User's Manual

MDR2400-SR, MDR5800-SR and Orion 5825-SR
Issue 10 Page 122
Technical Description
System Overview
The functionality required to establish a protected radio link is already built into the
MDR- and Orion-type Software Radios. This implies that the user can set up a
protected radio link by interconnecting the equipment for two parallel radio links
through a 1U protection panel and a dedicated communications cable.
Each Indoor Unit in a protected radio system continuously monitors the status of the
radio link it uses, as well as the radio link provided through the redundant system
running in parallel. Indoor Units forming part of a redundant link at each end of the
radio link share status information through a cable connecting the two Auxiliary ports
of the Indoor Units.
Only the tributary payload data channels are protected by the redundant link i.e. there
is no protection for Ethernet data. Tributary payload data is split and combined
between links through a 1U protection panel that connects to the user network
equipment as well as the two Indoor Units used at each end of the redundant link.
Although both radio links are functioning continuously, only one of the Indoor Units is
actively driving the tributary channels of the user network at any given time.
Each Indoor Unit continuously monitors the level of the Packet Error Ratio (PER) for
the radio link on which it is receiving user data. When the PER exceeds a predefined
ratio of 10 consecutive seconds, the Indoor Unit driving the tributary channels of the
user network will signal the redundant Indoor Unit to take over processing the data it
receives over the radio link.
The value of the PER threshold is configurable and can be changed through the Orion
NMS if required. The default value is set at 30%.
There is no notion of a primary and secondary link in this redundancy system. The
first link to be configured successfully will start driving the tributary payload channels.
Switch over will only take place when the aforementioned condition occurs. In the
event where the link to which the data was switched over fails at a later stage, the
system will attempt to switch the data back to the original link.
NOTE 1 A situation can arise where the up- and downstream user tributary data is
carried by separate radio links, i.e. link A carries the upstream data, and link B carries
the downstream data.
NOTE 2 Due to the architecture of the redundancy system, the process of switching
over from one link to another is not hitless and user tributary data will be lost for a few
seconds (< 10)
System Configuration
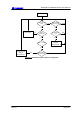
The block diagram in Figure 10 illustrates a typical redundancy system configuration.
Note that this system is managed over an Ethernet LAN, where the two local Indoor
Units are connected to the LAN using a hub. It is important to note that the IP
addresses for each Indoor Unit should be unique. It is however possible to configure