Specifications
DS - 10 Design Ver. 0002
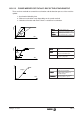
The capability demanded from the motor is determined by the following formulae:
Capacity required by the Motor
in the constant torque area (0 < N
M
< N
B
):
Capacity required by the Motor
in the constant torque and constant
power area (0 < N
M
< N
Max
) :
where:
J
M
is the inertia of the load in kg.m
2
as viewed from the motor shaft
P
N
is the rated power at the base speed, kW.
N
MAX
is the maximum motor speed in rpm.
N
B
is the base motor speed in rpm.
N
M
is the motor speed in rpm reached after a time period t.
t is the acceleration time in seconds until the N
M
is reached.
We will now give several examples of calculations using a mechanical specification and for a
standard Motor. The results could vary from real ones through mechanical losses, fluctuations
in mains voltage, or inaccuracies of mechanical data.
Example.
· Acceleration time: From 0 to 1500 rpm. in 0.5 sec. (1)
From 0 to 6000 rpm. in 2.5 sec. (2)
· Motor inertia: J
M
: 0,13 kg·m
2
· Motor base speed: N
B
: 1500 rpm.
Calculations :
1.- When the speed ranges from 0 to 1500 r.p.m.
2.- When the speed ranges from 0 to 6000 r.p.m.
P
JN
t
N
MM
=
=
2
60 1000
2
60
0 13 1500
1000 0 5
641
2
2
2
2
ππ
(kW) = (kW)
,*
*,
,
P
JN N
t
N
MM B
=
+
+
2
60 2000
2
60
0 13 6000 1500
2000 2 5
2
22
2
22
ππ
()
,*( )
*,
(kW) = = 10,89 (kW)
(1)
(2)
P
JN N
t
N
MM B
=
+
2
60 2000
2
22
π
()
(kW)
P
JN
t
N
MM
=
2
60 1000
2
2
π
(kW)