Manual
16
THE HAZARD
Most equipment with a 2-Wire Plug is Transformerless
Most recent television receivers and other consumer products
such as stereo amplifiers, tuners, tape decks, etc. do not contain
an isolation transformer. Such products often have a plastic or
wood cabinet which completely insulates the chassis and prevents
the user from touching it. However, when the cabinet is removed
for servicing the product, the chassis is exposed and may become
an electrical shock hazard to the service technician.
Bridge Rectifier Transformerless Equipment
One of the most commonly used types of power supply circuits
in television receivers and audio equipment is the transformerless
full wave bridge rectifier shown in Fig 7. In such cases, the
chassis is always “hot”, regardless of which way the 2-wire ac
plug is inserted. Touching a “hot” chassis is hazardous and can
cause fatal electrical shock.
Just because a unit uses a polarized power plug does not
guarantee safety. Some equipment with a bridge rectifier uses a
polarized power plug, and as mentioned above, always has a
“hot” chassis.
Transformerless Half-Wave Rectifier Equipment
Another commonly used transformerless power supply circuit
is a half-wave rectifier where one side of the ac power line
connects directly to the chassis (also shown in Fig. 7). Unless the
equipment is equipped with a polarized plug to prevent insertion
the “wrong” way, the chassis may be “hot” (120VAC with
respect to earth ground) and cause an electrical shock if touched.
Other Transformerless Hazards
Equipment with voltage doubler power supplies may also be of
the “hot Chassis” variety and pose the same safety hazard. In
fact, and equipment with a 2-wire ac power plug should be treated
as hazardous “hot” chassis type and the safety precautions listed
on the next page should be taken.
Test Equipment Damage Hazard
In addition, to the electrical shock hazard if the “hot” chassis is
touched, there is also a high probability of damaging any ac-
powered test equipment used to service the equipment. Most test
equipment with a 3-wire power cord, such as oscilloscopes and
signal generators, have an earth ground chassis (connected to
earth ground through the third wire of the ac power plug).
Touching the ground lead of any such test equipment probe to a
“hot” chassis shorts the hot side of the power line through the
ground lead and instrument. Since the path through the
instrument is intended only as a signal ground, the excessive
current of a direct power line short may cause extensive damage
to the test equipment or to the equipment under test.
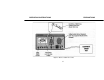
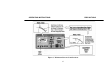
Troubleshooting: Use As Isolation Transformer OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS
TROUBLESHOOTING: USING THE AC POWER SUPPLY AS ISOLATION TRANSFORMER
WARNING
n
t Considerations.