User`s guide
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
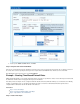
Step 3. Verify the Order of the Firewall Rules
Because rules are processed from top to bottom, arrange your rules in the correct order. You must especially ensure that your rules are placed
above the BLOCKALL rule; otherwise, the rules are blocked.
After adjusting the order of the rules, click .Save Changes
For more information, see .Firewall Rules Order
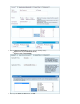
Monitoring Traffic for Detected Applications
To view blocked or throttled connections, go to the page. In the column for each connection, the detectedBASIC > IPS Events Service
application is listed. To view specific connections, you can filter the list of recent connections.
Example - Creating Connection Objects for Failover and Link Balancing
To balance traffic among multiple links, create a firewall rule that uses a connection object that you configure. This
connection object references all of the links and configures how to balance the traffic among them. You can also
specify one link that is used for all the traffic matching the firewall rule, as long as it is available. If that link fails, then
the next link is used in its place.
To create the connection object:
Go to the page. FIREWALL > Connection Objects
Click . Add Connection Object
From the list in the window, select either (to use the IP address that you specify) or NAT Type Add Connection Object Explicit From In
(to use the IP address of the link).terface
In the section, configure the following settings:Failover and Load Balancing
Multilink Policy – Defines what happens if multiple links are configured. Available policies are:
None – No fallback or source address cycling. This is not what you want for this object.
Failover – Falls back to the first alternate addresses and interface, called Alternate 1. If Alternate 1 fails, fail over to
Alternate 2 and so on. When the original link (the one configured in the top section) becomes available, the Barracuda
Firewall automatically resumes directing traffic to that interface.
Weighted Round Robin – Uses the IP addresses and interfaces configured as Alternate 1, 2, and 3, along with this
interface, in weighted-round robin fashion.
Random – Randomly uses one of the available IP addresses and interfaces specified in this object.
Specify the following for each of the alternate links:
NAT Type – Select one of these options:
From Interface – Source NAT the first IP address on the interface selected from the list.using Interface
Explicit – Uses the IP address in the address field.IP
Weight – Only used for the weighted round robin policy. The weight numbers represent the traffic balancing ratio of the
available links. The higher the relative number, the more the link is used. For example, if four links are configured in this
object, weight values of 6, 2, 1, and 1 mean that traffic is balanced over the configured interfaces in a ratio of 6:2:1:1. As
a result, 60% percent of the traffic passes over Link #1, 20% of the traffic over Alternate 1, 10% of the traffic ispasses
directed to Alternate 2, and 10% to Alternate 3.
Click .Add
After you have successfully created this connection object, you can go to the page and apply it to a rule that directsFIREWALL > Firewall Rules
outgoing traffic.
Example - Routing Traffic Over Two Different ISP Connections
The Barracuda Firewall can classify and identify traffic to be routed via specific links.
There are predefined connection objects for a number of ISP uplink types. In addition,
you can create your own connection objects. The connection object defines the egress
interface and source (NAT) IP address for traffic matching the firewall rule.
To route traffic over different ISP connections, you must configure a firewall rule for
each connection type.
This article provides an example of how to configure firewall rules to route HTTP traffic
through a primary ISP connection and FTP traffic through a secondary ISP connection.
The following settings are used for the example scenario: