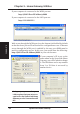
Chapter 3 - Home Gateway Utilities 3. SpaceLink Home Gateway Utilities 3. Utilities After installation, you can launch the utilities through the Start menu. Connecting to the SpaceLink Web Manager Wired Ethernet Connection Besides using a network hub, you can also connect a LAN cable from your computer’s network card to the Home Gateway using either a straight or crossover cable because the SpaceLink Home Gateway LAN and WAN RJ-45 ports have auto-crossover capability.
Chapter 3 - Home Gateway Utilities If your computer is connected to the WAN port use http://(WAN Port IP Address):8080 If your computer is connected to the LAN port use: http://192.168.123.1 3. Utilities Web access through the WAN port (over the Internet) is disabled by default so that the above private IP can be used for configuration access. If Internet access through the WAN port is enabled by the user, port 8080 must be used for configuration access.
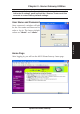
Chapter 3 - Home Gateway Utilities If you cannot find any the SpaceLink Home Gateways due to a problem in the IP settings, push and hold the “Restore” button over five seconds to restore factory default settings. User Name and Password 3. Utilities Once connected, a window will ask for the User name and Password in order to log in. The factory default values are “admin” and “admin”. Home Page After logging in, you will see the ASUS HomeGateway home page.
Chapter 3 - Home Gateway Utilities Login Password You can find “Login Password” on the Main Menu. This page will allow you to change the default password “admin” (lower case) to any password of you choice. You can enter any usable characters between 1-16 characters long (cannot be left blank). Click Modify button to save your new password. If you forget the SpaceLink Home Gateway’s password, you can reset the SpaceLink Home Gateway to its factory settings (see troubleshooting).
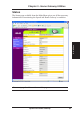
Chapter 3 - Home Gateway Utilities Status 3. Utilities The Status page available from the Main Menu gives you all the necessary information for monitoring the SpaceLink Home Gateway’s condition. See next page for information on this page.
Chapter 3 - Home Gateway Utilities Status Details Details of the Status page items are described in the configuration pages following this page. Wireless Number of Associated Stations - Tells you how many wireless mobile clients are connected to the SpaceLink Home Gateway. LAN DHCP Server - This shows either Enabled or Disabled. LAN Port Link State - Linked or Not Linked (indicates whether the cable is plugged in or not). 3.
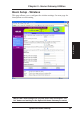
Chapter 3 - Home Gateway Utilities Basic Setup - Wireless 3. Utilities This page allows you to configure the wireless settings. See next page for descriptions on each setting. IMPORTANT: New settings will only take effect after clicking the “Finish” button and waiting for the SpaceLink Home Gateway to restart.
Chapter 3 - Home Gateway Utilities SSID & Channel The SSID is an identification string of up to 32 ASCII characters that differentiate one SpaceLink Home Gateway or Access Point from another. The SSID is also referred to as the “ESSID” or “Extended Service Set ID.” You can use the default SSID and radio channel unless more than one SpaceLink Home Gateway or Access Point is deployed in the same area.
Chapter 3 - Home Gateway Utilities Supported Clients 802.11b products can operate at 11 Mbps, 5.5 Mbps, 2 Mbps or 1 Mbps. This allows 802.11b devices to communicate with any existing 802.11 direct sequence devices that operate only at 1 or 2 Mbps. By default, the SpaceLink Home Gateway will support both 802.11b and 2 Mbps 802.11 direct sequence clients. WEP The IEEE 802.
Chapter 3 - Home Gateway Utilities makes 128 bits (104 + 24). Some vendors refer to this level of WEP as 104 bits and others refer to this as 128 bits. ASUS SpaceLink products use the term 128 bits when referring to this higher level of encryption. Magic Word & Generate Automatically generate four WEP keys. A WEP key is either 10 or 26 hexadecimal digits (0~9, a~f, and A~F) based on whether you select 64 bit or 128 bit in the WEP pull-down menu.
Chapter 3 - Home Gateway Utilities Basic Setup - LAN Configuration 3. Utilities This page does not require any settings for general use. Click the “Finish” button to save your new settings and restart the SpaceLink Home Gateway or click “Save” and restart later.
Chapter 3 - Home Gateway Utilities Basic Setup - WAN Configuration The settings that you need to perform will vary depending on the role that your SpaceLink Home Gateway will play. Network Backbone No software setting is necessary in the SpaceLink Home Gateway. Wireless SpaceLink Home Gateway 3.
Chapter 3 - Home Gateway Utilities Agent to an ISP Internet Internet Service Provider 3.
