2008
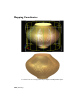
Map Bias
On the right, increased map bias makes the dog appear to float.
Map bias moves the shadow toward or away from the shadow-casting object
(or objects).
By default, this value is 1.0 world coordinate unit. Increasing the bias moves
the shadow away from the object, and decreasing the bias moves the shadow
closer to the object. The Map Bias value can be any positive floating-point
number.
For example, if a shadow-casting object intersects another object but its shadow
doesn't meet properly at the intersection, the bias is too high. This effect varies
with the angle of the spotlight to the object. Extremely shallow spotlight
angles usually require higher bias values.
Another purpose of bias is to avoid problems with objects that cast shadows
onto themselves. If you see streaks or moiré patterns on the surface of the
object, the bias value is too low. If you increase the bias so much that the
shadow becomes disconnected from the object, reduce the bias and increase
the shadow map Size value instead.
Glossary | 7835