5 Ch. VHF Radio Repeater Equipment (Bi-directional Amplifier) For Day Wireless Systems AFL Works Order AFL Product Part No. Q116073 50-189201 (5 Ch. VHF System 80dB) 5 Ch.
Table of Contents 1. INTRODUCTION.......................................................................................................................... 4 1.1. Scope and Purpose of Document ............................................................................................. 4 1.2. Limitation of Liability Notice ...................................................................................................... 4 2. SAFETY CONSIDERATIONS .........................................................
8.8 General Maintenance Procedures .......................................................................................... 42 8.9 Module Removal (LNAs, general procedure).......................................................................... 42 8.10 Module Replacement (general) ........................................................................................... 42 8.11 Power Amplifiers...............................................................................................................
1. INTRODUCTION 1.1. Scope and Purpose of Document This handbook is for use solely with the equipment identified by the Aerial Facilities Limited (AFL) Part Number shown on the front cover. It is not to be used with any other equipment unless specifically authorised by AFL. This is a controlled release document and, as such, becomes a part of Aerial Facilities’ Total Quality Management System. Alterations and modification may therefore only be performed by AFL.
2. SAFETY CONSIDERATIONS 2.1. Earthing of Equipment Equipment supplied from the mains must be connected to grounded outlets and earthed in conformity with appropriate local, national and international electricity supply and safety regulations. 2.2.
2.5. Chemical Hazard Beryllium Oxide, also known as Beryllium Monoxide, or Thermalox™, is sometimes used in devices within equipment produced by Aerial Facilities Ltd. Beryllium oxide dust can be toxic if inhaled, leading to chronic respiratory problems. It is harmless if ingested or by contact. Products that contain beryllium are load terminations (dummy loads) and some power amplifiers. These products can be identified by a yellow and black “skull and crossbones” danger symbol (shown above).
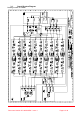
3. EQUIPMENT OVERVIEW 5 channel radio repeater 50-189201 is supplied in three 43U equipment mounting racks. Rack 1 (50-189212) houses the main amplification modules along with the various splitters and combiners. Rack 2 (50-189213) houses the Cavity FIlters for the TX (Downlink) path Rack 3 (50-189214) houses the Cavity FIlters for the RX (Uplink) path Downlink. Channel 1 – 154.190MHz Channel 2 – 154.070MHz Channel 3 – 158.910MHz Channel 4 – 155.700MHz Channel 5 – 158.
3.1. Overall System Diagram Drawing number 50-189281 5 Ch.
4.
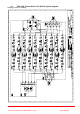
4.1. BDA VHF System Rack 1 (50-189212) System diagram Drawing number 50-189292 5 Ch.
4.2.
Bottom of rack I J K L M N 1U Blanking Panel BDA VHF Uplink Output Combiner 50-189209 BDA VHF Downlink Input Splitter 50-189207 VHF/UHF System PSU 24v 50-146512 2U Blanking Panel 3U Blanking Panel Rack interconnections are on the top of the rack rack Ant E1 E2 E3 G1 G2 G3 H1 H2 H3 Connection to RX Antenna D/L Channel 4 to Cavity Combiner Rack 2 Combined D/L Channel 1 & 2 to Cavity Combiner Rack 2 Combined D/L Channel 3 & 5 to Cavity Combiner Rack 2 Combined U/L Channel 3 & 4 from first stage Cavity Comb
4.3.
4.3.2. BDA VHF Downlink Output Combiner (50-189208) System diagram Drawing number 50-189288 5 Ch.
4.4. BDA VHF Uplink Input Splitter (50-189210) BDA VHF Uplink Input Splitter (50-189210) takes the three signal path inputs from the first stage uplink cavity filter in rack 2 and splits two of the signals to produce five signal paths which are then fed to the crystal filters. The outputs from the five crystal filters then leave the Uplink Input Splitter shelf to go to the uplink sections of the Channelised Amplifier shelves. This is a passive shelf and has no connection to the PSU and no alarms, 4.4.1.
4.4.2. BDA VHF Uplink Input Splitter (50-189210) System diagram Drawing number 50-189290 5 Ch.
4.5. BDA VHF Channel Shelves (50-189202 to 50-189206) Rack 1 contains five Channelised Amplifier shelves, one shelf for each channel. Each shelf is composed of identical sub-modules, the only differences being the frequency that the modules are configured to pass and the part numbers of the crystal filters employed. Each shelf is powered by a 24V DC feed from the PSU (50-146512) and has alarm outputs.
