User`s manual
Table Of Contents
- Introduction
- User Interface
- Display Elements
- Cross Country Tasks
- Glide Computer
- Atmosphere and Instruments
- Airspace, Traffic and Team Flying
- Avionics and Airframe
- Quickstart
- InfoBox Reference
- Configuration
- Data Files
- About XCSoar
- GNU General Public License
7 AIRSPACE, TRAFFIC AND TEAM FLYING
7 Airspace, Traffic and Team Flying
A database of Special Use Airspace (SUA) can be loaded into XCSoar and used for both display
of the airspace regions as well as detecting when the glider enters and leaves the regions.
Two airspace files can be set in the configuration settings (page ‘Site’). The first of these is intended
for use as the primary SUA database, the second is intended for use with short-term or changing
airspace such as the airspace defined in NOTAMs.
It is the user’s responsibility to ensure that the SUA database (airspace file) is up-to-
date.
Through a connected FLARM device, the glide computer can also display information relating to
FLARM-equipped nearby traffic and obstacle threats.
A team code function allows teams of pilots to exchange their positions via radio in a short code,
encoded and decoded by the computer.
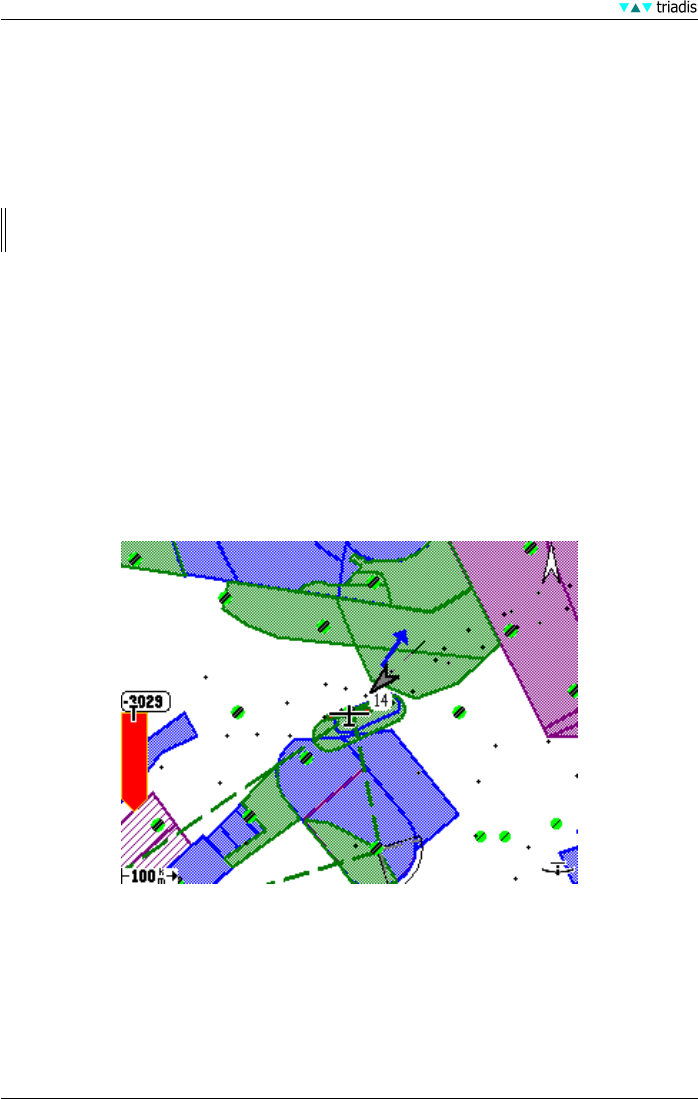
7.1 Airspace display
Local special use airspace regions are drawn on the map as shaded areas with thick borders. The
colour and pattern of the areas are specific to different airspace categories and may be configured
by the user. Depending on the settings, the user may choose to display no airspace, only airspace
above, only airspace within a particular height separation, or automatic display where XCSoar
decides when it is important to display the regions.
The patterns used to display airspace areas include opaque, transparent (hollow) and several
hatched and stippled patterns. The non-opaque patterns are partially transparent with respect to
terrain and topology but are not transparent with respect to overlapping airspace. However, where
overlapping airspace occurs, all borders are visible. That is, even though airspace patterns are not
mutually transparent, all airspace borders are drawn on top of the airspace areas.
Both the display and warning of airspace classes can be individually enabled or disabled by the
user as described in subsection 7.7.
65 XCSoar Manual (Altair version) • XCSoar-A-EN










