Installation guide
Table Of Contents
Application Note
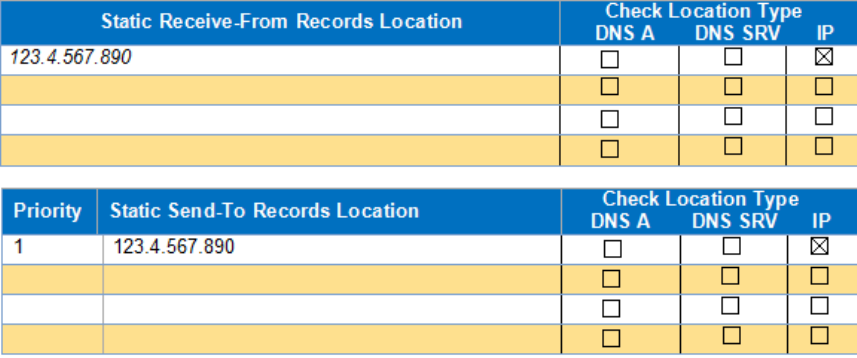
receiv
e calls from your system. These two sections are only utilized if you provided
static IP address information or DNS information. Broadvox can send calls to entirely
separate systems from the ones it is configured to receive calls from. This allows you
to split your inbound and outbound traffic for any reason you may have, including
but not limited to load distribution over several systems or multiple Internet
connections. In addition, Broadvox can randomly load-balance calls across several
systems using an identical priority for the Send-To records. These options should
allow you to engineer your traffic flow to suit your particular needs.
Figure6:SignalingConfiguration
SRV Records
Service records (SRV) are a form of Domain Name System (DNS) record. They
contain information about where to send requests for a particular service offered at a
specific domain. In the case of Broadvox GO! SIP Trunking, they provide the IP
addresses, port numbers, and preferences to use for sending SIP calls over UDP to
Broadvox. The SRV location to use for sending calls to Broadvox for each of your
trunk groups is in your Welcome letter.
Preferred and Alternate Codecs
Broadvox allows you to select preferred and alternate codecs to simultaneously meet
your bandwidth requirements and provide greater end-to-end support. In the event
that your destination party or your destination party’s carrier cannot support your
preferred codec or alternate codecs, Broadvox will automatically transcode your call
to a supported codec.
When configuring codecs, please keep in mind that G.711 μLaw (ulaw) consumes
approximately 87.2 Kbps of bandwidth per simultaneous call. G.729 Annex B (g729)
will consume approximately 31.2 Kbps of bandwidth per simultaneous call. Also,
keep in mind that G.711 offers superior call quality when compared to G.729, but
only if you have enough bandwidth to support all of your simultaneous calls.
If the SIP Gateway Is Behind a Firewall
If the SIP Gateway is behind a NAT, then it is almost certainly behind a firewall. It is
also possible that the SIP Gateway uses a public IP address but is still behind a
firewall. If you use a Cisco PIX, SonicWALL, Shorewall, Firebox, or any other brand of
firewall, you may need to perform additional configuration steps on the firewall
6