Parts specific to Shelf 1, 50-189202 Component Part 93-980196 93-980222 Component Part Description Crystal Filter 154.785MHz Crystal Filter 154.070MHz Qty Per Assembly 1 1 Parts specific to Shelf 2, 50-189203 Component Part 93-980223 93-980225 Component Part Description Crystal Filter 154.190MHz Crystal Filter 154.830MHz Qty Per Assembly 1 1 Parts specific to Shelf 3, 50-189204 Component Part 93-980226 93-980227 Component Part Description Crystal Filter 155.700MHz Crystal Filter 155.
Top View – lid removed A B C D E F Downlink Input Downlink Output Uplink Input Uplink Output Alarm Output DC Input (24V) Close-up of attenuator switches 5 Ch.
4.5.2. BDA VHF Channel 1 Shelf (50-189202) System diagram Drawing number 50-189282 5 Ch.
4.5.3. BDA VHF Channel 2 Shelf (50-189203) System diagram Drawing number 50-189283 5 Ch.
4.5.4. BDA VHF Channel 3 Shelf (50-189204) System diagram Drawing number 50-189284 5 Ch.
4.5.5. BDA VHF Channel 4 Shelf (50-189205) System diagram Drawing number 50-189285 5 Ch.
4.5.6. BDA VHF Channel 5 Shelf (50-189206) System diagram Drawing number 50-189286 5 Ch.
4.6. BDA VHF UPLINK OUTPUT COMBINER (50-189209) The Uplink Output Combiner (50-189209) takes the five separate uplink outputs from the Channelised Amplifier shelves and combines them into three signal paths Channels 3 and 4 are combined by a Hybrid Combiner, Channels 5 and 1 are combined by a second Hybrid Combiner. Channel 2 passes straight through. The three resultant outputs are then fed to the second stage of the cavity filter in rack 3 4.6.1.
4.6.2. BDA VHF Uplink Output Combiner (50-189209) System Diagram Drawing number 50-189289 5 Ch.
4.7. BDA VHF DOWNLINK INPUT SPLITTER (50-189207) Downlink Input Splitter (50-189207) shelf receives Downlink VHF signals from the off-air RX antenna, the signal is split into three paths and each path is then pased through a Bandpass Notch Filter. The outputs of two of the filters are then further divided to produce the five required channels. Each channel then passes through a Crystal Filter before leaving the Input Splitter shelf and going to a dedicated Channelised Amplifier. 4.7.1.
4.7.2. BDA VHF Downlink Input Splitter (50-189207) System Diagram Drawing number 50-189287 5 Ch.
4.8. 24V PSU Shelf (50-146512) The power supply shelf (50-146512) consists of two, 400Watt 24V DC, O.E.M modules which are commonly supplied from the mains but separately switched. The DC outputs are separately monitored and this data becomes half of the alarm data for the shelf (the two monitor loops are summed to form a single alarm relay contact pair).
Top View – lid removed A B C D E F G H I Fuses (PSU 1) 24V DC Outputs (PSU 1) Fuses (PSU 2) 24V DC Outputs (PSU 2) On/Off switch (PSU 1) On/Off switch (PSU 2) AC Input Alarm Output Ground Connection 5 Ch.
4.8.2. 24V PSU Shelf (50-146512) System Diagram Drawing number 60-163486 5 Ch.
5. BDA VHF SYSTEM RACK 2 (50-189213) Rack 2, the Downlink cavity combiner takes the three signals from Downlink Output Combiner (50189208) and passes each of them through a cavity filter stage, the combined D/L channels 1 & 2 are passed through a chain of three cavitiy filters, D/L channel 4 and the combined D/L channels 3 & 5 are each passed through a chain of two cavity filters.
Rack Interconnections (see below) A B C D Three cavity filter section for combined D/L channels 1 & 2 Two cavity filter section for D/L channel 4 Two cavity filter section for combined D/L channels 3 & 5 Hybrid Splitter/Combiner Tray (50-189211) Rack interconnections are on the top of the rack rack E1 E2 E3 K1 LCX LCX D/L Channel 4 from Rack 1 Combined D/L Channel 1 & 2 from Rack 1 Combined D/L Channel 3 & 5 from Rack 1 Combined U/L feed to Rack 3 Connection to LCX Connection to LCX 5 Ch.