Chapter 3 - Home Gateway Utilities Agent to an ISP (Cont.) 3. Utilities Static IP Address IP Address - Normally, this is Dynamic (because fixed IP accounts cost more) and should be set to Automatic IP. Do not use “Static IP” if your ISP’s documentation does not mention an IP Address. If your ISP provided an IP Address with instructions to use it, select Static IP from “IP Addressing Method” and enter the address into the provided field.
Chapter 3 - Home Gateway Utilities Agent to an ISP (Cont.) Password - Enter the password for your Internet account. Retype your password - Re-enter the password for confirmation. DNS Settings DNS Server - Normally this is automatic and you would answer “NO” to the question about manually assigning DNS. If you are given instructions from your ISP to enter DNS addresses, select “YES” to manually assigning DNS and enter the IP addresses here.
Chapter 3 - Home Gateway Utilities Agent to Another Network Network Backbone Wireless WAN LAN SpaceLink Home Gateway 3. Utilities Wireless Client Wireless Client Wired Client To connect to an existing network, the IP address of the home gateway can be assigned manually or automatically obtained from a DHCP server. In the first case, fill in the IP address and the DNS address(es). Automatic IP This parameter determines if the SpaceLink Home Gateway will send out a DHCP request during bootup.
Chapter 3 - Home Gateway Utilities Static IP 3. Utilities The SpaceLink Home Gateway also accepts a static IP address. You may manually configure the IP address and subnet mask on the “IP Config” page. Enter an IP address and a subnet mask in the field provided to assign the SpaceLink Home Gateway a static IP address. If you don’t now your Gateway setting, leave it empty (not 0.0.0.0).
Chapter 3 - Home Gateway Utilities Firewall The SpaceLink Home Gateway does not only use basic NAT to protect your local network. The SPI (Stateful Packet Inspection) firewall filters out advanced forms of attacks from the Internet. A SPI firewall remembers the context of connections and continuously updates this information in dynamic connection tables. 3. Utilities Select the security level for the firewall that you require. “Low” should be good enough for most home users.
Chapter 3 - Home Gateway Utilities 3. Utilities Wireless Access Control (Redundant portion intentionally removed) To add security, the SpaceLink Home Gateway has the ability to only associate with or not associate with wireless mobile clients that have their MAC address entered into this page. The default setting of “Disable” will allow any wireless mobile client to connect. “Accept” will only allow those entered into this page to connect.
Chapter 3 - Home Gateway Utilities Advanced WAN Configuration 3. Utilities IP Addressing Method - This displays the current selection in the Basic Setup WAN Configuration. PPPoE Options The SpaceLink Home Gateway can automatically terminate the connection to your Internet Service Provider (ISP) when the connection is idle over a specific time. Click the “Finish” button to save your new settings and restart the SpaceLink Home Gateway or click “Save” and restart later.
Chapter 3 - Home Gateway Utilities Disconnect when idle time exceeds seconds - Enter the number of seconds of inactivity to disconnect you from your ISP. Always connected - This will always keep you connected to your ISP and reconnect if connection fails. The following two items may be specified by some ISPs. Check with your ISP and fill them in if required. Service Name - Fill this in if required by your ISP. Access Concentrator Name - Fill this in if required by your ISP.
Chapter 3 - Home Gateway Utilities Virtual Server 3. Utilities To make services, like WWW, FTP, provided by a server in your local network accessible for outside users, you should specify a local IP address to the server. Then, add the IP address and network protocol type, port number, and name of the service in the following list. Based on the list, the gateway will forward service request from outside users to the corresponding local server.
Chapter 3 - Home Gateway Utilities List of Servers Enter the IP address of the servers under the SpaceLink Home Gateway. Select a protocol, port number, and enter any description you want for the service name. Removing an Entry To remove one of the 8 entries, select the “Item” (1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8) number and click the Remove button. SpaceLink Home Gateway 3. Utilities Adding an Entry Besides entering the data manually, you can also select from a commonly used entries.
Chapter 3 - Home Gateway Utilities Special Application 3. Utilities Enable or disable specific application traffic to pass through the home gateway despite any firewall settings in the SpaceLink Home Gateway. Application Status - These commonly used applications are normally allowed to pass through the firewall. Choose Disable if you do not want users to use the following applications: ICQ, MSN, FTP, TELNET, MIRC, REALPLAYER, QUICKTIME, NETMEETING.
Chapter 3 - Home Gateway Utilities 3. Utilities Firewall Bypass Zone The medium or high security level may hinder some normal traffic from passing through the firewall. A local machine with an IP address in the following list will be only protected by the low security level despite of the firewall settings. Firewall Bypass IP Address - Enter the IP address of the computer you wish to have access through the firewall.
