User's Manual
Use of Radios for Backhaul
Installation and User Guide: Airgo Access Point 135
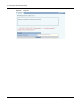
Figure 98: Frequency Bands and Hops in Wireless Backhaul Networks
The alternating band requirement carries implications for the number of backhaul hops that may be
desired to support network clients. The Airgo Access Point can technically support up to 7
backhaul hops from a client upstream to the wired AP; however, in practice, it is desirable to limit
the number of hops for the following reasons:
• Legacy client support: To support a wide range of legacy clients, the link from clients to the
downstream APs should be in the 2.4GHz band. Restricting the number of backhaul hops to
two allows the client links to operate at 2.4GHz and the backhaul link to operate at 5GHz. All
client types are served, and the two access point radios operate in different bands, as required
(Figure 98).
• Performance: As the number of hops increases, maintaining performance may require
advanced tuning of network parameters and restrictions on the number of supported APs and
clients.
Wireless Backhaul Trunks
A trunk is a wireless connection from one access point radio to another. An access point that is not
connected to the wired network or an access point radio explicitly configured in the BP mode tries
to establish a wireless trunk connection to another access point. A succession of trunks established
between access points provides a path from client stations through the wireless network to the
wired network.
If a trunk connection fails or a backhaul link goes down, the access point that established the trunk
re-scans the wireless environment and attempts to connect to another AP radio with compatible
wireless and network characteristics. This process is called retrunking.
Backhaul retrunking usually occurs quickly (in two to three seconds) if uplink candidates are
available. Subnets do not change as a result of retrunking. If a backhaul trunk fails and the BP radio
cannot reestablish (recover) backhaul within 30 minutes, all backhaul links formed with its uplink
AP radio are brought down. This gives an opportunity for the downlink nodes to attempt to form
alternate backhaul paths.
Second hop: 2.4 GHz
Good for legacy clients
5 GHz
First hop: 5 GHz
Root AP:
2.4 and
5 GHz
A0059