User`s guide
Table Of Contents
- Ascend Customer Service
- How to use this guide
- What you should know
- Documentation conventions
- How to use the on-board software
- Manual set
- Configuring WAN Connections
- Configuring IP Routing
- Introduction to IP routing on the Pipeline
- Managing the routing table
- Parameters that affect the routing table
- Static and dynamic routes
- Configuring static routes
- Specifying default routes on a per-user basis
- Enabling the Pipeline to use dynamic routing
- Route preferences
- Viewing the routing table
- Fields in the routing table
- Removing down routes to a host
- Identifying Temporary routes in the routing table
- Configuring IP routing connections
- Ascend Tunnel Management Protocol (ATMP)
- IP Address Management
- Connecting to a local IP network
- BOOTP Relay
- DHCP services
- Dial-in user DNS server assignments
- Local DNS host address table
- Network Address Translation (NAT) for a LAN
- Configuring IPX Routing
- How the Pipeline performs IPX routing
- Adding the Pipeline to the local IPX network
- Working with the RIP and SAP tables
- Configuring IPX routing connections
- Configuring the Pipeline as a Bridge
- Defining Filters and Firewalls
- Setting Up Pipeline Security
- Pipeline System Administration
- Pipeline 75 Voice Features
- IDSL Implementations
- APP Server utility
- About the APP Server utility
- APP Server installation and setup
- Configuring the Pipeline to use the APP server
- Using App Server with Axent SecureNet
- Creating banner text for the password prompt
- Installing and using the UNIX APP Server
- Installing and using the APP Server utility for DO...
- Installing and using the APP Server utility for Wi...
- Installing APP Server on a Macintosh
- Troubleshooting
- Upgrading system software
- What you need to upgrade system software
- Displaying the software load name
- The upgrade procedure
- Untitled
Configuring IP Routing
Introduction to IP routing on the Pipeline
Pipeline User’s Guide Preliminary January 30, 1998 2-5
198.5.248.40/29
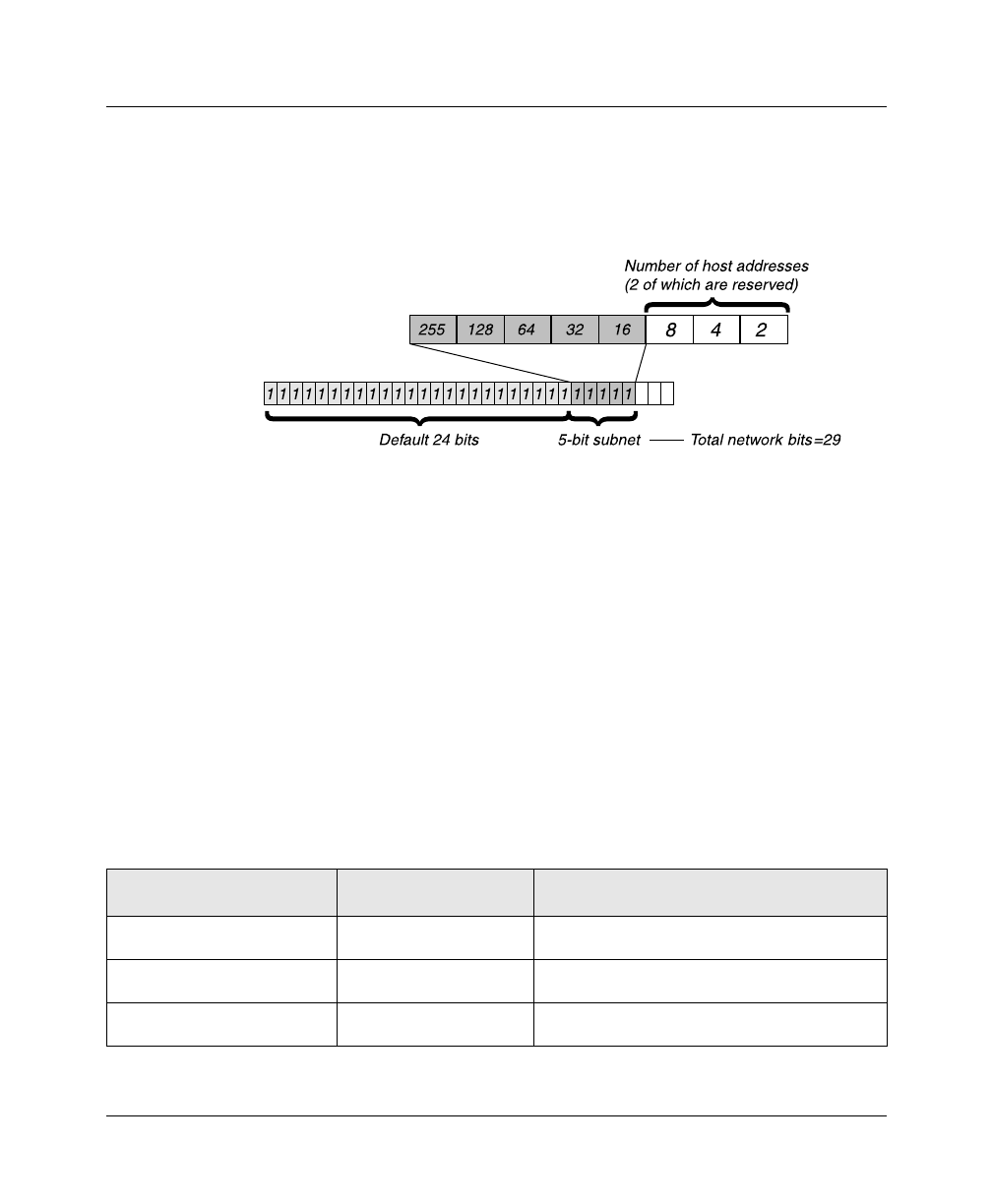
In the example address shown above, the /29 specification indicates that an
additional 5 bits of the address will be interpreted as a subnet number.
Figure 2-3. A 29-bit netmask and number of supported hosts
Eight bit-combinations are possible in 3 bits. Of those eight possible host
addresses, two are reserved:
000 — Reserved for the network base (the cable)
001
010
100
110
101
011
111 — Reserved for the broadcast address of the subnet
Table 2-2 shows how standard subnet address format relates to Ascend notation
for a class C network number.
Table 2-2. Standard netmasks and Ascend netmask notation
Netmask Ascend notation Number of host addresses
255.255.255.0 /24 254 hosts + 1 broadcast, 1 network base
255.255.255.128 /25 126 hosts + 1 broadcast, 1 network base
255.255.255.192 /26 62 hosts + 1 broadcast, 1 network base










