User guide
Table Of Contents
- Cyclone V Hard IP for PCI Express User Guide
- Contents
- 1. Datasheet
- 2. Getting Started with the Cyclone V Hard IP for PCI Express
- 3. Getting Started with the Avalon-MM Cyclone Hard IP for PCI Express
- Running Qsys
- Customizing the Cyclone VHard IP for PCI Express IP Core
- Adding the Remaining Components to the Qsys System
- Completing the Connections in Qsys
- Specifying Clocks and Interrupts
- Specifying Exported Interfaces
- Specifying Address Assignments
- Simulating the Example Design
- Simulating the Single DWord Design
- Understanding Channel Placement Guidelines
- Adding Synopsis Design Constraints
- Creating a Quartus II Project
- Compiling the Design
- Programming a Device
- 4. Parameter Settings for the Cyclone V Hard IP for PCI Express
- 5. Parameter Settings for the Avalon-MM Cyclone V Hard IP for PCI Express
- 6. IP Core Architecture
- Key Interfaces
- Protocol Layers
- Multi-Function Support
- PCI Express Avalon-MM Bridge
- Avalon-MM Bridge TLPs
- Avalon-MM-to-PCI Express Write Requests
- Avalon-MM-to-PCI Express Upstream Read Requests
- PCI Express-to-Avalon-MM Read Completions
- PCI Express-to-Avalon-MM Downstream Write Requests
- PCI Express-to-Avalon-MM Downstream Read Requests
- Avalon-MM-to-PCI Express Read Completions
- PCI Express-to-Avalon-MM Address Translation for Endpoints
- Minimizing BAR Sizes and the PCIe Address Space
- Avalon-MM-to-PCI Express Address Translation Algorithm
- Single DWord Completer Endpoint
- 7. IP Core Interfaces
- Cyclone V Hard IP for PCI Express
- Avalon-MM Hard IP for PCI Express
- Physical Layer Interface Signals
- Test Signals
- 8. Register Descriptions
- Configuration Space Register Content
- Altera-Defined Vendor Specific Extended Capability (VSEC)
- PCI Express Avalon-MM Bridge Control Register Access Content
- Avalon-MM to PCI Express Interrupt Registers
- PCI Express Mailbox Registers
- Avalon-MM-to-PCI Express Address Translation Table
- Root Port TLP Data Registers
- Programming Model for Avalon-MM Root Port
- PCI Express to Avalon-MM Interrupt Status and Enable Registers for Root Ports
- PCI Express to Avalon-MM Interrupt Status and Enable Registers for Endpoints
- Avalon-MM Mailbox Registers
- Correspondence between Configuration Space Registers and the PCIe Spec 2.1
- 9. Reset and Clocks
- 10. Transaction Layer Protocol (TLP) Details
- 11. Interrupts
- Interrupts for Endpoints Using the Avalon-ST Application Interface
- Interrupts for Root Ports Using the Avalon-ST Interface to the Application Layer
- Interrupts for Endpoints Using the Avalon-MM Interface to the Application Layer
- Interrupts for End Points Using the Avalon-MM Interface with Multiple MSI/MSI-X Support
- 12. Optional Features
- 13. Flow Control
- 14. Error Handling
- 15. Transceiver PHY IP Reconfiguration
- 16. SDC Timing Constraints
- 17. Testbench and Design Example
- Endpoint Testbench
- Root Port Testbench
- Chaining DMA Design Examples
- Test Driver Module
- Root Port Design Example
- Root Port BFM
- BFM Procedures and Functions
- 18. Debugging
- A. Transaction Layer Packet (TLP) Header Formats
- Additional Information
1–6 Chapter 1: Datasheet
IP Core Verification
Cyclone V Hard IP for PCI Express December 2013 Altera Corporation
User Guide
IP Core Verification
To ensure compliance with the PCI Express specification, Altera performs extensive
validation of the Cyclone V Hard IP Core for PCI Express.
The simulation environment uses multiple testbenches that consist of
industry-standard BFMs driving the PCI Express link interface. A custom BFM
connects to the application-side interface.
Altera performs the following tests in the simulation environment:
■ Directed and pseudo random stimuli areCyclone V applied to test the Application
Layer interface, Configuration Space, and all types and sizes of TLPs.
■ Error injection tests that inject errors in the link, TLPs, and Data Link Layer
Packets (DLLPs), and check for the proper responses
■ PCI-SIG
®
Compliance Checklist tests that specifically test the items in the checklist
■ Random tests that test a wide range of traffic patterns
Performance and Resource Utilization
Because the Cyclone V Hard IP for PCI Express IP core is implemented in hardened
logic, it uses less than 1% of Cyclone V resources. The Avalon-MM Cyclone V Hard IP
for PCI Express includes a bridge implemented in soft logic. Table 1–5 shows the
typical expected device resource utilization for selected configurations of the
Avalon-MM Cyclone V Hard IP for PCI Express using the current version of the
Quartus II software targeting a Cyclone V (5CGXFC7D6F31C7) device. With the
exception of M10K memory blocks, the numbers of ALMs and logic registers in
Table 1–5 are rounded up to the nearest 100. Resource utilization numbers reflect
changes to the resource utilization reporting starting in the Quartus II software v12.1
release 28 nm device families and upcoming device families.
f For information about Quartus II resource utilization reporting, refer to Fitter
Resources Reports in the Quartus II Help.