Chapter 3 - Home Gateway Utilities PPTP Server 3. Utilities The Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol (PPTP) is used to encrypt network data traffic. For remote users who want to access the local network through the Internet, it secures your data against eavesdroppers. For local wireless users, it provides an extra protection other than WEP. The home gateway supports up to 8 concurrent PPTP connections. To establish a connection with the home gateway, a user should use a valid account in the following list.
Chapter 3 - Home Gateway Utilities Firmware Upgrade 3. Utilities This page reports the Flash Code (Firmware) version installed in the SpaceLink Home Gateway. Periodically, a new Flash Code is available for the SpaceLink Home Gateways on ASUS’s Web site. You can update the SpaceLink Home Gateway’s Flash Code using the Firmware Upgrade page under the Advanced Setup menu of the Web Manager.
Chapter 3 - Home Gateway Utilities Restoring Factory Default Settings Web Manager You can reset all settings to their factory defaults through the web manager using the “Factory Default” page in “Advanced Setup”. Click the Restore button and wait about 30 seconds before trying to access the SpaceLink Home Gateway. Hardware You can reset all settings to their factory defaults manually by pushing the “Restore” button in a hole on the back of the SpaceLink Home Gateway while it is ON.
Chapter 3 - Home Gateway Utilities Firmware Restoration This utility will automatically search out failed SpaceLink Home Gateways and upload a firmware that you specify. The process takes about 3 to 4 minutes and during this process the PWR, AIR, and WAN LEDs will remain lit while the LAN LED will flash slowly. 3. Utilities The Firmware Restoration utility is an emergency rescue tool to restore a SpaceLink Home Gateway which has failed during a previous firmware upload.
Chapter 3 - Home Gateway Utilities Printer Setup Wizard This utility helps you setup your computers to utilize the printer server function of the SpaceLink Home Gateway. Add Printer Wizard You should add your printer to your computer to simplify the SpaceLink Home Gateway Printer Setup Wizard. If you run the “Printer Setup Wizard” without your printer driver installed, it will direct you to the “Add Printer Wizard”. 3.
Chapter 3 - Home Gateway Utilities 3. Utilities (5) Find your manufacturer and model. (6) Click Next to set this as your default Click Have Disk if you cannot find it in printer. the list and use the driver provided with your printer. (7) You can print a test page. (8) Click Finish to close the wizard. Your printer will show in the “Printers and Faxes” window and the check mark shows that it is set as your default printer.
Chapter 3 - Home Gateway Utilities Printer Setup Wizard The wizard will explore all available SpaceLink Home Gateways and model information of the printers attached to them in your local network. 3. Utilities (1) If you already have your printer installed on your printer port (LPT1), it will make this setup process much easier. See next page for instructions. Run the Printer Setup Wizard from the Windows Start menu. (2) If the printer is found, the name of the printer will be shown on this screen.
Chapter 3 - Home Gateway Utilities After setting up the printer, a printer icon will appear in Windows’ “Printers and Faxes”. Right click the printer icon and choose Properties to configure the printer. 3. Utilities Verifying Your Printer If your printer was previously setup, the SpaceLink Home Gateway printer setup wizard will change your printing port from your local LPT1 (parallel) port to “Remote Port”.
Chapter 3 - Home Gateway Utilities VPN Client A virtual private network (VPN) is the extension of a private network that encompasses links across shared or public networks like the Internet. A VPN enables you to send data between two computers across a shared or public intranet in a manner that emulates the properties of a point-to-point private link. The VPN Client utility help you to create and configure the VPN connections.
Chapter 3 - Home Gateway Utilities VPN Connection Wizard 3. Utilities The VPN Connection Wizard helps you create a new virtual private network (VPN) connection. On the main window, double-click Make New Connection from the connections list box, then the VPN Connection Wizard dialog box appears. Follow the on-screen instructions to specify settings for your connection. Enter a unique name for this new Enter the host name or IP address of the connection entry.
Chapter 3 - Home Gateway Utilities Connection Properties Select a connection name in the VPN Client window and click Edit. Connection Name Types the name you want to use for this connection entry in the Name field. The name is used to identify this connection. This name is not case-sensitive. 3. Utilities Properties Opens the standard DUN properties dialog for the currently selected connection. Let user to change or set parameters for a connection entry.
