User Guide
64-Bit Media Programming 215
24592—Rev. 3.15—November 2009 AMD64 Technology
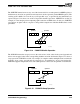
The PSHUFW instruction moves any one of the four words in its second operand (an MMX register or
64-bit memory location) to specified word locations in its first operand (another MMX register). The
ordering of the shuffle can occur in any of 256 possible ways, as specified by the immediate-byte
operand. Figure 5-14 shows one of the 256 possible shuffle operations. PSHUFW is useful, for
example, in color imaging when computing alpha saturation of RGB values. In this case, PSHUFW
can replicate an alpha value in a register so that parallel comparisons with three RGB values can be
performed.
Figure 5-14. PSHUFW Shuffle Operation
The PSWAPD instruction swaps (reverses) the order of two 32-bit values in the second operand and
writes each swapped value in the corresponding doubleword of the destination. Figure 5-15 shows a
swap operation. PSWAPD is useful, for example, in complex-number multiplication in which the
elements of one source operand must be swapped (see “Accumulation” on page 226 for details).
PSWAPD supports independent source and result operands so that it can also perform a load function.
Figure 5-15. PSWAPD Swap Operation
513-126.eps
operand 2operand 1
result
63 0
63 0
63 0
513-132.eps
operand 1
result
63 0
operand 2
63 0
63 0