Guide
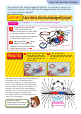
Whenthecommutation
brushtouchesthemetallic
partofthecommutator,
theelectriccurrentflows
onthearmature.Whenthe
electriccurrentflows,the
armaturebecomesan
electromagnet.TheN-pole
andS-poleofthe
electromagnetare
attractedbytheS-pole
andN-poleofthemagnets
thatareplacedoneither
sideofthearmature,soit
startstorotate.
1
2
Afterrotatingthe
armaturebyattractingthe
N-poleandS-poletoeach
other,thecommutation
brushandmetallicpartof
thecommutatorseparate.
Becauseofthis
separation,theelectric
currentcannotflowonthe
armature.Thiscausesthe
armaturetolosetheforce
oftheelectromagnet.
Ifyoulookclosely,the
commutatorhasametallic
partandanon-metallicpart.
Metallicpart
non-metallicpart.
MagnetMagnet
N
S
S
N
S
Metallicpartstouch
eachother
Metallicpartsdonot
toucheachother
Magnet
Magnet
Usingtherotationofamotor,
youcanoperateelectrical
appliancesorrotatethewheels
ofanelectriccar.
Becauseofthelossofthe
magneticforceofthe
electromagnet,thearmature
andthemagnetarenot
attractedtoeachother.
Howeverthearmaturekeeps
rotatingusingtheextra
rotationalforcethatitgained.
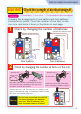
Thearmaturerotatesusingthe
extrarotationalforce,andthe
commutationbrushtouchesthe
metallicpartofcommutator
again.Atthistime,theelectric
currentflowsoppositetothe
directionitflowedinsetup.
Thentheelectromagnet's
N-poleandS-polesare
switched.Byrepulsingthe
samepoles(N-poleandN-pole,
andS-poleandS-pole)the
armaturegainsforceandkeeps
rotating.
Byrepeating
stepsto,
themotorkeeps
rotating.
3
4
1
1
4
Therearemotors
invacuum
cleanersand
fans,aren't
there?
Magnet
Magnet
N
S
N S
Magnet
Magnet
S
S
14
Mechanism of the motor