User Guide
214 64-Bit Media Programming
AMD64 Technology 24592—Rev. 3.15—November 2009
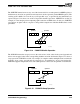
Figure 5-13. PUNPCKLWD Unpack and Interleave Operation
If one of the two source operands is a vector consisting of all zero-valued elements, the unpack
instructions perform the function of expanding vector elements of 1x size into vector elements of 2x
size (for example, word-size to doubleword-size). If both source operands are of identical value, the
unpack instructions can perform the function of duplicating adjacent elements in a vector.
The PUNPCKx instructions—along with MOVD and MOVQ—are among the most frequently used
instructions in 64-bit media procedures (both integer and floating-point).
Extract and Insert. These instructions copy a word element from a vector, in a manner specified by
an immediate operand.
• PEXTRW—Packed Extract Word
• PINSRW—Packed Insert Word
The PEXTRW instruction extracts a 16-bit value from an MMX register, as selected by the immediate-
byte operand, and writes it to the low-order word of a 32-bit or 64-bit general-purpose register, with
zero-extension to 32 or 64 bits. PEXTRW is useful for loading computed values, such as table-lookup
indices, into general-purpose registers where the values can be used for addressing tables in memory.
The PINSRW instruction inserts a 16-bit value from a the low-order word of a 32-bit or 64-bit general
purpose register or a 16-bit memory location into an MMX register. The location in the destination
register is selected by the immediate-byte operand. The other words in the destination register operand
are not modified.
Shuffle and Swap. These instructions reorder the elements of a vector.
• PSHUFW—Packed Shuffle Words
• PSWAPD—Packed Swap Doubleword
513-144.eps
operand 1
result
63 0
63 0
operand 2
63 0