Manual
74
Permissions: Right-clicking on a file or folder and then selecting “Properties” followed by the
“Permissions” tab will allow you to configure detailed access permissions for the file or folder.
If the top-level shared folder does not have Windows ACL enabled, the options for configuring
permissions will be:
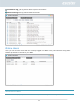
Owner: The owner of the folder or file
Group: The group that has been assigned to the folder or file
Others: All other users on the system or network that are not owners or part of the group that
has been assigned to the folder or file.
The permission types that you will be able to configure are: RW (Read & Write), RO (Read Only)
and DA (Deny Access).
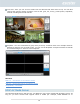
If the top-level shared folder has Windows ACL enabled, you will be able to configure file
permissions for all users and groups. In total, there will be 13 types of configurable permissions.
These types of permissions are as follows:
Reminder: An individual file or folder can utilize up to a maximum of 250 Windows ACL
permissions (including inherited permissions).
Traverse folder / execute file
List folder / read data
Read attributes
Read extended attributes
Create files / write data
Create folders / append data
Write attributes
Write extended attributes
Delete
Delete subfolders and files
Read permissions
Change permissions
Take ownership
Include inheritable permissions from this object’s parent: This option is enabled by default. The
system will automatically configure sub folders and files to inherit permissions from the object
above it. Disabling this option will reject all inheritable permissions and only keep newly added
permissions.
Replace all child object permissions with inheritable permissions from this object: Enabling this
option will replace all sub folder and file permissions with ones from the parent object.