User guide
Table Of Contents
- Cyclone V Hard IP for PCI Express User Guide
- Contents
- 1. Datasheet
- 2. Getting Started with the Cyclone V Hard IP for PCI Express
- 3. Getting Started with the Avalon-MM Cyclone Hard IP for PCI Express
- Running Qsys
- Customizing the Cyclone VHard IP for PCI Express IP Core
- Adding the Remaining Components to the Qsys System
- Completing the Connections in Qsys
- Specifying Clocks and Interrupts
- Specifying Exported Interfaces
- Specifying Address Assignments
- Simulating the Example Design
- Simulating the Single DWord Design
- Understanding Channel Placement Guidelines
- Adding Synopsis Design Constraints
- Creating a Quartus II Project
- Compiling the Design
- Programming a Device
- 4. Parameter Settings for the Cyclone V Hard IP for PCI Express
- 5. Parameter Settings for the Avalon-MM Cyclone V Hard IP for PCI Express
- 6. IP Core Architecture
- Key Interfaces
- Protocol Layers
- Multi-Function Support
- PCI Express Avalon-MM Bridge
- Avalon-MM Bridge TLPs
- Avalon-MM-to-PCI Express Write Requests
- Avalon-MM-to-PCI Express Upstream Read Requests
- PCI Express-to-Avalon-MM Read Completions
- PCI Express-to-Avalon-MM Downstream Write Requests
- PCI Express-to-Avalon-MM Downstream Read Requests
- Avalon-MM-to-PCI Express Read Completions
- PCI Express-to-Avalon-MM Address Translation for Endpoints
- Minimizing BAR Sizes and the PCIe Address Space
- Avalon-MM-to-PCI Express Address Translation Algorithm
- Single DWord Completer Endpoint
- 7. IP Core Interfaces
- Cyclone V Hard IP for PCI Express
- Avalon-MM Hard IP for PCI Express
- Physical Layer Interface Signals
- Test Signals
- 8. Register Descriptions
- Configuration Space Register Content
- Altera-Defined Vendor Specific Extended Capability (VSEC)
- PCI Express Avalon-MM Bridge Control Register Access Content
- Avalon-MM to PCI Express Interrupt Registers
- PCI Express Mailbox Registers
- Avalon-MM-to-PCI Express Address Translation Table
- Root Port TLP Data Registers
- Programming Model for Avalon-MM Root Port
- PCI Express to Avalon-MM Interrupt Status and Enable Registers for Root Ports
- PCI Express to Avalon-MM Interrupt Status and Enable Registers for Endpoints
