User Guide
218 64-Bit Media Programming
AMD64 Technology 24592—Rev. 3.15—November 2009
Multiply-Add
• PMADDWD—Packed Multiply Words and Add Doublewords
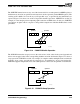
The PMADDWD instruction multiplies each 16-bit signed value in the first operand by the
corresponding 16-bit signed value in the second operand. The instruction then adds the adjacent 32-bit
intermediate results of each multiplication, and writes the 32-bit result of each addition into the
corresponding doubleword of the destination. PMADDWD thus performs two signed (16 × 16 = 32) +
(16 × 16 = 32) multiply-adds in parallel. Figure 5-16 shows the PMADDWD operation.
The only case in which overflow can occur is when all four of the 16-bit source operands used to
produce a 32-bit multiply-add result have the value 8000h. In this case, the result returned is
8000_0000h, because the maximum negative 16-bit value of 8000h multiplied by itself equals
4000_0000h, and 4000_0000h added to 4000_0000h equals 8000_0000h. The result of multiplying
two negative numbers should be a positive number, but 8000_0000h is the maximum possible 32-bit
negative number rather than a positive number.
Figure 5-16. PMADDWD Multiply-Add Operation
PMADDWD can be used with one source operand (for example, a coefficient) taken from memory and
the other source operand (for example, the data to be multiplied by that coefficient) taken from an
MMX register. The instruction can also be used together with the PADDD instruction (page 216) to
compute dot products, such as those required for finite impulse response (FIR) filters, one of the
commonly used DSP algorithms. Scaling can be done, before or after the multiply, using a vector-shift
instruction (page 219).
513-119.eps
operand 1
result
63 0
63 0
operand 2
63 0
127 0
*
+
+
* *
*