User guide
Table Of Contents
- Cyclone V Hard IP for PCI Express User Guide
- Contents
- 1. Datasheet
- 2. Getting Started with the Cyclone V Hard IP for PCI Express
- 3. Getting Started with the Avalon-MM Cyclone Hard IP for PCI Express
- Running Qsys
- Customizing the Cyclone VHard IP for PCI Express IP Core
- Adding the Remaining Components to the Qsys System
- Completing the Connections in Qsys
- Specifying Clocks and Interrupts
- Specifying Exported Interfaces
- Specifying Address Assignments
- Simulating the Example Design
- Simulating the Single DWord Design
- Understanding Channel Placement Guidelines
- Adding Synopsis Design Constraints
- Creating a Quartus II Project
- Compiling the Design
- Programming a Device
- 4. Parameter Settings for the Cyclone V Hard IP for PCI Express
- 5. Parameter Settings for the Avalon-MM Cyclone V Hard IP for PCI Express
- 6. IP Core Architecture
- Key Interfaces
- Protocol Layers
- Multi-Function Support
- PCI Express Avalon-MM Bridge
- Avalon-MM Bridge TLPs
- Avalon-MM-to-PCI Express Write Requests
- Avalon-MM-to-PCI Express Upstream Read Requests
- PCI Express-to-Avalon-MM Read Completions
- PCI Express-to-Avalon-MM Downstream Write Requests
- PCI Express-to-Avalon-MM Downstream Read Requests
- Avalon-MM-to-PCI Express Read Completions
- PCI Express-to-Avalon-MM Address Translation for Endpoints
- Minimizing BAR Sizes and the PCIe Address Space
- Avalon-MM-to-PCI Express Address Translation Algorithm
- Single DWord Completer Endpoint
- 7. IP Core Interfaces
- Cyclone V Hard IP for PCI Express
- Avalon-MM Hard IP for PCI Express
- Physical Layer Interface Signals
- Test Signals
- 8. Register Descriptions
- Configuration Space Register Content
- Altera-Defined Vendor Specific Extended Capability (VSEC)
- PCI Express Avalon-MM Bridge Control Register Access Content
- Avalon-MM to PCI Express Interrupt Registers
- PCI Express Mailbox Registers
- Avalon-MM-to-PCI Express Address Translation Table
- Root Port TLP Data Registers
- Programming Model for Avalon-MM Root Port
- PCI Express to Avalon-MM Interrupt Status and Enable Registers for Root Ports
- PCI Express to Avalon-MM Interrupt Status and Enable Registers for Endpoints
- Avalon-MM Mailbox Registers
- Correspondence between Configuration Space Registers and the PCIe Spec 2.1
- 9. Reset and Clocks
- 10. Transaction Layer Protocol (TLP) Details
- 11. Interrupts
- Interrupts for Endpoints Using the Avalon-ST Application Interface
- Interrupts for Root Ports Using the Avalon-ST Interface to the Application Layer
- Interrupts for Endpoints Using the Avalon-MM Interface to the Application Layer
