User manual User guide
Table Of Contents
- 1 Preface
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Getting Started
- 4 LCM Configuration
- 5 Web Configuration
- 6 CLI Configuration
- 7 Link Modes and Applications
- 7.1 Link Mode Configuration
- 7.2 Link Mode Applications
- 7.2.1 TCP Server Application: Enable Virtual COM
- 7.2.2 TCP Server Application: Enable RFC 2217
- 7.2.3 TCP Client Application: Enable Virtual COM
- 7.2.4 TCP Client Application: Enable RFC 2217
- 7.2.5 TCP Server Application: Configure SE5416A Series as a Pair Connection Master
- 7.2.6 TCP Client Application: Configure SE5416A Series as a Pair Connection Slave
- 7.2.7 TCP Server Application: Enable Reverse Telnet
- 7.2.8 UDP Application: Multi-Point Pair Connection
- 7.2.9 TCP Server Application: Multiple TCP Connections
- 7.2.10 TCP Server Application: Multi-Point TCP Pair Connections
- 8 VCOM Installation & Troubleshooting
- 9 Specifications
- 10 Upgrade System Firmware
- 11 Warranty
Atop Industrial Serial Device Server
SE5408A/SE5416A Series
User Manual V 1.0
84
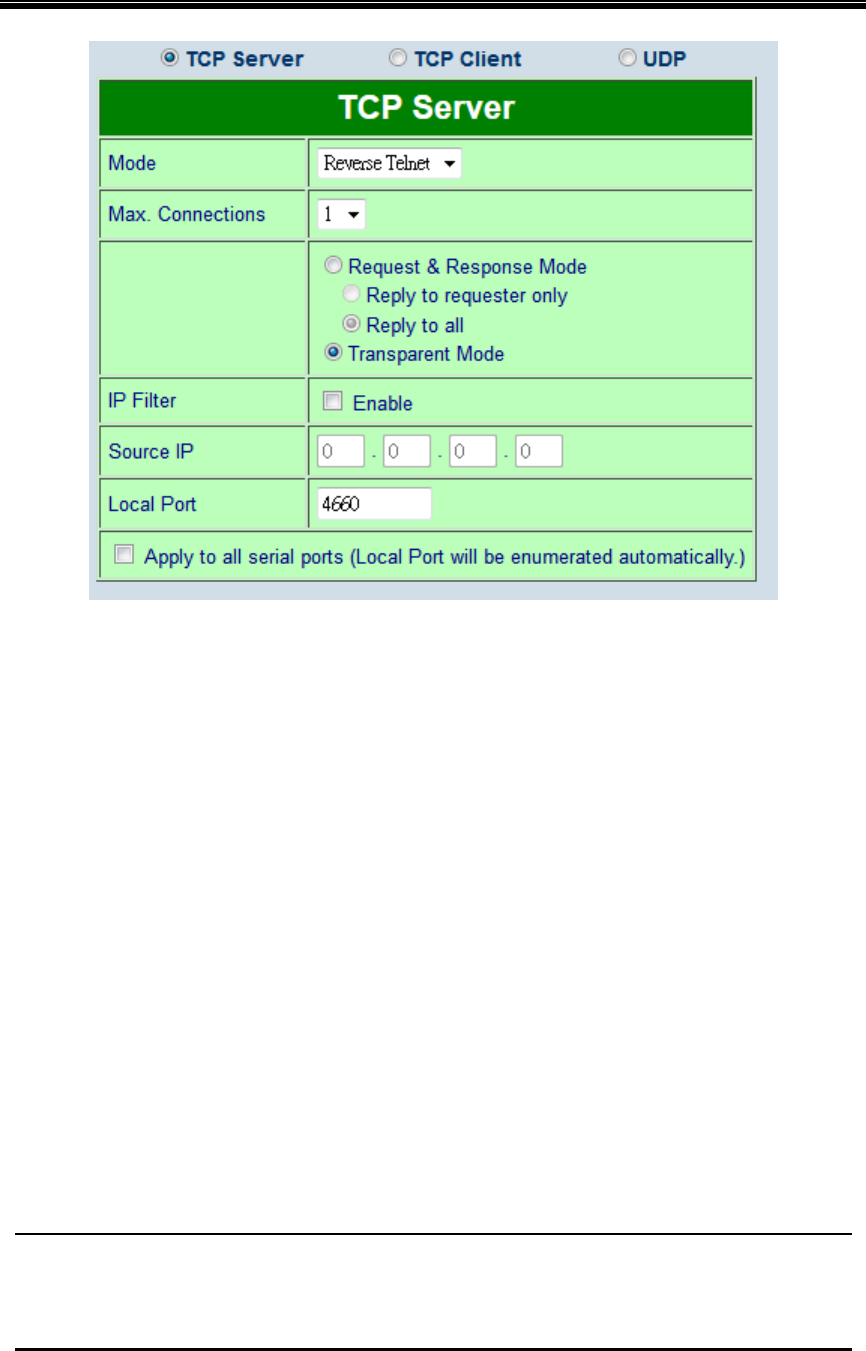
Figure 7.11
Follow Sec. 7.2.1 to configure SE5416A Series in TCP Server mode properly.
Click on the dropdown box of the Mode option and switch to “Reverse Telnet” to enabled
Reverse Telnet application in SE5416A Series.
Scroll to the bottom of the page and click on “Save Configuration” button to save the
changes.
7.2.8 UDP Application: Multi-Point Pair Connection
It is also possible to setup pair connection in UDP mode to have more than one Pair
Connection Master or Slave to communicate to each other. For example, it is possible to setup
one Modbus Master and six Modbus Slaves in UDP, Figure 7.12. Note again that UDP does
not guarantee data delivery and only data would be transmitted over Ethernet; other serial
pings are not transmitted. If RS-232 along with flow control, it is recommended to use
Multi-Point Pair Connection in TCP, see Sec. 7.2.10.
Note: the destination IP and Port of the Slaves need to be equal to the Master’s IP and Port.
Local Listening Port for the Slaves need to be equal to the Master’s Destination Port, see table
below for an example.