- Avalon-MM Mailbox Registers
- Correspondence between Configuration Space Registers and the PCIe Spec 2.1
- 9. Reset and Clocks
- 10. Transaction Layer Protocol (TLP) Details
- 11. Interrupts
- Interrupts for Endpoints Using the Avalon-ST Application Interface
- Interrupts for Root Ports Using the Avalon-ST Interface to the Application Layer
- Interrupts for Endpoints Using the Avalon-MM Interface to the Application Layer
- Interrupts for End Points Using the Avalon-MM Interface with Multiple MSI/MSI-X Support
- 12. Optional Features
- 13. Flow Control
- 14. Error Handling
- 15. Transceiver PHY IP Reconfiguration
- 16. SDC Timing Constraints
- 17. Testbench and Design Example
- Endpoint Testbench
- Root Port Testbench
- Chaining DMA Design Examples
- Test Driver Module
- Root Port Design Example
- Root Port BFM
- BFM Procedures and Functions
- 18. Debugging
- A. Transaction Layer Packet (TLP) Header Formats
- Additional Information
Chapter 7: IP Core Interfaces 7–27
Cyclone V Hard IP for PCI Express
December 2013 Altera Corporation Cyclone V Hard IP for PCI Express
User Guide
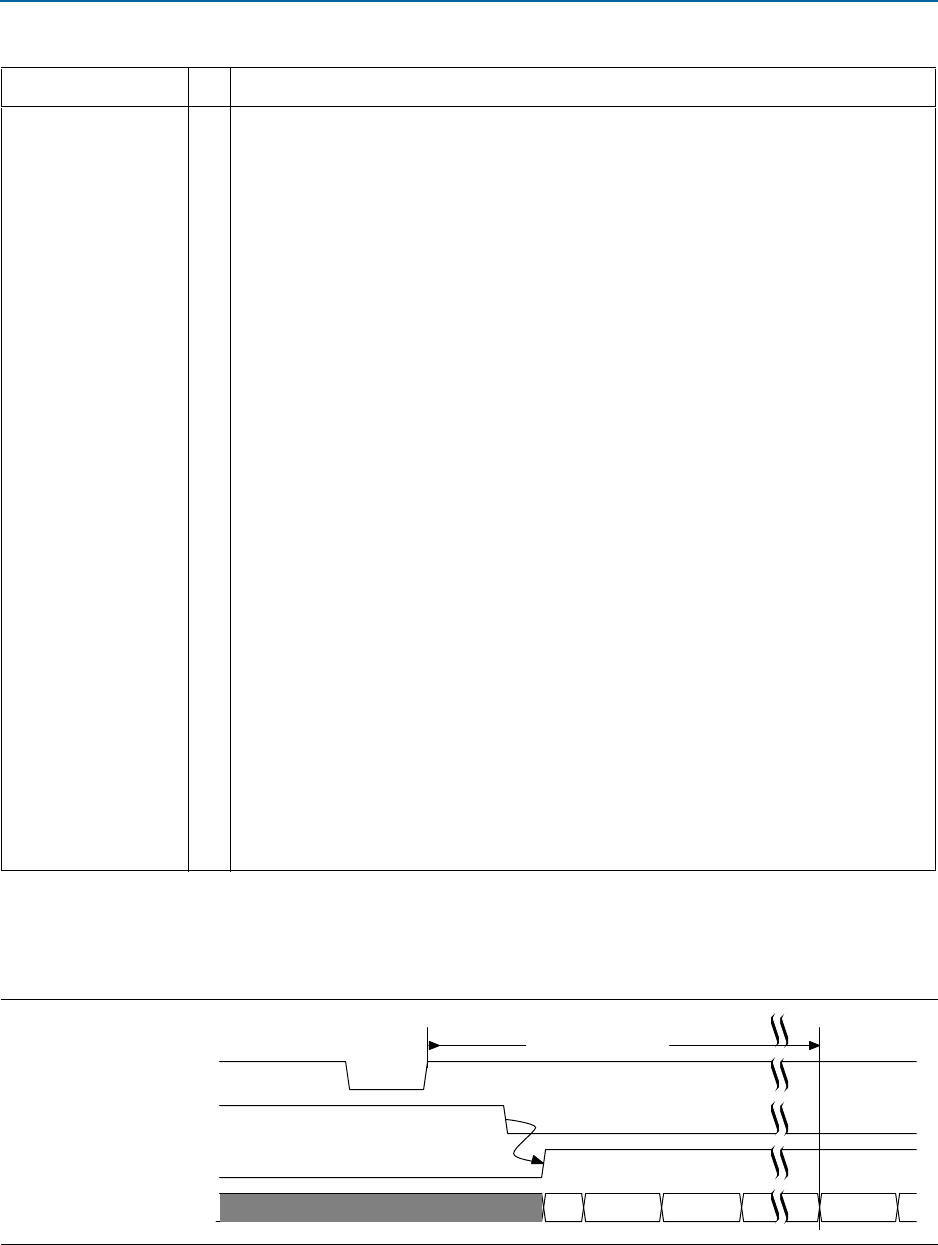
Figure 7–29 illustrates the timing relationship between
npor
and the LTSSM L0 state.
dl_ltssm[4:0]
O
LTSSM state: The LTSSM state machine encoding defines the following states:
■ 00000: detect.quiet
■ 00001: detect.active
■ 00010: polling.active
■ 00011: polling.compliance
■ 00100: polling.configuration
■ 00101: polling.speed
■ 00110: config.linkwidthstart
■ 00111: config.linkaccept
■ 01000: config.lanenumaccept
■ 01001: config.lanenumwait
■ 01010: config.complete
■ 01011: config.idle
■ 01100: recovery.rcvlock
■ 01101: recovery.rcvconfig
■ 01110: recovery.idle
■ 01111: L0
■ 10000: disable
■ 10001: loopback.entry
■ 10010: loopback.active
■ 10011: loopback.exit
■ 10100: hot.reset
■ 10101: L0s
■ 10110: L1.entry
■ 10111: L1.idle
■ 11000: L2.idle
■ 11001: L2.transmit.wake
■ 11010: recovery.speed
Table 7–6. Reset and Link Training Signals (Part 3 of 3)
Signal I/O Description
Figure 7–29. 100 ms Requirement
npor
IO_POF_Load
PCIe_LinkTraining_Enumeration
dl_ltssm[4:0]
detect.
quiet
detect.active
polling.active
L0
100 ms (maximum)