- Interrupts for End Points Using the Avalon-MM Interface with Multiple MSI/MSI-X Support
- 12. Optional Features
- 13. Flow Control
- 14. Error Handling
- 15. Transceiver PHY IP Reconfiguration
- 16. SDC Timing Constraints
- 17. Testbench and Design Example
- Endpoint Testbench
- Root Port Testbench
- Chaining DMA Design Examples
- Test Driver Module
- Root Port Design Example
- Root Port BFM
- BFM Procedures and Functions
- 18. Debugging
- A. Transaction Layer Packet (TLP) Header Formats
- Additional Information
7–44 Chapter 7: IP Core Interfaces
Avalon-MM Hard IP for PCI Express
Cyclone V Hard IP for PCI Express December 2013 Altera Corporation
User Guide
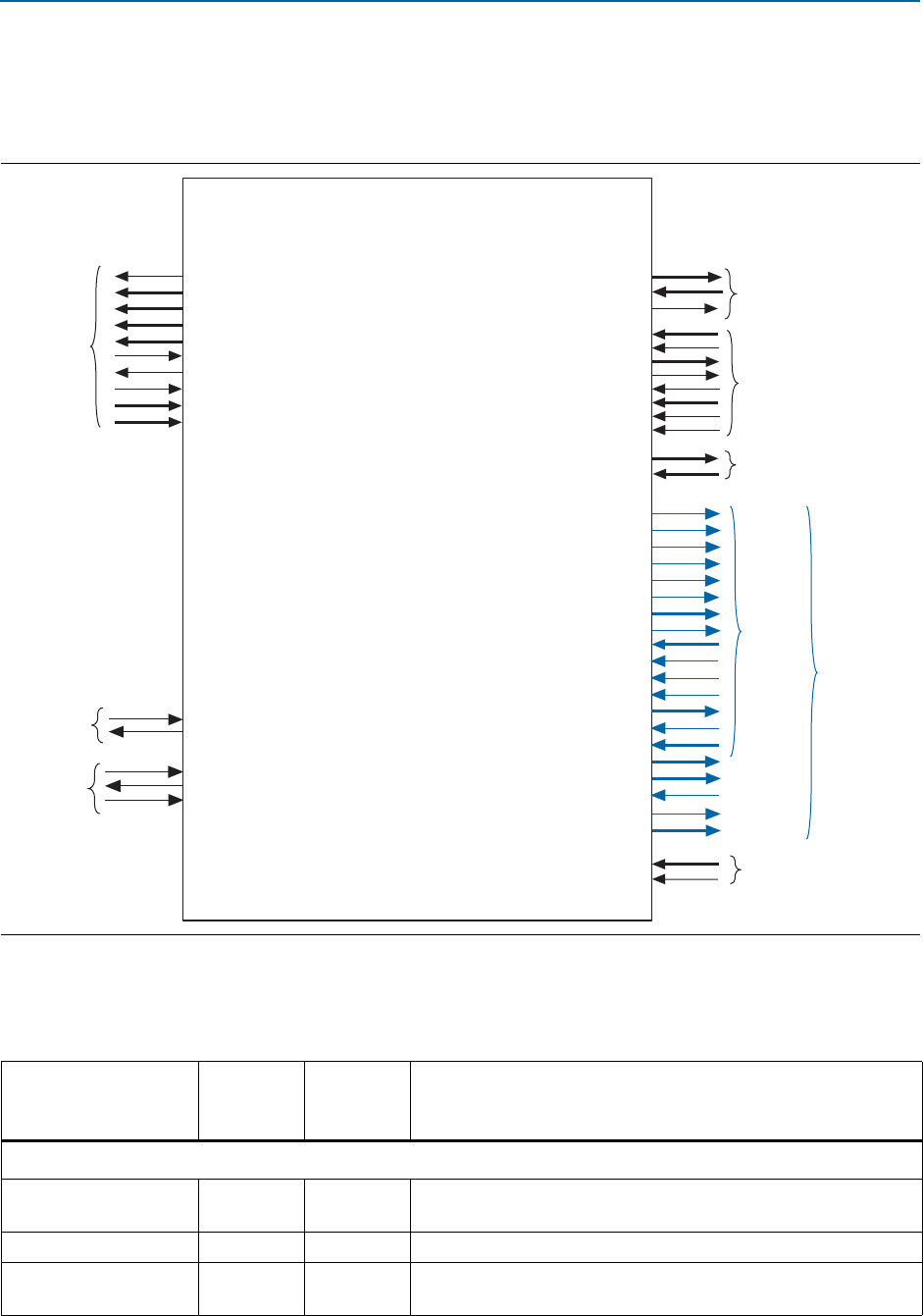
Figure 7–36 illustrates the signals of a completer-only Cyclone V Hard IP for PCI
Express using the Avalon-MM interface available in the Qsys design flow. This
Endpoint can only accept requests from up-stream devices.
Table 7–19 lists the interfaces for these IP cores with links to the sections that describe
them.
Figure 7–36. Signals in the Qsys Avalon-MM Completer-Only Cyclone V Hard IP for PCI Express
tx_out0[
<n>
:0]
rx_in0[
<n>
:0]
1-Bit Serial
Hard IP for PCI Express IP Core
Completer-Only Single DWord
Test
Interface
test_in[31:0]
simu_mode_pipe
RxmWrite_<n>_o
RxmAddress_<n>_o[3
1
:0]
RxmWriteData_<n>_o[<w>
-1
:0]
RxmByteEnable_<n>_o[<w>-1/8:0]
RxmBurstCount_<n>_o[6 or 5:0]
RxmWaitRequest_<n>_o
RxmRead_<n>_o
RxmReadData_<n>[<w>
-1:
0]_i
RxmReadDataValid_<n>_i
RxmIrq[<m>:0]_i, <m> < 16
64-Bit
Avalon-MM TX
Master Port
reconfig_fromxcvr[<n>69-1:0]
reconfig_toxcvr[<n>45-1:0]
busy_xcvr_reconfig
recong_mgmt_address[6:0]
recong_mgmt_read
recong_mgmt_readdata[31:0]
recong_mgmt_waitrequest
recong_mgmt_write
recong_mgmt_writedata[31:0]
mgmt_rst_reset
mgmt_clk_clk
Transceiver
Reconfiguration
Reconfiguration
Management
Interface
txdatak0
txdata0[7:0]
txdetectrx0
txelectidle0
rxpolarity0
txcompl0
powerdown0[1:0]
tx_deemph0
rxdatak0
rxdata0[7:0]
rxvalid0
phystatus0
eidleinfersel0[2:0]
rxelectidle0
rxstatus0[2:0]
sim_ltssmstate[4:0]
sim_pipe_rate0[1:0]
sim_pipe_pclk_in
txswing0
txmargin0[2:0]
PIPE Interface
Simulation Only
8-Bit PIPE
Clocks
npor
nreset_status
pin_perstn
Reset &
Lock Status
refclk
coreclkout_hip
Table 7–19. Signal Groups in the Avalon-MM Cyclone V Hard IP for PCI Express Variants (Part 1 of 2)
Signal Group
Full
Featured
Completer
Only Single
DWord
Description
Logical
Avalon-MM CRA Slave v —
“32-Bit Non-Bursting Avalon-MM Control Register Access (CRA)
Slave Signals” on page 7–45
Avalon-MM RX Master vv“RX Avalon-MM Master Signals” on page 7–46
Avalon-MM TX Slave v —
“64- or 128-Bit Bursting TX Avalon-MM Slave Signals” on
page 7–46










