Specifications
Print2CAD OCR 2013 - 108
17.3 Raster Image Compression
“Image compression is the application of data compression on digital images. In effect,
the objective is to reduce redundancy of the image data in order to be able to store or
transmit data in an efcient form:
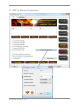
A chart showing the relative quality of various jpg settings and also compares saving a
le as a jpg normally and using a “save for web” technique. Image compression can be
lossy or lossless. Lossless compression is preferred for archival purposes and often med-
ical imaging, technical drawings, clip art or comics. This is because lossy compression
methods, especially when used at low bit rates, introduce compression artifacts. Lossy
methods are especially suitable for natural images such as photos in applications where
minor (sometimes imperceptible) loss of delity is acceptable to achieve a substantial
reduction in bit rate. The lossy compression that produces imperceptible differences can
be called visually lossless. (...)”
Source: Wikipedia, subject “Image Compression”
License Agreement: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/
17.3.1 LZW Compression
“Lempel–Ziv–Welch (LZW) is a universal lossless data compression algorithm created by
Abraham Lempel, Jacob Ziv, and Terry Welch. It was published by Welch in 1984 as an
improved implementation of the LZ78 algorithm published by Lempel and Ziv in 1978.
The algorithm is designed to be fast to implement but is not usually optimal because it
performs only limited analysis of the data.
The simple scheme described above focuses on the LZW algorithm itself. Many appli-
cations apply further encoding to the sequence of output symbols. Some package the
coded stream as printable characters using some form of Binary-to-text encoding; this
will increase the encoded length and decrease the compression frequency. Conversely,
increased compression can often be achieved with an adaptive entropy encoder. Such a
coder estimates the probability distribution for the value of the next symbol, based on
the observed frequencies of values so far. A standard entropy encoding such as Huffman
coding or arithmetic coding then uses shorter codes for values with higher probabilities.”
Source: Wikipedia, subject “LZW Compression”
License Agreement: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/