Technical data
Table Of Contents
- EMC Measurement Application Measurement Guide
- Table of Contents
- 1 EMC Measurements
- 2 Conducted Emissions Measurements
- 3 Radiated Emissions Measurements
- A: Line Impedance Stabilization Networks (LISN)
- B: Antenna Factors
- C: Basic Electrical Relationships
- D: Detectors Used in EMI Measurements
- Glossary of Acronyms and Definitions
27
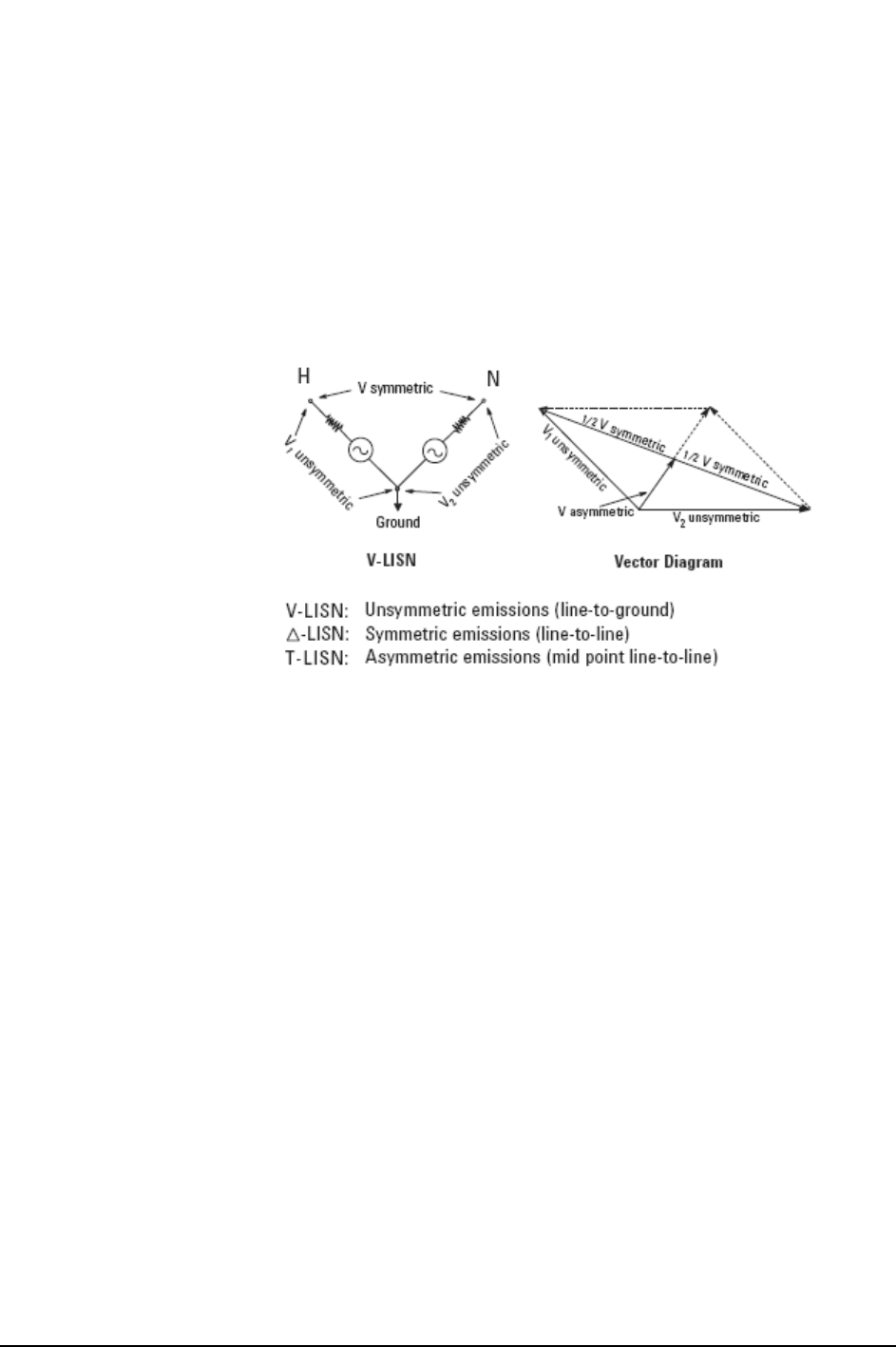
Line Impedance Stabilization Networks (LISN)
Types of LISNs
Types of LISNs
The most common type of LISN is the V-LISN. It measures the unsymmetric voltage
between line and ground. This is done for both the hot and the neutral lines or for a
three phase circuit in a “Y” configuration, between each line and ground. There are
other specialized types of LISNs. A delta LISN measures the line-to-line or symmetric
emissions voltage. The T-LISN, sometimes used for telecommunications equipment,
measures the asymmetric voltage, which is the potential difference between the
midpoint potential between two lines and ground.
Transient Limiter Operation
The purpose of the limiter is to protect the input of the EMC analyzer from large
transients when connected to a LISN. Switching DUT power on or off can cause large
spikes generated in the LISN.
The Agilent 11947A transient limiter incorporates a limiter, high-pass filter, and an
attenuator. It can withstand 10 kW for 10 μsec and has a frequency range of 9 kHz to
200 MHz. The high-pass filter reduces the line frequencies coupled to the EMC
analyzer.