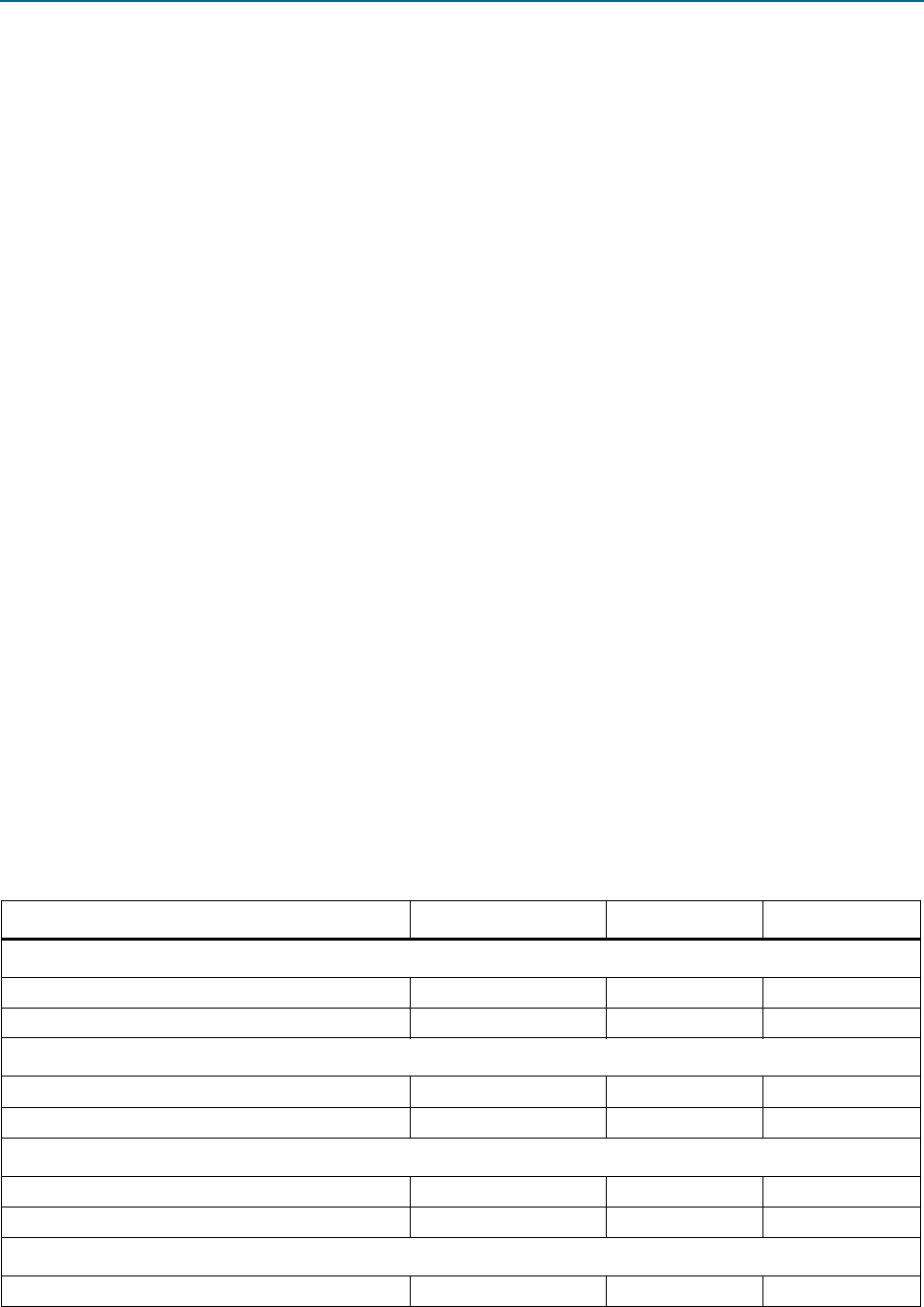
Table 1–4. Performance and Resource Utilization
ALMs Memory M10K Logic Registers
Avalon-MM Bridge
Gen1 ×4 1250 27 1700
Gen2 ×8 2100 35 3050
Avalon-MM Interface–Burst Capable Requester/Single DWord Completer
64 1150 23 1700
128 1600 29 2550
Avalon-MM Interface-Burst Capable Completer Only
64 600 11 900
128 1350 22 2300
Avalon-MM Interface–Completer Only
64 160 0 230










