Service manual
STP 11-25R13-SM-TG
D - 3
D-5. Theory, Operational Characteristics, and Troubleshooting Procedures for Bipolar and FET-
Type Amplifiers.
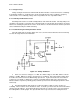
a. The CE amplifier, shown in Figure D-2, is probably the most widely used type of amplifier in
existence, because it is the only bipolar configuration capable of amplifying both voltage and current.
b. As you recall, Rl and R2 form a voltage divider network that provides the forward biasing
potential for Ql. R3 provides the collector with a load for proper operation. Refer to Table D-1 for the
function of each component.
Table D-1. CE Component Functions
Figure D-2. CE Amplifier
c. In the quiescent state, Ql will be conducting at some point on the load line. When a signal that
aids the biasing potential is applied to the base of Ql, Ql will increase its conduction, decreasing the
output voltage. When the input signal opposes the bias, Ql will decrease its conduction, increasing the
output voltage. Remember that the output of the common emitter amplifier is always out of phase with
the input.
D-6. Common Base (CB) Amplifier.
a. The CB amplifier, shown in Figure D-3, is used when voltage amplification is necessary with no
phase shift or when the impedance of two stages must be matched. Remember that the CB amplifier has
low input impedance and high output impedance. Refer to Table D-2 for the function of each component.
Table D-2. CB Component Functions
Figure D-3. CB Amplifier