User's Manual
8.4 + 3.2 + 0 = 11.6.
Calculating the data for all remaining cells
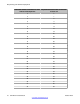
T
able 10: Example of a completed estimate table
Estimate for: 1C1 1C2 1C3 1C4 1C5 1C6 1C7
Users inside the cell with
an of
fice
8.4 0.7 21.0 14.7 0.7 4.9 2.1
Users with an office
outside of a cell who walk
into the cell
3.2 3.7 2.3 2.7 3.7 3.4 3.6
Users without an office 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Users in a cell 11.6 4.4 23.3 17.7 4.4 8.3 5.7
Calculating the data for all remaining cells
1. Repeat the previous four procedures to calculate the remaining user cell
estimates.
2. Enter the result in the estimate table.
The information in Figure 33: Example of dividing the coverage area and recording
offices on page
63, is entered into
Table 10: Example of a completed estimate
table on page 67.
This table shows the results of the calculations for cells that
require reengineering.
Creating a table to document telephone types in a cell
Use a table like
Table 11: Telephone types in a cell on page 67 to record the various telephone
types in each cell.
T
able 11: Telephone types in a cell
Telephone type 1C1 1C2 1C3 1Cn
User telephone types
Use the following symbols in each cell to denote the type of telephones in use in the cell.
•
H&W for a cell in which all the users have both wired and handsets (wireless phones).
• H for a cell in which users have only handsets (wireless phones).
• M for a mix of H and H&W users
Creating a table to document telephone types in a cell
1. Make a Telephone types table.
2. Label the row User telephone types and include a column for each cell center.
3. Label each column heading with the cell center indicator.
System deployment
SIP DECT Fundamentals October 2012 67