Chapter 3 - Home Gateway Utilities Advanced Properties Host name or IP address of destination Enter the host name or IP address of the remote VPN server to which you are connecting, and then click Next. Dial another connection first 3. Utilities Check this checkbox if you want the VPN connection to first make a call to an ISP. You must then select a dial-up connection from the drop-down list box.
Chapter 4 - Wireless Performance 4. Wireless Performance This section provides the user with ideas for how to improve the performance of a SpaceLink 802.11b network. Site Topography For optimal performance, locate wireless mobile clients and the SpaceLink Home Gateways away from transformers, heavy-duty motors, fluorescent lights, microwave ovens, refrigerators, and other industrial equipment. Signal loss can occur when metal, concrete, walls or floors block transmission.
Chapter 4 - Wireless Performance Range Every environment is unique with different obstacles, barriers, materials, etc. and, therefore, it is difficult to determine the exact range that will be achieved without testing. However, has developed some guidelines to estimate the range that users will see when the product is installed in their facility, but there are no hard and fast specifications. Radio signals may reflect off of some obstacles or be absorbed by others depending on their construction.
Chapter 5 -Troubleshooting 5. Troubleshooting The SpaceLink Home Gateway is designed to be very easy to install and operate. However, if you experience difficulties, use the information in this chapter to help diagnose and solve problems. If you cannot resolve a problem, contact Technical Support, as listed on the front of this manual.
Chapter 5 -Troubleshooting Problem The SpaceLink Home Gateway Web Manager still cannot find or connect to the SpaceLink Home Gateway after verifying the IP address and LAN cable, changes cannot be made, or password is lost. Solution In case the SpaceLink Home Gateway is inaccessible, you can restore the SpaceLink Home Gateway’s factory default settings.
Chapter 5 -Troubleshooting Problem My 802.11b PC Card will not associate with the SpaceLink Home Gateway. Solution Follow these steps: 1. Try to bring the devices closer together; the PC Card may be out of range of the SpaceLink Home Gateway. 2. Confirm that the SpaceLink Home Gateway and PC Card have the same SSID. 3. Confirm that the SpaceLink Home Gateway and PC Card have the same Encryption settings, if enabled. 4. Confirm that the SpaceLink Home Gateway’s Air and Link LEDs are solid green. 5.
Chapter 5 -Troubleshooting Problem I cannot find the SpaceLink Home Gateways using the SpaceLink Home Gateway Discovery. Solution To configure the SpaceLink Home Gateway through a wireless LAN card, your computer must be in the same subnet of the SpaceLink Home Gateway. You cannot find the SpaceLink Home Gateways with subnet different from your computer within the same gateway. You must change your computer to the same subnet as the SpaceLink Home Gateway.
Appendix 6. Appendix Operating frequency range The DSSS PHY shall operate in the frequency range of 2.4 GHz to 2.4835 GHz as allocated by regulatory bodies in the USA and Europe or in the 2.471 GHz to 2.497 GHz frequency band as allocated by regulatory authority in Japan. Number of operating channels The channel center frequencies and CH ID numbers shall be as shown below. The FCC (US), IC (Canada), and ETSI (Europe) specify operation from 2.4 GHz to 2.4835 GHz. For Japan, operation is specified as 2.
Appendix SpaceLink Home Gateway Specifications The following technical specification is for reference purposes only. Actual product’s performance and compliance with local telecommunications regulations may vary from country to country. ASUS will only ship products that are type approved in the destination country. WAN Ethernet Port LAN Ethernet Port Wireless Support: Both Ethernet and 802.3 with Max.
Appendix Glossary Access Point - An access point is a device that allows wireless clients to connect to other wireless clients and it acts as a bridge between wireless clients and a wired Ethernet network. Broadband - A type of data transmission in which a single medium (such as cable) carries several channels of data at once. Channel - Wireless access points allows you to choose different radio channels in the wireless spectrum. A wireless LAN device operates within the 2.
Appendix Firewall - A firewall determines which information passes in and out of a network. NAT can create a natural firewall by hiding a local network’s IP addresses from the Internet. A Firewall prevents anyone outside of your network from accessing your computer and possibly damaging or viewing your files. Gateway - A network point that manages all the data traffic of your network, as well as to the Internet and connects one network to another.
Appendix PPP (Point-to-Point Protocol) - PPP is a protocol for communication between computers using a serial interface, typically a personal computer connected by phone line to a server. PPPoE (Point-to-Point Protocol over Ethernet) - Point-to-Point Protocol is a method of secure data transmission. PPP using Ethernet to connect to an ISP. Subnet Mask - A subnet mask is a set of four numbers configured like an IP address. It is used to create IP address numbers used only within a particular network.