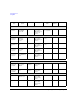
Technical data
Agilent Signal Generators Programming Guide 25
2 Using IO Interfaces
NOTE For the N5161A/62A the softkey menus and features mentioned in this chapter are only
available through the Web–Enabled MXG or through SCPI commands. Refer to “Using the
Web Browser” on page 11 and to the SCPI Command Reference.
Using the programming examples with GPIB, LAN, RS–232, and USB interfaces:
• Using GPIB on page 25
• Using LAN on page 31
• Using RS–232 (ESG and PSG Only) on page 61
• Using USB (Agilent MXG) on page 69
Using GPIB
GPIB enables instruments to be connected together and controlled by a computer. GPIB and its
associated interface operations are defined in the ANSI/IEEE Standard 488.1–1987 and ANSI/IEEE
Standard 488.2–1992. See the IEEE website, http://www.ieee.org, for details on these standards.
The following sections contain information for installing a GPIB interface card or NI–GPIB interface
card for your PC or UNIX–based system.
• “Installing the GPIB Interface” on page 25
• “Set Up the GPIB Interface” on page 27
• “Verify GPIB Functionality” on page 28
Installing the GPIB Interface
NOTE You can also connect GPIB instruments to a PC USB port using the Agilent 82357A
USB/GPIB Interface Converter, which eliminates the need for a GPIB card. For more
information, refer to the table on page 26 or go to http://www.agilent.com/find/gpib.
A GPIB interface card can be installed in a computer. Two common GPIB interface cards are the
Agilent GPIB interface card and the National Instruments (NI) PCI–GPIB card. Follow the interface
card instructions for installing and configuring the card. The following table provide lists on some of
the available interface cards. Also, see the Agilent website, http://www.agilent.com for details on
GPIB interface cards.