Technical data
TCP/IP Network Basics 7
Agilent Connectivity Guide 161
Within the site LAN, every device (PC, router, server, etc.) is called a
host. A host is any device on a network that has a TCP/IP address.
TCP/IP addresses are called IP addresses, and each device on the
network must have a unique IP address. A typical IP address for a
device is 156.140.105.50. In general, communication within the site
LAN and to private LANs is behind a firewall.
Communication among devices on the site LAN is controlled by
routers. A router is a host that interfaces with other networks and can
move data (called packets) from one network to another or can move
data within the network, depending on the IP addresses of the hosts that
are communicating with each other.
The servers on the site LAN can supply addressing and naming
services, such as Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) to
automatically assign IP addresses to hosts on the network or Domain
Name Service (DNS) or Windows Internet Naming Service (WINS) that
allow hostnames to be associated with their IP addresses.
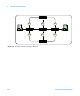
Private LAN Topology
A private LAN (also called a local or isolated network) can operate as a
local network (not connected to any other network) or can be connected
to a site LAN or to another local network. This figure shows an example
private LAN with three hosts (PC and two instruments).
Communication between the PC and the instruments is via a
switch or
hub. You can also connect a single instrument to a PC by using a
crossover cable.