5.1. BDA VHF System Rack 2 (50-189213) System Diagram Drawing number 50-189293 5 Ch.
5.2. Hybrid Splitter/Combiner Tray (50-189211) In the Downlink direction the Hybrid Splitter/Combiner Tray (50-189211) receives the downlink signal from the Downlink Cavity Combiner and splits it into two separate signal paths to provide the two LCX feeds In the Uplink direction the Hybrid Splitter/Combiner Tray (50-189211) takes the two seperate LCX feeds and combines them before passing the signal on to Uplink Input Splitter (50-189210) In rack 1 5.2.1.
5.2.2. Hybrid Splitter/Combiner Tray (50-189211) System Diagram 5 Ch.
6. BDA VHF SYSTEM RACK 3 (50-189214) Rack 3, the Uplink Cavity Combiner comprises two stages.
Rack Interconnections (see below) A B C First stage Cavity Combiner Second stage Cavity Combiner Bandpass Notch Filter Rack interconnections are on the top of the rack rack Ant K1 G1 G2 G3 H1 H2 H3 Connection to TX Antenna Combined U/L feed from rack 2 Combined U/L Channel 3 & 4 to Rack 1 U/L Channel 2 to Rack 1 Combined U/L Channel 1 & 5 to Rack 1 Combined U/L Channel 3 & 4 from Rack 1 U/L Channel 2 from Rack 1 Combined U/L Channel 1 & 5 from Rack 1 5 Ch.
6.1. BDA VHF System Rack 3 (50-189214) System Diagram 5 Ch.
7. INSTALLATION 7.1 Initial Installation Record When this equipment is initially commissioned, please use the equipment set-up record sheet in Appendix B. This will help both the installation personnel and AFL should these figures be needed for future reference or diagnosis. 8. FAULT FINDING & MAINTENANCE 8.1 General Fault Finding Procedures In the event that the performance of the system is suspect, a methodical and logical approach to the problem will reveal the cause of the difficulty.
8.3 Uplink Testing the uplink involves a similar procedure to the downlink except that the frequencies used are those transmitted by the mobile equipment. 8.4 Fault repair Once a faulty component has been identified, a decision must be made on the appropriate course to carry out a repair. A competent engineer can quickly remedy typical faults such as faulty connections or cables.
8.8 General Maintenance Procedures Many of the active modules contain semiconductor devices utilising MOS technology, which can be damaged by electrostatic discharge. Correct handling of such modules is mandatory to ensure their long-term reliability. To prevent damage to a module, it must be withdrawn/inserted with care. The module may have connectors on its underside, which might not be visible to the service operative. 8.
8.12 Low Power Amplifier Replacement Disconnect the mains power supply and disconnect the 24V dc supply connector for the LPA. Disconnect the RF input and output cables from the LPA. Disconnect the alarm connector. Remove the alarm monitoring wires from (D type connector) pins 9 and 10. Remove the LPA module by removing the four retaining screws, replace with a new LPA module and secure it with the screws. Connect the RF cables to the LPA input and output connectors.
APPENDIX A A.1. Glossary of Terms used in this document Repeater or Cell Enhancer Band Selective Repeater Channel Selective Repeater AC AGC BBU BTS CEMS C/NR DC Downlink (D/L) FO GND ID LED LNA LPA MOU M.S. MTBF N/A N/C OFR OIP3 P1dB PA RF RSA RX S/N TX Uplink (U/L) VSWR WDM A Radio Frequency (RF) amplifier which can simultaneously amplify and re-broadcast Mobile Station (MS) and Base Transceiver Station (BTS) signals.
Document Number 50-189201HBK – Issue 1 ) ( ' & % $ 5 Ch. VHF Radio Repeater Equipment Page 45 of 48 *' $33' 10/05/00 '$7( 5) $// ',0(16,216 $5( ,1 PP 81/(66 27+(5:,6( 67$7(' 0% &+.' PL '5$:1 5) )5(48(1&< 352*5$00,1* '$7$ % : WR N+] %76 +, ,1 /2: 287 5 6 $ /((.
A.3.
A.4. Amendment List Record Sheet Issue No. A Date 05/12/2007 Incorporated by AJS 1 21/12/2007 AJS Page Nos. Reason for new issue Amended Draft First Issue Document Ref. 50-189201HBK 5 Ch.
APPENDIX B Initial Equipment Set-Up Calculations General Information Site Name: Client Name: Date: AFL Equip. Model No. Antenna Systems Model Gain Azimuth Comments Type Loss Length Comments A - Service Antenna B – Donor Antenna C – Service Feeder D – Donor Feeder Initial Parameters E – CE Output Power F – Antenna Isolation G – Input signal level from donor BTS Operating Voltage Downlink Calculations Parameter Input signal level (G) CE max.