 URL Filter
- 38 ACL Configuration
- 39 DoS
- 40 Firmware Update
- 41 Backup/Restore
- 42 Password
- 43 Commit/Reboot
- 44 Time Zone
- 45 Log
- 46 Diagnostic
User’s Guide Configuring your Computers
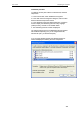
5. Select the following entries from the “Networking Services”
window and then click "OK":
If you are using Windows XP, select:
• "Universal Plug and Play".
If you are using Windows XP SP1, select:
• "Internet Gateway Device discovery and Control Client".
• "Universal Plug and Play".
If you are using Windows XP SP2, select:
• "Internet Gateway Device discovery and Control Client".
• "UPnP User Interface".
6. Reboot your system.
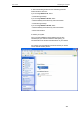
Once you have installed the UPnP software and you have
rebooted (and your network includes the IGD system), you
should be able to see the IGD controlled device on your network.
For example, from the Network Connections window you should
see the Internet Gateway Device:
150