Technical information
RMS Resource Management Suite
9
RMS - Administrator’s Guide
Parameter Values
Each parameter has a set of values used to determine what conditions indicate a problem and what type of
problem this condition represents. These values are supplied when the parameter is registered, and consist of
the following:
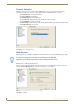
Parameter Values
• Name This is the name of parameter. This name is displayed on the RMS application con-
sole and readily identifies the parameter. Parameters are tracked by name so this
name must be unique within the parameters of a given device.
For instance, you can have multiple "Lamp Hours" parameters as long as there is
only one "Lamp Hours" parameter per monitored device.
• Parameter Type This indicates if the value is a number or a string. This information is used to
determine how to perform certain operation, such as addition and comparisons
between the new and threshold values.
For instance, comparing "10" and "2" as strings results in "10" less than "2" but
comparing them as numbers results in "2" less than "10".
• Value and Units This is the current value of the parameter. Units are appended to the value when
displayed in the web console.
• Threshold Value and
Comparison Operator
The threshold value is the value for which this parameter is considered to indicate a
problem or fault. The comparison operator is used to detect when the value changes
from the un-faulted to the faulted condition.
• The comparison operators "Less Than", "Less Than or Equal To", "Greater Than",
"Greater Than or Equal To", "Equal To", and "Not Equal To" can be used for string
and number parameters.
• The comparison operators "Contains" and "Does Not Contain" are primarily used
for string parameters.
For example, "Lamp Hours" might have a threshold value of 1000 and any value over
this would require maintenance. The comparison operator would then be "Greater
Than".
• When this parameter changes from a value that is not greater than 1000 to a value
that is greater than 1000, the fault status is set.
• When the value changes from a value greater than 1000 to a value not greater than
1000, the fault status is cleared.
These values are supplied during registration, but can be modified by the
administrator from the RMS application console.
• Status Type The status represents the type of problem a faulted condition represents. Status
Types include "Help Request", "Maintenance Request", "Room Communication
Error", "Control System Error", "Network Error", "Security", and "Equipment Usage."
For example, when "Lamp Hours" changes from an un-faulted (not greater than
1000) to a faulted (greater than 1000), this change represents a "Maintenance
Request" status that requires an AV technician to repair the equipment. If the "Device
Online" parameter changes from "Online" to "Offline", this change could represent a
"Security" or "Control System Error" status.
These values are supplied during registration, but can be modified by the
administrator from the RMS application console.
• Reset Flag and
Reset Value
These values determine if and how the parameter can be reset from the RMS
application console.
If the Reset Flag is set, then the administrator can reset the value remotely. When
the administrator selects "Reset" from the console, the Reset Value is copied to the
Value and the faulted condition is cleared.
These values are useful for parameters such as VCR "Run Time" which would be
manually reset when the VCR is cleaned.
• Minimum and
Maximum Values
These values are used to restrict the range of the threshold and reset values that the
administrator can enter on the RMS application console.
These values would be used when the parameter represents a value with a bounded
range, such as a Volume Level.