9H Science series Electricity 196455 nciples of Pri Study Guide ★Batteries sold separately. Electric Current CHOKING HAZARD - Small parts. Not for children under 3 yrs.
Two cycles for turning a child into a science lover Planning Focusing Action Analysis Thinking Inquisitive learning approach Experiential learning approach Improvement Aspiration Accomplishment Inquisitive learning approach nurtures the abilities of... Experiential learning approach nurtures the abilities of...
Check the contents. ◆ Contents ◆ ① ① Battery holder × 1 ② ② Motor case × 1 ③ 200-turn coil × 1 ③ ④ Bobbin × 1 ⑤ ④ ⑤ Plastic core × 1 ⑥ ⑥ Compass × 1 ⑦ ⑦ Enameled wire × 1 ⑧ Coated wire × 1 ⑨ Armature × 1 ⑩ Shaft retainer × 1 ⑨ ⑩ ⑧ ⑪ ⑫ ⑬ ⑭ ⑪ Connecting plug × 4 ⑫ Sandpaper × 1 What if the N-pole needle does not point north? S S S S 西 N N S 西 南W 東 E S 南 Warning 北 北西 NW N 東 北E ○ Battery (1.
What is an Electromagnet? What is an Electromagnet ? A magnet will always remain a magnet. But in the case of an electromagnet, it only becomes a magnet when current flows through it. Let's make it! Assembly Assemble the electromagnet (100-turn coil). What you need from the kit: ① Battery holder ④ Bobbin ⑤ Plastic core ⑦ Enameled wire ⑪ Connecting plug ⑫ Sandpaper What you need from home: ● Battery (1.5V D/R20) × 1 ● Tape 1 Sandpaper Buff the wire until the color changes.
What is an Electromagnet? 5 After the wire has been wound, wind it around the stopper twice, then the coil is finished. 6 Tie up the extra enameled wire with tape. 100-turn coil Battery holder Connection plug Insert all the way How to attach the connecting plugs to the enameled wires 4cm Slot 1. Thread the wire end 2.Wind it around through the hole to about 4 cm and fold it back. Insert all the way the plug several times. Attach a connecting plug to the free end of the enameled wire.
What is an Electromagnet? Results 1 When the coil is carrying an electric current, it attracts iron like a magnet. When the coil is not carrying an electric current, nothing happens.
Check the pole of electromagnet We learned the electromagnet attracts iron when it carries an electrical current. Does the electromagnet have an S-pole and an N-pole like a magnet? Experiment What you need from the kit: Let's check the electromagnet's poles! ⑥ Compass ○ The assembled electromagnet 1 Insert the iron core into the 100-turn coil. Move the compass toward the iron core which is carrying an electric current, then check whether the electromagnet has an S-pole and N-pole or not.
Check the strength of an electromagnet Make the electromagnet stronger! Unlike bar magnets, electromagnets can change the strength of their magnetic force. How can the strength be changed? There are two ways to change it, as shown below in 1 and 2 .
Check the strength of an electromagnet Experiment Check the strength of an electromagnet! ⑫ Sandpaper ⑬ Iron core ○ The assembled electromagnet What you need from the kit: Compare the arrangement of one battery and two batteries (connected in series). Count the number of iron bars on the iron core, and write it down in the table on next page.
Check the strength of an electromagnet Results Write down the number of iron bars on the iron core in the table below for each case of one and two batteries. Experiment Number of batteries 1 One battery 2 Two batteries Number of iron bars on the iron core Bars Bars Write down the number of iron bars on the iron core in the table below for each case of one and two batteries.
Check the strength of an electromagnet The strength of the electromagnet when you change the number of batteries ■ One battery(100-turn coil) ■ Two batteries(100-turn coil) Weak Strength of the electromagnet Strong Do The strength of the electromagnet in relation to the number of coil turns ■ 100-turn coil (one battery ) ■ 200-turn coil (one battery ) Weak Strength of the electromagnet Strong 10
Make a motor! We can see that there are lots of electric appliances that use electromagnets. Almost all of them are built with a motor in the appliance which uses the force of an electromagnet.
Mechanism of the motor When the motor does not start to rotate ● Check the connections of the wires → See page 11 and recheck how to make a motor. ● Check the battery level → If it is low, change to a new battery. ● Is there an iron core in the coil? → Check that the coil has an iron core in it. ● Check that the enamel of the enameled wire is stripped off → Buff the enameled wire with sandpaper again. ● Turn the starting knob easily with your fingers→ See page 11 and check section 3 .
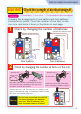
Mechanism of the motor If you look closely, the commutator has a metallic part and a non-metallic part. Metallic part non-metallic part. 1 2 13 When the commutation brush touches the metallic part of the commutator, the electric current flows on the armature. When the electric current flows, the armature becomes an electromagnet. The N-pole and S-pole of the electromagnet are attracted by the S-pole and N-pole of the magnets that are placed on either side of the armature, so it starts to rotate.
Mechanism of the motor 3 4 Because of the loss of the magnetic force of the electromagnet, the armature and the magnet are not attracted to each other. However the armature keeps rotating using the extra rotational force that it gained. The armature rotates using the extra rotational force, and the commutation brush touches the metallic part of commutator again. At this time, the electric current flows opposite to the direction it flowed in setup 1 .
Using electricity and magnetism Electricity and magnetism at work for the future of our world. Recently, vehicles have been developed that run on electricity and use magnetism. There are coils in locomotives and some train bodies have magnets magnets. By sending an electric current to them them, we can switch the N-pole and S-pole of the electromagnet. Then a train can move by the forces of attraction and repulsion. Pictures of a linear motor car engine.