User's Manual
361
Chapter 7, IBASIC Controller
Interfacing to the IBASIC Controller using Serial Ports
Serial Port 9. Serial Port 9 is used for developing and editing IBASIC programs
since it can be connected directly to the
IBASIC Command Line field. It can also
be used for data I/O from an IBASIC program. Settings can be changed from the
I/O CONFIGURE screen, using IBASIC commands executed from the
IBASIC
Command Line
field, or using IBASIC commands executed from an IBASIC
program.
Serial Port 10. Serial Port 10 is primarily used for data I/O from an IBASIC
program to a device-under-test- (DUT). Settings can be changed using IBASIC
commands executed from the
IBASIC Command Line field, or using IBASIC
commands executed from an IBASIC program but not from the I/O CONFIGURE
screen.
Reason for Two Serial Ports
A typical application uses serial port 10 to send and receive data to and from a
DUT and uses serial port 9 to print or log test results to a serial printer or PC.
In the program development environment, serial port 9 can be used to
communicate with the external PC or terminal, and serial port 10 can be
connected to a serial printer for generating program listings or as the destination
printer for the program itself. This is schematically shown in
Figure 26 on page
364
. If simultaneous multiple serial I/O is not a requirement then only use serial
port 9 as it can directly access the
IBASIC Command Line field.
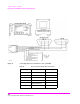
For your convenience, Figure 25 on page 363 and Table 39 on this page, show the cables
and adapters that are available from Agilent Technologies for connecting external devices
to the Test Set’s serial I/O ports. See Figure 26 on page 364 for a wiring diagram to
construct your own cables. RJ-11 cables and adapters can be wired several ways. If you
buy a cable or adapter other than the Agilent parts listed in Table 39, verify the
connections for the pins indicated, before connecting the cables to the Test Set.