Specifications
Comparison of liquid temperature control methods
31
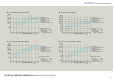
The inverter control is Kanto Seiki’s unique control method (patented) that uses a
combination of “variable frequency control” of inverter chiller, “refrigerant flow control” of
pulse expansion valve, and “cooling capacity switching control” by gas bypass expansion
valve. This method controls liquid temperature with high precision by linearly changing
the cooling capacity according to the amount of heat generated by a machine to match
the heat load even if the load fluctuates from low load to maximum load. With this
method, a wide range of cooling capacity adjustment, etc., which was impossible with
conventional inverter control, has become possible.
Series
C, V, MR and W
Microcomputer inverter control
Return oil temperature control (accuracy: ±0.1-0.2°C)
Without steady-state deviation of oil temperature
<Patent pending> Data example of controlled oil temperature <reference
temperature 25°C>
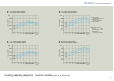
The gas bypass PID control is a non-inverter (patent pending) control method that
controls liquid temperature with high precision within a wide range from low load to the
maximum load by “variably controlling the cooling capacity with the bypass flow control of
refrigerant hot gas” with use of a gas bypass pulse valve and linearly changing the
cooling capacity according to the amount of heat generated by a machine to match the
heat load.
Series
CL
Gas bypass PID control
Return oil temperature control (accuracy: ±0.1-0.2°C)
Without steady-state deviation of oil temperature
<Patent pending> Data example of controlled oil temperature <reference
temperature 25°C>
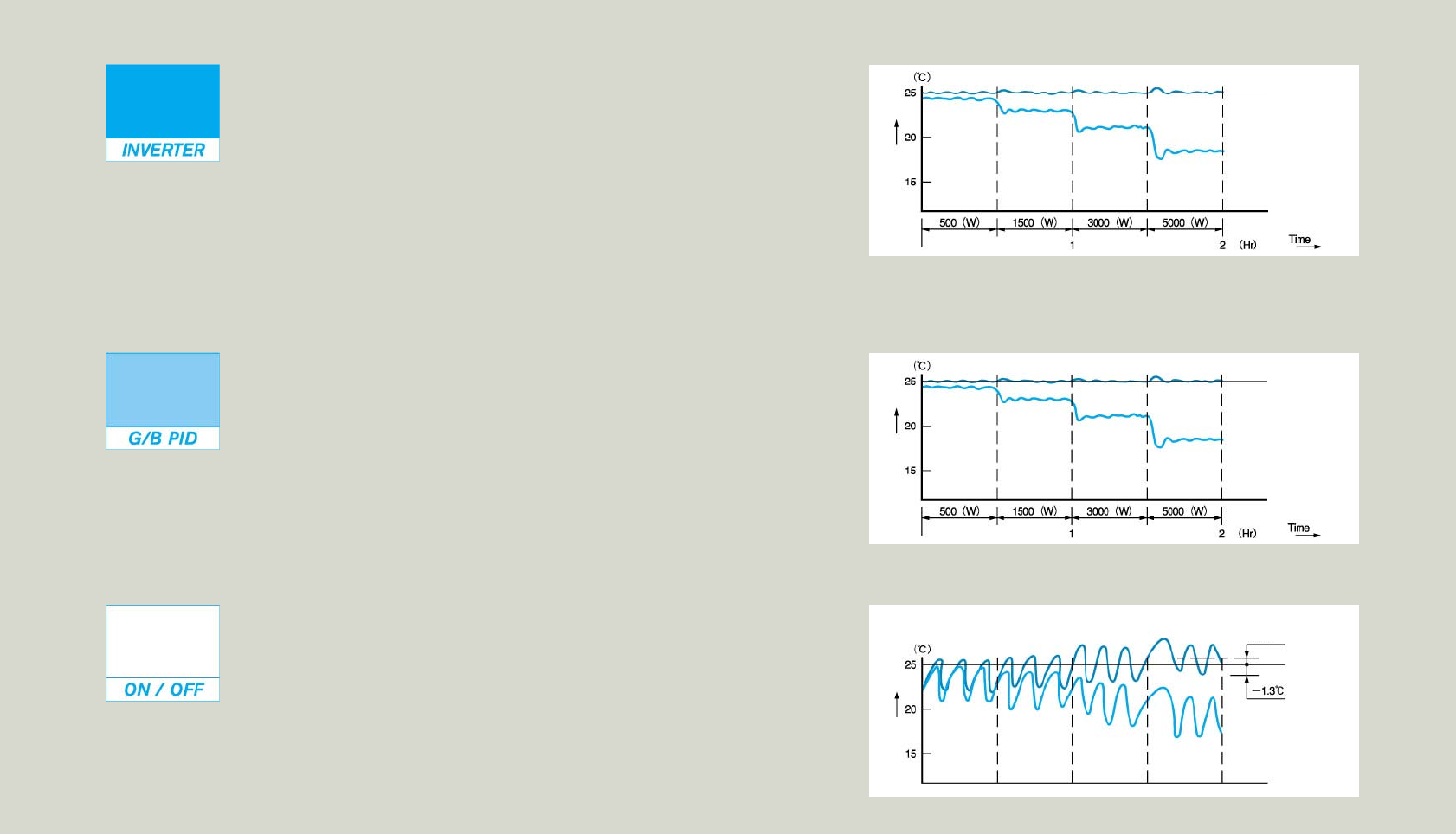
The chiller ON-OFF (2-position) control is a method of controlling temperature by turning
on or off a chiller according to the temperature deviation between the temperature
detected by a liquid temperature sensor and the preset temperature. This method is often
used since the control method and components are simple.
Series
ML, KTV and KTC
Chiller ON-OFF control
Return oil temperature control (accuracy: ±1.5-2°C)
With steady-state deviation of oil temperature
Data example of controlled oil temperature <reference temperature 25°C>
Inverter
control
method
Sending oil
temperature
Constant deviation
0.5°C
Return oil
temperature
( With feed-forward control)
Amount of heat generation
( With feed-forward control)
Amount of heat generation
ON
-
OFF
control
method
Gas bypass
PID control
method