Technical data
106 Agilent N8201A Performance Downconverter Synthetic Instrument Module, 250 kHz to 26.5 GHz
5 Det/Demod
Detector Auto Manual
This menu allows you to select a specific type of detector, or choose Auto to let the
instrument select the appropriate detector for a particular measurement.
Auto
The system selects normal detection as the default, but if a condition arises where a
different type of detection scheme would be better utilized, the system uses the alternate
scheme. For example, when in Auto mode, the Marker Noise function uses Average
detection because the system determines that the average detector has better speed or
variance trade-offs for noise-type signals.
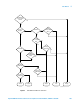
Refer to Figure 1 on page 109, which shows a decision tree of how detection type is
determined.
When the Detector choice is Auto, the detector selected depends on marker functions,
trace functions, and the trace averaging function.
See Figure 1 on page 109 for information on the Auto detector selection.
When you manually select a detector (instead of selecting Auto), that detector is used
regardless of other N8201A settings.
The detector choices are:
• Normal - displays the peak of CW-like signals and maximums and minimums of
noise-like signals.
• Average - displays the average of the signal within the bucket. The averaging method
depends upon Avg Type selection (voltage, power or log scales).
• Peak - displays the maximum of the signal within the bucket.
• Sample - displays the instantaneous level of the signal at the center of the bucket
represented by each display point.
• Negative Peak - displays the minimum of the signal within the bucket.
• Quasi Peak - a fast-rise, slow-fall detector used in making CISPR compliant EMI
measurements.
EMI Average − displays the instantaneous level of the signal at the center of the bucket,
just like the sample detector. Also changes the auto coupling of VBW, RBW and Avg/VBW
Type and the set of available RBWs. Used in making CISPR-compliant measurements.
•
EMI Peak − the same as the Peak detector but uses CISPR related bandwidths.
•
MIL Peak − the same as the Peak detector but uses MIL related bandwidths.
Because they may not find the true peak of a spectral component, neither average nor
sample detectors measure amplitudes of CW signals as accurately as peak or normal, but
they do measure noise without the biases of peak detection.