User's Manual
Table Of Contents
- GENERAL MANUAL INFORMATION
- PREPARATION FOR STORAGE OR SHIPMENT
- DESCRIPTION OF EQUIPMENT
- LOCATIONS AND DESCRIPTIONS OF MAJOR COMPONENTS
- EQUIPMENT CHARACTERISTICS
- INSTALLING THE RADIO EQUIPMENT
- INTERCONNECTIONS
- CABLE AND GROUND REQUIREMENTS
- COMPONENT JACK LOCATIONS
- INITIAL PREPARATION FOR USE
- RADIO APPLICATION CODE UPGRADE
- PN SPREADING CODE SELECTION
- ANTENNA AND CABLE INSTALLATION
- CONTROLS AND INDICATORS
- STARTUP AND SHUTDOWN PRODECURES
- OUTPUT POWER SETTINGS
- ANTENNA PLACEMENT
- FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION OF EQUIPMENT
- PREVENTIVE MAINTENANCE, INSPECTION, AND CLEANING
- TROUBLESHOOTING
- CORRECTIVE MAINTENANCE
- TEST PROCEDURES
- MDR TESTS
- BDR TESTS
- RADIO DATA PORT TO USER SUPPLIED EQUIPMENT INTERFACE
- PARTS LIST
- BASE DATA RADIO MECHANICAL OUTLINE
- DIAGNOSTIC MENU
- MDR DIAGNOSTIC LCP MENU
- LCP COMMANDS
385700-1006-006 OPERATIONS
Document use is restricted to that described on cover 4-2
4.1.2 RADIO NETWORK ARCHITECTURE
The typical communication flow consists of wayside equipment (user control equipment and
BDRs) communicating with mobile equipment (user control equipment and MDRs). Wayside
to mobile communication can be distributed over a single or a number of radio networks. Each
control region is considered as a single radio network. The regional control equipment uses a
simple roll-call polling technique to communicate with all the vehicles in the region during a
communication cycle. When a train approaches a region boundary it is handed over to the
next region's radio network by using a software hand-off algorithm.
4.1.2.1 RF TRANSMISSIONS
Full duplex operation is achieved by utilizing separate frequency ranges within the 2400 -
2483.5 MHz band for each direction of communications. Data is transmitted from base radio to
mobile using one range and from mobile to base radio over another frequency range. Refer
to Table 1-2 Mobile Data Radio Assembly Specifications and Table 1-3 Base Station Radio
Assembly Specifications.
4.1.2.2 BASEBAND DATA RATE
The radio network operates at a synchronous baud rate of 64Kbps.
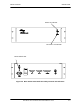
4.1.2.3 OSI LAYERS
The radio network is developed following the ISO (International Standard Organization) Open
Systems Interconnection (OSI) Reference Model. The radio network is modular in design.
Industry standard protocol, interfaces and hardware are used to easily interface third party
equipment.
Figure 4-1 Radio Network OSI Layers